
Among\[[Ni{{(CO)}_{4}}],{{[NiC{{l}_{4}}]}^{2-}},[Co{{(N{{H}_{3}})}_{4}}C{{l}_{2}}]Cl,N{{a}_{3}}[Co{{F}_{6}}],N{{a}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}\] and $Cs{{O}_{2}}$ the total number of paramagnetic compound is:
A.$2$
B.$3$
C.$4$
D.$5$
Answer
546k+ views
Hint:We know that using the crystal field theory and identifying the unpaired electrons present in the compound the compound can be classified as paramagnetic or diamagnetic. When an electron in an atom or ion is unpaired, it makes the entire atom or ion paramagnetic whereas the compounds that contain no unpaired electrons are known as diamagnetic. The magnetic properties of a compound can be determined from its electron configuration and the size of its atoms.
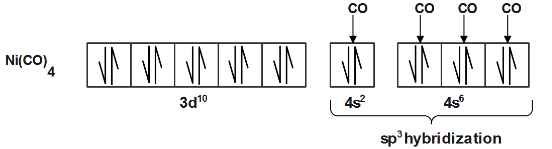
Complete step-by-step answer:For the given compounds the unpaired electrons are calculated via electronic configuration of the central metal ion. In the compound $[Ni{{(CO)}_{4}}]$ Electronic configuration is $3{{d}^{10}}s{{p}^{3}}$ which has no unpaired electron making it diamagnetic.
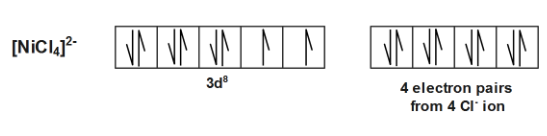
In the compound ${{[Ni{{(Cl)}_{4}}]}^{2-}}$ electronic configuration is $3{{d}^{8}}s{{p}^{3}}$ .there is loss of two electron due to $-2$ charge on $Ni$ . Due to presence of unpaired electrons it is paramagnetic in nature.
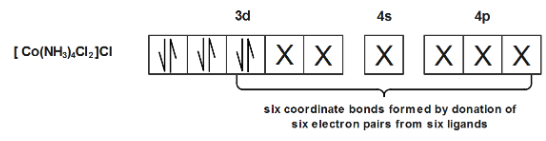
In another compound $[Co{{(N{{H}_{3}})}_{4}}C{{l}_{2}}]$ the electronic configuration is \[3{{d}^{6}},{{d}^{2}}s{{p}^{3}}\] which again has no unpaired electrons making it diamagnetic in nature.
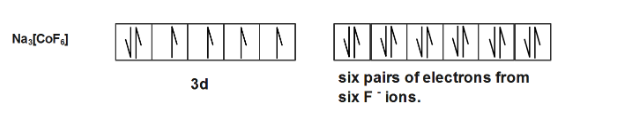
In compound $N{{a}_{3}}[Co{{F}_{6}}]$ the electronic configuration is \[3{{d}^{6}},s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}\] giving it $4$ unpaired electrons giving it paramagnetic property.
Similarly in $N{{a}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}$ the ${{O}_{2}}^{2-}$ unpaired electron is zero making it diamagnetic in nature. Lastly in the compound $Cs{{O}_{2}}$ the ${{O}_{2}}^{2-}$ the unpaired electron is one making it paramagnetic in nature. Therefore total paramagnetic compounds in given statement are: ${{[Ni{{(Cl)}_{4}}]}^{2-}}$,$N{{a}_{3}}[Co{{F}_{6}}]$, $Cs{{O}_{2}}$.
Therefore there are three paramagnetic compounds. The correct option is option (B).
Note: Note that if the compound is paramagnetic, it will be pulled visibly towards the electromagnet, which is the distance proportional to the magnitude of the compound is paramagnetic. If the compound, however, is diamagnetic, it will not be pulled towards the electromagnet, instead, it might even slightly be repelled by it. The change is directly proportional to the amount of unpaired electrons in the compound.
Complete step-by-step answer:For the given compounds the unpaired electrons are calculated via electronic configuration of the central metal ion. In the compound $[Ni{{(CO)}_{4}}]$ Electronic configuration is $3{{d}^{10}}s{{p}^{3}}$ which has no unpaired electron making it diamagnetic.

In the compound ${{[Ni{{(Cl)}_{4}}]}^{2-}}$ electronic configuration is $3{{d}^{8}}s{{p}^{3}}$ .there is loss of two electron due to $-2$ charge on $Ni$ . Due to presence of unpaired electrons it is paramagnetic in nature.

In another compound $[Co{{(N{{H}_{3}})}_{4}}C{{l}_{2}}]$ the electronic configuration is \[3{{d}^{6}},{{d}^{2}}s{{p}^{3}}\] which again has no unpaired electrons making it diamagnetic in nature.

In compound $N{{a}_{3}}[Co{{F}_{6}}]$ the electronic configuration is \[3{{d}^{6}},s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}\] giving it $4$ unpaired electrons giving it paramagnetic property.

Similarly in $N{{a}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}$ the ${{O}_{2}}^{2-}$ unpaired electron is zero making it diamagnetic in nature. Lastly in the compound $Cs{{O}_{2}}$ the ${{O}_{2}}^{2-}$ the unpaired electron is one making it paramagnetic in nature. Therefore total paramagnetic compounds in given statement are: ${{[Ni{{(Cl)}_{4}}]}^{2-}}$,$N{{a}_{3}}[Co{{F}_{6}}]$, $Cs{{O}_{2}}$.
Therefore there are three paramagnetic compounds. The correct option is option (B).
Note: Note that if the compound is paramagnetic, it will be pulled visibly towards the electromagnet, which is the distance proportional to the magnitude of the compound is paramagnetic. If the compound, however, is diamagnetic, it will not be pulled towards the electromagnet, instead, it might even slightly be repelled by it. The change is directly proportional to the amount of unpaired electrons in the compound.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




