
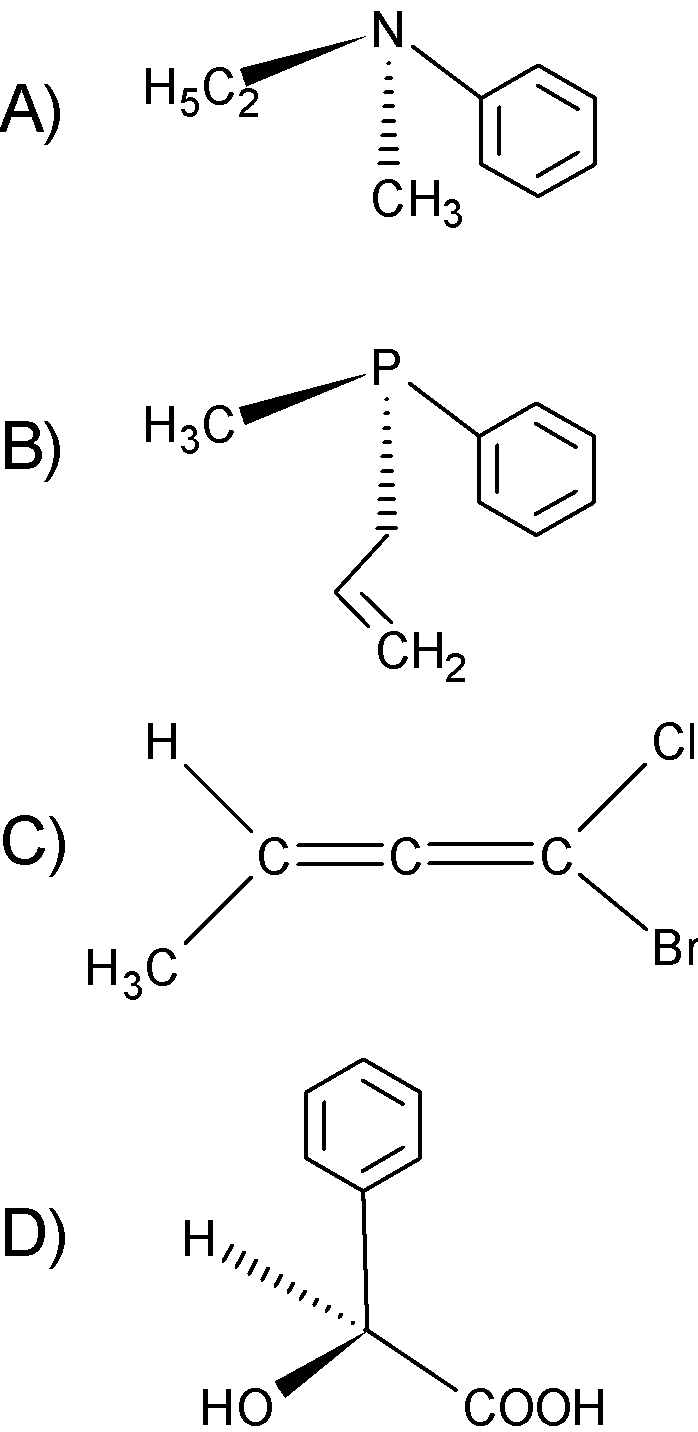
Among the following, the optically inactive compound is:

Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: The optical activity is a measure of the ability of the substance to rotate the polarised light if the solution is placed in the path of the plane polarised light. The compound that has the chiral centre is optically active. However, the amine undergoes the pyramidal inversion and thus cannot be resolved.
Complete step by step answer:
Optical activity is a property of the compound. If a compound can rotate the plane-polarized light which is produced by passing through the Nicol prism, such compounds are called the optically active compounds.
But when passed through the solutions cannot change or rotate the plane polarised light are called as the optically inactive compounds.
