
An alternating voltage $v\left( t \right) = 220\sin 100\pi t$ volt voltage is applied to a purely resistance load of $50\Omega $ . The time taken for the current to rise from half of the peak value of the peak value is:
$\left( a \right)\,\,2.2ms$
$\left( b \right)\,\,5ms$
$\left( c \right)\,\,3.3ms$
$\left( d \right)\,\,7.2ms$
Answer
548.4k+ views
Hint: Voltage leads current by or $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ . The equation of the current will be $I(t) = 220\sin \left( {100\pi t - 90^\circ } \right)$ . Write it in the cosine form. Calculate the phase angle, where the value of cosine will be $\dfrac{1}{2}$ . Equate the $\omega t$ and that angle.
Formula used: If the angular velocity of a coil is $\omega $ , time period $T$ and phase angle is $2\pi $ , then, $T = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{\omega }$
Complete step by step answer: Let, at time $t$ , peak value becomes $\dfrac{1}{2}$ . We know that voltage leads current by $90^\circ $ or $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$
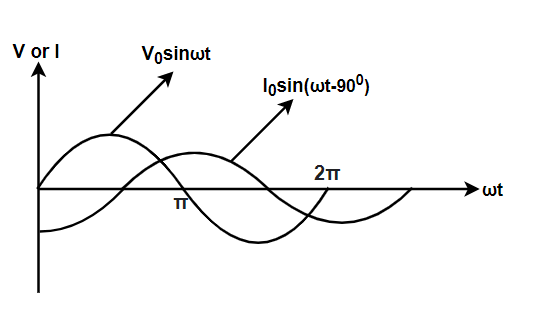
We are given the equation of applied voltage, $v\left( t \right) = 220\sin 100\pi t$ So, the equation of current will be $I(t) = 220\sin \left( {100\pi t - 90^\circ } \right)$ So, the equation of current, in the form of cosine will be $I(t) = 220\cos \left( {100\pi t} \right)$
Also, we know that $\cos 60^\circ = \cos \dfrac{\pi }{3} = \dfrac{1}{2}$
So, the time taken for the current to rise from half of the peak value of the peak value will be at $t = \dfrac{\pi }{3}$
So, $\dfrac{\pi }{3} = 100\pi t$
$ \Rightarrow t = \dfrac{\pi }{{3 \times 100\pi }} = \dfrac{1}{{300}} = 3.3ms$
Hence, the option $\left( c \right)$ is correct.
Additional information: The definite time interval in which a complete cycle repeats itself, is called the time period of an alternating current or AC.
If the angular velocity of a coil is $\omega $ , time period $T$ and phase angle is $2\pi $ , then, $T = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{\omega }$
The number of complete waves produced in unit time is called the frequency $\left( n \right)$ of an alternating current. So, $n = \dfrac{1}{T} = \dfrac{\omega }{{2\pi }}$ Note that frequency is the most important quantity in the expression of an alternating current.
Also, let the equation of alternating current be $i = {i_0}\sin \left( {\omega t + \alpha } \right)$ Now, the state of alternating current at any moment is expressed by its phase. In the above equation of the alternating current $\left( {\omega t + \alpha } \right)$ is the phase of the alternating current.
Note: For the equation $i = {i_0}\sin \left( {\omega t + \alpha } \right)$ and $v = {v_0}\sin \left( {\omega t + \alpha } \right)$ , as $ - 1 \leqslant \sin \theta \leqslant 1$ , we can say that the maximum and minimum values of emf ${v_0}$ and $ - {v_0}$ respectively. Also, the maximum and minimum values of the currents are ${i_0}$ and $ - {i_0}$ respectively. These magnitudes, ${v_0}$ and ${i_0}$ are the peak values of the emf and current. Also, it should be noted that the peak value of current varies inversely with the resistance of the circuit.
Formula used: If the angular velocity of a coil is $\omega $ , time period $T$ and phase angle is $2\pi $ , then, $T = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{\omega }$
Complete step by step answer: Let, at time $t$ , peak value becomes $\dfrac{1}{2}$ . We know that voltage leads current by $90^\circ $ or $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$

We are given the equation of applied voltage, $v\left( t \right) = 220\sin 100\pi t$ So, the equation of current will be $I(t) = 220\sin \left( {100\pi t - 90^\circ } \right)$ So, the equation of current, in the form of cosine will be $I(t) = 220\cos \left( {100\pi t} \right)$
Also, we know that $\cos 60^\circ = \cos \dfrac{\pi }{3} = \dfrac{1}{2}$
So, the time taken for the current to rise from half of the peak value of the peak value will be at $t = \dfrac{\pi }{3}$
So, $\dfrac{\pi }{3} = 100\pi t$
$ \Rightarrow t = \dfrac{\pi }{{3 \times 100\pi }} = \dfrac{1}{{300}} = 3.3ms$
Hence, the option $\left( c \right)$ is correct.
Additional information: The definite time interval in which a complete cycle repeats itself, is called the time period of an alternating current or AC.
If the angular velocity of a coil is $\omega $ , time period $T$ and phase angle is $2\pi $ , then, $T = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{\omega }$
The number of complete waves produced in unit time is called the frequency $\left( n \right)$ of an alternating current. So, $n = \dfrac{1}{T} = \dfrac{\omega }{{2\pi }}$ Note that frequency is the most important quantity in the expression of an alternating current.
Also, let the equation of alternating current be $i = {i_0}\sin \left( {\omega t + \alpha } \right)$ Now, the state of alternating current at any moment is expressed by its phase. In the above equation of the alternating current $\left( {\omega t + \alpha } \right)$ is the phase of the alternating current.
Note: For the equation $i = {i_0}\sin \left( {\omega t + \alpha } \right)$ and $v = {v_0}\sin \left( {\omega t + \alpha } \right)$ , as $ - 1 \leqslant \sin \theta \leqslant 1$ , we can say that the maximum and minimum values of emf ${v_0}$ and $ - {v_0}$ respectively. Also, the maximum and minimum values of the currents are ${i_0}$ and $ - {i_0}$ respectively. These magnitudes, ${v_0}$ and ${i_0}$ are the peak values of the emf and current. Also, it should be noted that the peak value of current varies inversely with the resistance of the circuit.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




