
An ammeter reads up to 1 ampere. Its internal resistance is $0.81\Omega $. To increase the range to 10 A the value of the required shunt is:
A. $0.03\Omega $
B. $0.3\Omega $
C. $0.9\Omega $
D. $0.09\Omega $
Answer
586.8k+ views
Hint: To solve the above problem we should know that adding a resistance in the parallel connection with any apparatus current gets divided into two branches according to the value of the resistance and the voltage across both branches remains the same.
Complete answer:
Firstly, we will draw a circuit diagram showing an ammeter and its internal resistance and a shunt which is connected in parallel with the ammeter. The diagram is as follows,
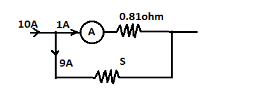
We see that the current of 10A coming to the ammeter gets divided. 1A current goes to the ammeter (since ammeter can read up to 1 ampere) and rest of the 9A current goes through the connected shunt, but the voltage drops through both the elements (shunt and ammeter) will be same (since the voltage drop through two branches of a parallel connection remains same).
Now we will equate the potential drop across ammeter and the shunt.
So, \[{V_{shunt}} = {V_{ammeter}}\]
$ \Rightarrow {I_{shunt}} \times S = {I_{ammeter}} \times {R_{ammeter}}$
$ \Rightarrow 9A \times S = 1A \times 0.81\Omega $-------(putting all the values)
$ \Rightarrow S = \dfrac{{0.81\Omega }}{9}$
$ \Rightarrow S = 0.09\Omega $
So, to increase the range of the ammeter to 10 A the value of the required shunt is $0.09\Omega $.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note:
Other than ammeter there is another device which indicates and measures the current, that is known as galvanometer. The limitation of the galvanometer is that it can only measure the small currents, to measure the large currents we will need ammeters. But the galvanometer can be converted into the ammeter by connecting a shunt (resistance of small magnitude) in parallel with the galvanometer. Also, the galvanometer can be converted into a voltmeter to measure the voltage by connecting a high resistance called multiplier in series to the galvanometer.
Complete answer:
Firstly, we will draw a circuit diagram showing an ammeter and its internal resistance and a shunt which is connected in parallel with the ammeter. The diagram is as follows,

We see that the current of 10A coming to the ammeter gets divided. 1A current goes to the ammeter (since ammeter can read up to 1 ampere) and rest of the 9A current goes through the connected shunt, but the voltage drops through both the elements (shunt and ammeter) will be same (since the voltage drop through two branches of a parallel connection remains same).
Now we will equate the potential drop across ammeter and the shunt.
So, \[{V_{shunt}} = {V_{ammeter}}\]
$ \Rightarrow {I_{shunt}} \times S = {I_{ammeter}} \times {R_{ammeter}}$
$ \Rightarrow 9A \times S = 1A \times 0.81\Omega $-------(putting all the values)
$ \Rightarrow S = \dfrac{{0.81\Omega }}{9}$
$ \Rightarrow S = 0.09\Omega $
So, to increase the range of the ammeter to 10 A the value of the required shunt is $0.09\Omega $.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note:
Other than ammeter there is another device which indicates and measures the current, that is known as galvanometer. The limitation of the galvanometer is that it can only measure the small currents, to measure the large currents we will need ammeters. But the galvanometer can be converted into the ammeter by connecting a shunt (resistance of small magnitude) in parallel with the galvanometer. Also, the galvanometer can be converted into a voltmeter to measure the voltage by connecting a high resistance called multiplier in series to the galvanometer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




