
Among Cyclopropane, cyclobutane and cyclohexane the common structure present in all hydrocarbon is:
A.
 B.
B.
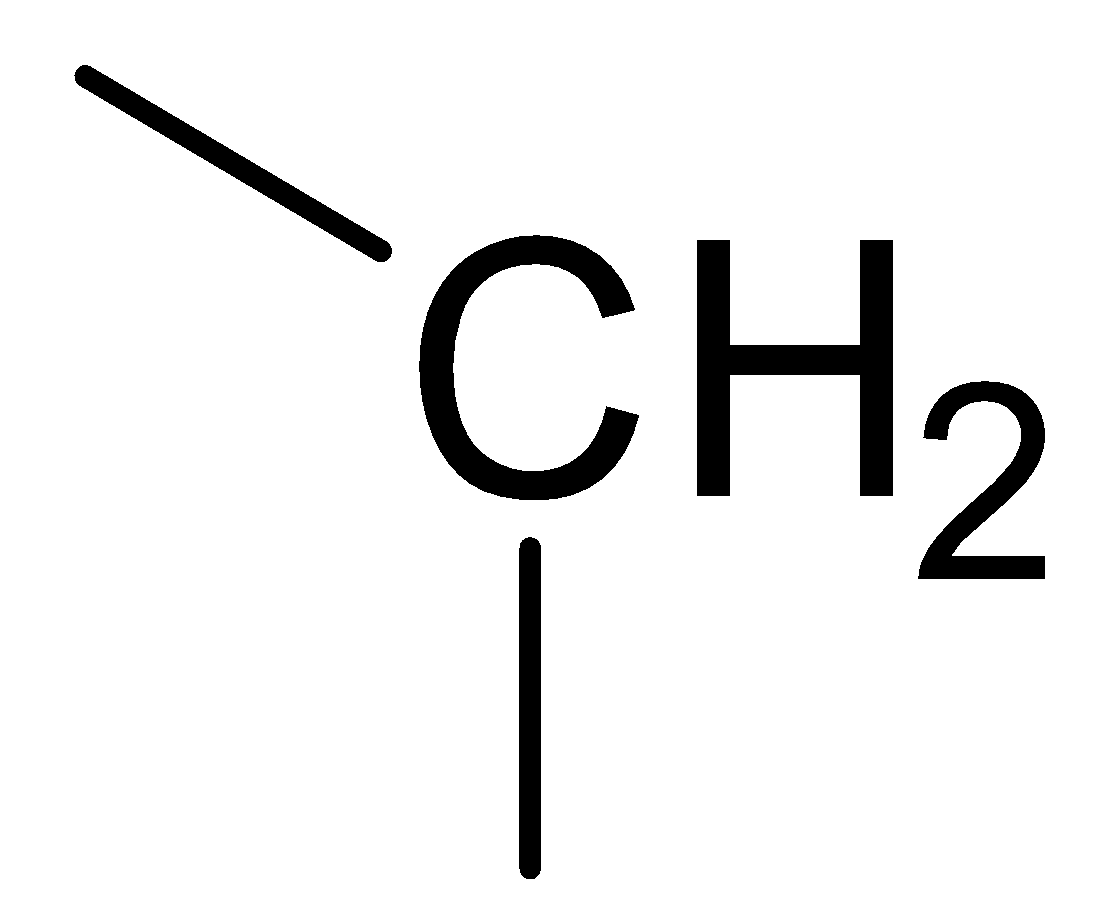 C.
C.
