
An a.c. supply of 100 volts is applied to a capacitor of capacitance $20\mu F$. If the current in the circuit is $0.628A$, the frequency of a.c. must be
a) 50 Hz
b) 60 Hz
c) 25 Hz
d) 40 Hz
Answer
558.3k+ views
Hint:The given circuit is a purely capacitive circuit. This means that only a capacitor is present in the circuit along with the alternating current source and no resistor or inductor is present. Therefore, only the capacitor is consuming energy and we must modify the formula of impedance accordingly. Impedance is the total resistance present against the current in the circuit.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Impedance of a LCR circuit is given as:
$Z=\sqrt{{{R}^{2}}+{{\left( {{X}_{L}}-{{X}_{C}} \right)}^{2}}}$
Where,
$R=$ Resistance of the resistor present
${{X}_{L}}=$Inductive reactance of the inductor present. It is further given as ${{X}_{L}}=\omega L$
$\omega =2\pi \nu $, $\Rightarrow {{X}_{L}}=2\pi \nu L$
Where, $\nu =$frequency of the alternating current provided to the circuit and $L=$inductance of inductor
${{X}_{C}}=$Capacitive reactance of the capacitor present. It is further given as ${{X}_{C}}=\dfrac{1}{\omega C}$
$\omega =2\pi \nu $, $\Rightarrow {{X}_{C}}=\dfrac{1}{2\pi \nu C}$ ………….. equation (1)
Where, $\nu =$frequency of the alternating current provided to the circuit and $C=$capacitance of capacitor
Since, no resistor or inductor is present in the circuit,
Therefore,
$\begin{align}
& Z=\sqrt{0+{{\left( 0-{{X}_{C}} \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow Z={{X}_{C}} \\
\end{align}$
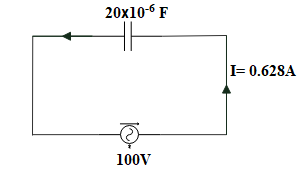
Now,
The voltage,$V$of the a.c. circuit is given as:
$V=IZ$
Here, $I=$current in circuit and $Z={{X}_{C}}$
$\Rightarrow {{X}_{C}}=\dfrac{V}{I}$
From equation (1),
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2\pi \nu C}=\dfrac{V}{I}$
Given that voltage = 100 volts, current = $0.628A$and capacitance =$20\mu F=20\times {{10}^{-6}}F$
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2\pi \nu \left( 20\times {{10}^{-6}} \right)}=\dfrac{100}{0.628} \\
& \Rightarrow \nu =\dfrac{0.628}{2\left( 3.14 \right)\left( 20\times {{10}^{-6}} \right)\left( 100 \right)} \\
& \Rightarrow \nu =\dfrac{1}{2}\times 100 \\
& \Rightarrow \nu =50Hz \\
\end{align}$
The frequency of alternating current must be 50Hz.
Therefore, the correct option is (a) 50Hz.
Note:
An AC (alternating current) analysis is where we limit ourselves to inputs to our circuits that look like sinusoids, cosines or sines. The voltage and current are represented as sinusoidal waves and written in sinusoidal equations which make their study comparatively easy. Such a current is not constant but fluctuates as a sine or cosine function of time.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Impedance of a LCR circuit is given as:
$Z=\sqrt{{{R}^{2}}+{{\left( {{X}_{L}}-{{X}_{C}} \right)}^{2}}}$
Where,
$R=$ Resistance of the resistor present
${{X}_{L}}=$Inductive reactance of the inductor present. It is further given as ${{X}_{L}}=\omega L$
$\omega =2\pi \nu $, $\Rightarrow {{X}_{L}}=2\pi \nu L$
Where, $\nu =$frequency of the alternating current provided to the circuit and $L=$inductance of inductor
${{X}_{C}}=$Capacitive reactance of the capacitor present. It is further given as ${{X}_{C}}=\dfrac{1}{\omega C}$
$\omega =2\pi \nu $, $\Rightarrow {{X}_{C}}=\dfrac{1}{2\pi \nu C}$ ………….. equation (1)
Where, $\nu =$frequency of the alternating current provided to the circuit and $C=$capacitance of capacitor
Since, no resistor or inductor is present in the circuit,
Therefore,
$\begin{align}
& Z=\sqrt{0+{{\left( 0-{{X}_{C}} \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow Z={{X}_{C}} \\
\end{align}$

Now,
The voltage,$V$of the a.c. circuit is given as:
$V=IZ$
Here, $I=$current in circuit and $Z={{X}_{C}}$
$\Rightarrow {{X}_{C}}=\dfrac{V}{I}$
From equation (1),
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2\pi \nu C}=\dfrac{V}{I}$
Given that voltage = 100 volts, current = $0.628A$and capacitance =$20\mu F=20\times {{10}^{-6}}F$
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2\pi \nu \left( 20\times {{10}^{-6}} \right)}=\dfrac{100}{0.628} \\
& \Rightarrow \nu =\dfrac{0.628}{2\left( 3.14 \right)\left( 20\times {{10}^{-6}} \right)\left( 100 \right)} \\
& \Rightarrow \nu =\dfrac{1}{2}\times 100 \\
& \Rightarrow \nu =50Hz \\
\end{align}$
The frequency of alternating current must be 50Hz.
Therefore, the correct option is (a) 50Hz.
Note:
An AC (alternating current) analysis is where we limit ourselves to inputs to our circuits that look like sinusoids, cosines or sines. The voltage and current are represented as sinusoidal waves and written in sinusoidal equations which make their study comparatively easy. Such a current is not constant but fluctuates as a sine or cosine function of time.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