In stereochemistry, the energy barrier between the enantiomers is very low. Thus the fluxional process takes place in pyramidal molecules. The inversion is so rapid at room temperature that even due to the presence of stereo enter the compound can be resolved and thus they are optically inactive. It is more observed in amine however, the energy is more in the case of phosphine.
Let's have a look at the molecules.
A) In structure A) the amino group $\text{ (-N) }$attached to the 3 different groups,$(\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}-)$ $(\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}-)$ and benzene ring. Here, amino is pyramidal in structure. The pyramidal inversion is a fluxional process. The compound A) undergoes the pyramidal inversion, the compound would otherwise be chiral because of the stereo enter, but pyramidal inversion racemizes the compound and thus it is optically active.
B) In compound B), the phosphine is attached to three different groups$(\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}-)$, benzene ring, and ethylene. The lone pair acts as the fourth group on the phosphine. The phosphorus is a stereo enter and therefore, the structure B) is an optically active compound. The rate of inversion is lesser than the amino.
C) The compound C) is allene. The allenes are chiral if the terminal groups on a side are not equal. That is$\text{A}\ne \text{ B}$. Here, the terminal groups are different which are $\text{ Ph , Br , Cl and C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$.there is no condition like $\text{A=B or C=D}$ , therefore the allene shows the optical activity. They can rotate the plane polarised light.
D) In compound D), the carbon is bonded to the four different acid groups $-\text{COOH}$ , hydrogen, $-\text{OH}$ and phenyl ring. The compound is chiral therefore, it is an optically active compound.
Hence, (A) is the correct option.
Note: The pyramidal molecules undergo the pyramidal inversion. The amines and phosphines are the compounds that can undergo the pyramidal inversion. The phosphines have a high energy barrier \[\text{ 132 }\!\!~\!\!\text{ kJ/mol}\] compared to amine and racemizes slowly at room temperature.
Complete step by step answer:
Optical activity is a property of the compound. If a compound can rotate the plane-polarized light which is produced by passing through the Nicol prism, such compounds are called the optically active compounds.
But when passed through the solutions cannot change or rotate the plane polarised light are called as the optically inactive compounds.
In stereochemistry, the energy barrier between the enantiomers is very low. Thus the fluxional process takes place in pyramidal molecules. The inversion is so rapid at room temperature that even due to the presence of stereo enter the compound can be resolved and thus they are optically inactive. It is more observed in amine however, the energy is more in the case of phosphine.
Let's have a look at the molecules.
A) In structure A) the amino group $\text{ (-N) }$attached to the 3 different groups,$(\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}-)$ $(\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}-)$ and benzene ring. Here, amino is pyramidal in structure. The pyramidal inversion is a fluxional process. The compound A) undergoes the pyramidal inversion, the compound would otherwise be chiral because of the stereo enter, but pyramidal inversion racemizes the compound and thus it is optically active.
B) In compound B), the phosphine is attached to three different groups$(\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}-)$, benzene ring, and ethylene. The lone pair acts as the fourth group on the phosphine. The phosphorus is a stereo enter and therefore, the structure B) is an optically active compound. The rate of inversion is lesser than the amino.
C) The compound C) is allene. The allenes are chiral if the terminal groups on a side are not equal. That is$\text{A}\ne \text{ B}$. Here, the terminal groups are different which are $\text{ Ph , Br , Cl and C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$.there is no condition like $\text{A=B or C=D}$ , therefore the allene shows the optical activity. They can rotate the plane polarised light.
D) In compound D), the carbon is bonded to the four different acid groups $-\text{COOH}$ , hydrogen, $-\text{OH}$ and phenyl ring. The compound is chiral therefore, it is an optically active compound.
Hence, (A) is the correct option.
Note: The pyramidal molecules undergo the pyramidal inversion. The amines and phosphines are the compounds that can undergo the pyramidal inversion. The phosphines have a high energy barrier \[\text{ 132 }\!\!~\!\!\text{ kJ/mol}\] compared to amine and racemizes slowly at room temperature.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