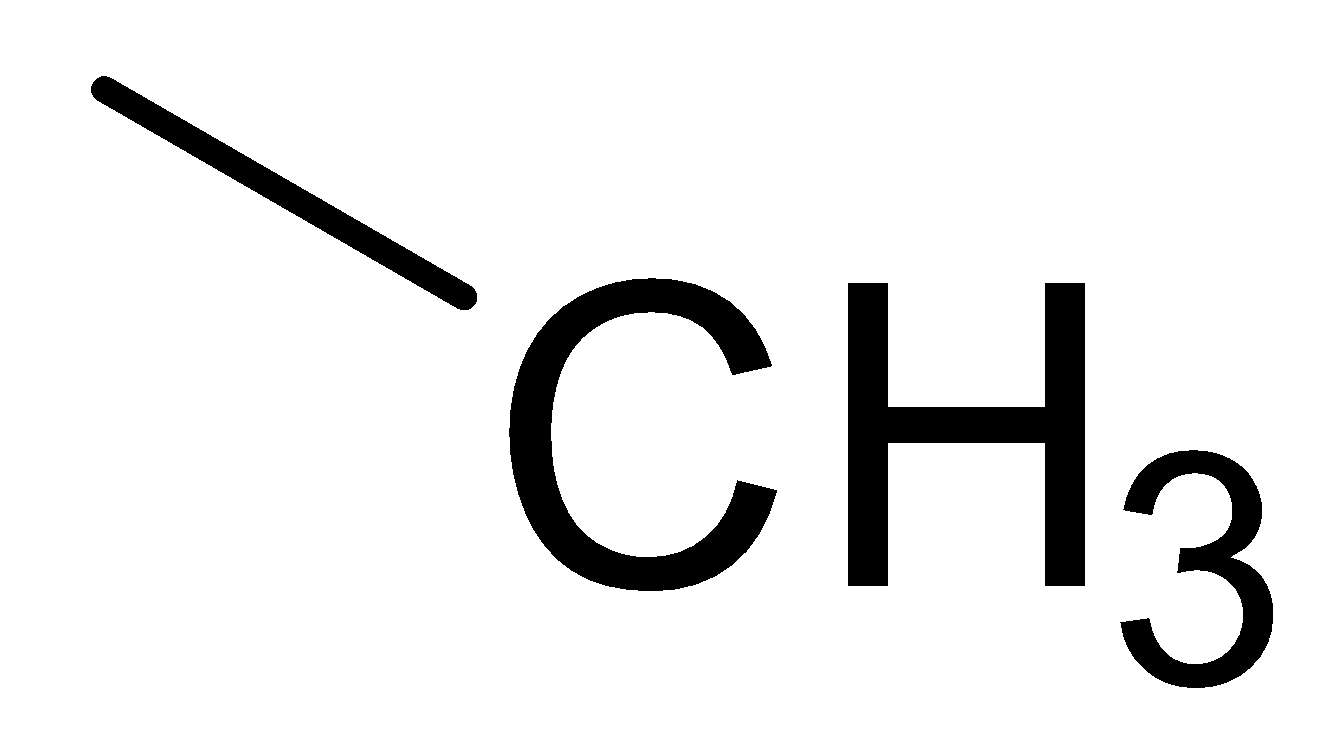 D.
D.
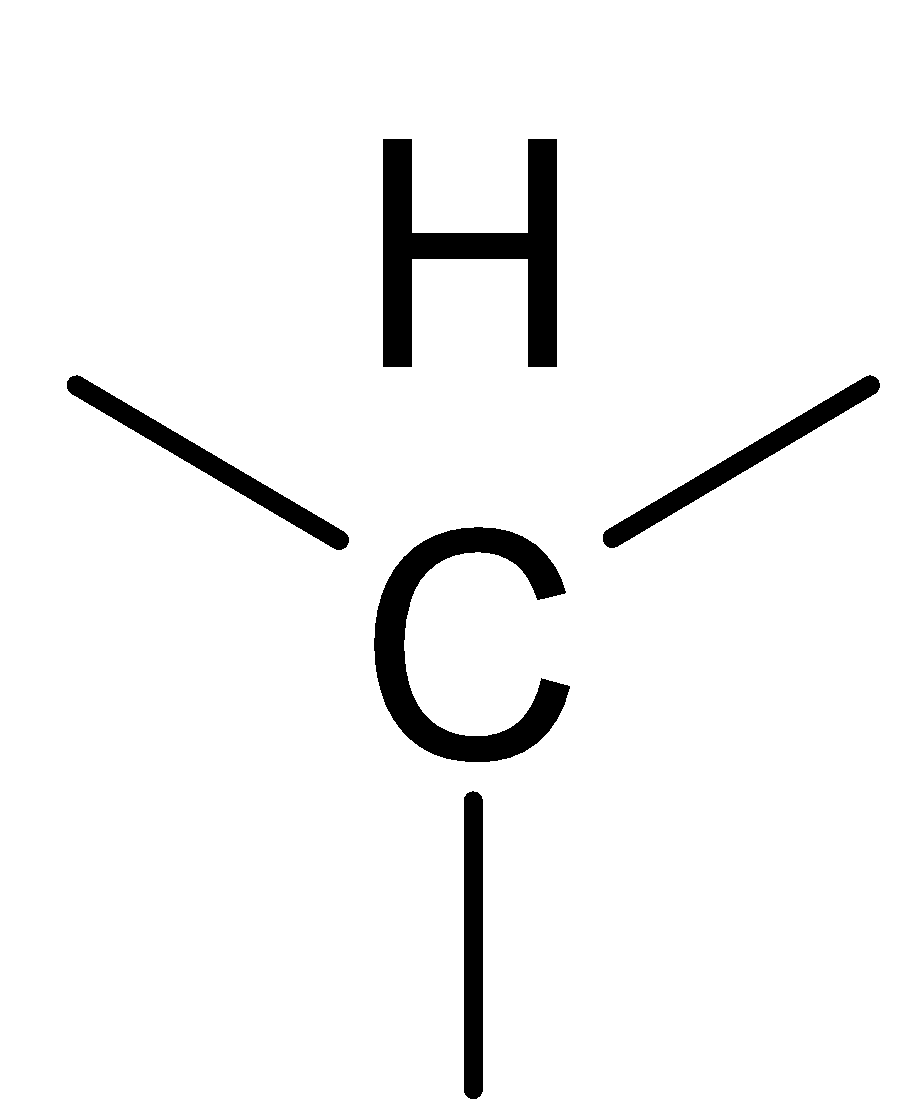




Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint:Hydrocarbons are made of Carbon-Carbon links with hydrogen atoms to complete valency. Linear Saturated hydrocarbons have repeating methylene groups and terminal methyl groups. If the compound is unsaturated the degree of unsaturation is , equal numbers of hydrogen are removed from the two carbons. Cyclic compounds have their degree of saturation as one between the terminal carbons.
