
Among the following, the correct statement(s) is (are):
(A) \[{\rm{B}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}\]has three -centre two electron bonds in its dimeric structure
(B) \[{\rm{Al}}{\left( {{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}} \right)_{\rm{3}}}\]has three-centre two electron bonds in its dimeric structure
(C) \[{\rm{AlC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{3}}}\]has three-centre two electron bonds in its dimeric structure
(D) The Lewis acidity of \[{\rm{BC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{3}}}\]is greater than that of \[{\rm{AlC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{3}}}\]
Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: As we know that, Lewis acids are those acids which are deficient in electrons, so these compounds are always found in dimer. In dimeric structures, electrons are always shared between the atoms. As we go down the group, the size of the orbital increases.
Complete step by step answer
As we know that boron and aluminium are found in \[{\rm{1}}{{\rm{3}}^{{\rm{th}}}}\] group and aluminium is the second element of this group. Boron and aluminium have three electrons in its outermost shell.
Let’s move towards options:
->\[{\rm{B}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}\] has six electrons in its octet and to complete its octet, it forms dimer. Boron atom shares one electron of the outermost shell to hydrogen to form bridged hydrogen bonding. Another boron atom also shares its electron to form bridging bonds with hydrogen as shown below.
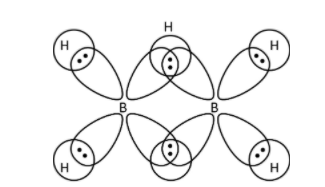
So, we can see that each bridged bond contains two electrons bonded with three atoms. Therefore, option (A)- \[{\rm{B}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}\] has three -centre two electron bonds in its dimeric structure is correct.
->\[{\rm{Al}}{\left( {{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}} \right)_{\rm{3}}}\] has six electrons in its octet and to complete its octet, it forms dimer. Aluminium atoms share one electron of the outermost shell with one electron of carbon to form bridged bonding. Other aluminium atoms also share their electrons to form bridging bonds with carbon atoms as shown below.
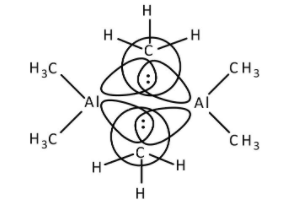
Therefore, option (B)- \[{\rm{Al}}{\left( {{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}} \right)_{\rm{3}}}\] has three centre- two electron bonds in its dimeric structure is correct.
->Option (C)- \[{\rm{AlC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{3}}}\] also forms dimeric structure because it also has six electrons in its octet and to complete its octet, it forms dimer. One aluminium atom shares one electron of outermost shell with one electron of chlorine atom to form bridged bonding and chlorine also donate its one lone pair of electrons to vacant orbital of aluminium atom to form coordinate bonding as shown below.
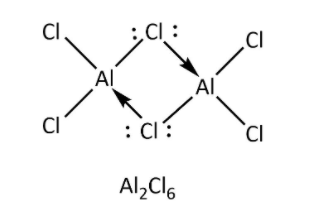
As we can see, bridging bonding contains three atoms with four electrons, so it does not form three centre -two electron bonds.
Therefore, this option is incorrect.
->Now, option (D)- The Lewis acidity of \[{\rm{BC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{3}}}\] is greater than that of \[{\rm{AlC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{3}}}\] is correct because boron’s \[{\rm{2p}}\]-orbital overlaps with chlorine’s \[{\rm{3p}}\]-orbital, hence, cannot form bond effectively. Therefore, Lewis acidity is greater. On the other hand, in \[{\rm{AlC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{3}}}\], overlapping is \[{\rm{3p - 3p}}\] between aluminium and chlorine.
Therefore, the correct options are option (A), option (B) and option (D).
Note:
From IR spectra, stretching frequency of bridging bonds is less than terminal bonds because electron density is less than the volume. Compounds like $Al_2Cl_6$ are very unique because this kind of structure is very rare.
Complete step by step answer
As we know that boron and aluminium are found in \[{\rm{1}}{{\rm{3}}^{{\rm{th}}}}\] group and aluminium is the second element of this group. Boron and aluminium have three electrons in its outermost shell.
Let’s move towards options:
->\[{\rm{B}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}\] has six electrons in its octet and to complete its octet, it forms dimer. Boron atom shares one electron of the outermost shell to hydrogen to form bridged hydrogen bonding. Another boron atom also shares its electron to form bridging bonds with hydrogen as shown below.

So, we can see that each bridged bond contains two electrons bonded with three atoms. Therefore, option (A)- \[{\rm{B}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}\] has three -centre two electron bonds in its dimeric structure is correct.
->\[{\rm{Al}}{\left( {{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}} \right)_{\rm{3}}}\] has six electrons in its octet and to complete its octet, it forms dimer. Aluminium atoms share one electron of the outermost shell with one electron of carbon to form bridged bonding. Other aluminium atoms also share their electrons to form bridging bonds with carbon atoms as shown below.

Therefore, option (B)- \[{\rm{Al}}{\left( {{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}} \right)_{\rm{3}}}\] has three centre- two electron bonds in its dimeric structure is correct.
->Option (C)- \[{\rm{AlC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{3}}}\] also forms dimeric structure because it also has six electrons in its octet and to complete its octet, it forms dimer. One aluminium atom shares one electron of outermost shell with one electron of chlorine atom to form bridged bonding and chlorine also donate its one lone pair of electrons to vacant orbital of aluminium atom to form coordinate bonding as shown below.

As we can see, bridging bonding contains three atoms with four electrons, so it does not form three centre -two electron bonds.
Therefore, this option is incorrect.
->Now, option (D)- The Lewis acidity of \[{\rm{BC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{3}}}\] is greater than that of \[{\rm{AlC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{3}}}\] is correct because boron’s \[{\rm{2p}}\]-orbital overlaps with chlorine’s \[{\rm{3p}}\]-orbital, hence, cannot form bond effectively. Therefore, Lewis acidity is greater. On the other hand, in \[{\rm{AlC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{3}}}\], overlapping is \[{\rm{3p - 3p}}\] between aluminium and chlorine.
Therefore, the correct options are option (A), option (B) and option (D).
Note:
From IR spectra, stretching frequency of bridging bonds is less than terminal bonds because electron density is less than the volume. Compounds like $Al_2Cl_6$ are very unique because this kind of structure is very rare.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