Complete answer:
Firstly we have to understand followings terms,
Hydrocarbon: They are the base of organic chemistry. These are compounds which are purely Hydrogen and carbon. They can be classified as alkane, alkene, alkyne on the basis of their degree of saturation
Alkanes: they are acyclic saturated hydrocarbon.an alkane consist of hydrogen and carbon atoms arranged in a tetrahedral structure in which there are only single bonds. Alkanes have the general chemical formula ${C_n}{H_{2n+2}}$.
Cycloalkanes: the cycloalkanes are the monocyclic saturated hydrocarbons, a cycloalkanes consisting only of carbon and hydrogen atoms arranged in a structure containing a single ring. Cycloalkanes having one ring have a general formula ${C_n}{H_{2n}}$.
Some common examples of cycloalkane are cyclopropane, cyclobutane, cyclohexane .
The number of the carbon atoms present in the compound decides the structure of cycloalkanes.
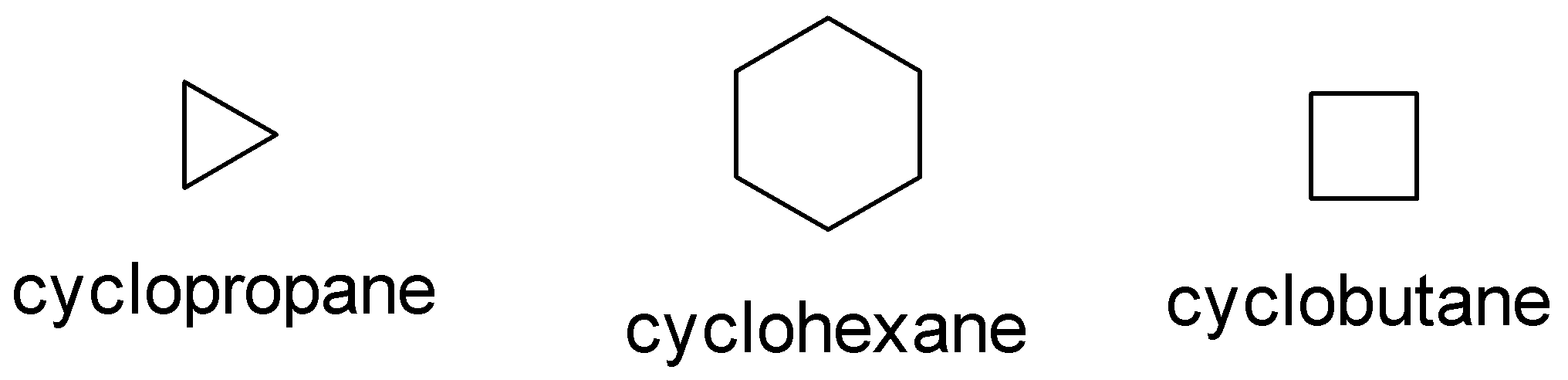
The molecular formula for the above compounds is:
A. Cyclopropane: ${C_3}{H_6}$
B. Cyclobutane:${C_4}{H_8}$
C: Cyclohexane: ${C_6}{H_{12}}$
These molecules follow the general formula for Cyclic hydrocarbon which is ${C_n}{H_{2n}}$
The least possible value of this unit can be, $C{H_2} $
In the above picture we can observe that each structure of the carbon atom is $sp_3$ hybridized which means that each carbon makes form two carbon hydrogen bonds and two carbon-carbon bonds. This implies that each structure contains.
Hence Option B is correct.
Note:
An Alternate method to determine the answer is that These molecules follow the general formula for Cyclic hydrocarbon which is ${C_n}{H_{2n}}$
The least possible value of this unit can be, $C{H_2} $. Hence, the repeating unit must be a methylene group.
Complete answer:
Firstly we have to understand followings terms,
Hydrocarbon: They are the base of organic chemistry. These are compounds which are purely Hydrogen and carbon. They can be classified as alkane, alkene, alkyne on the basis of their degree of saturation
Alkanes: they are acyclic saturated hydrocarbon.an alkane consist of hydrogen and carbon atoms arranged in a tetrahedral structure in which there are only single bonds. Alkanes have the general chemical formula ${C_n}{H_{2n+2}}$.
Cycloalkanes: the cycloalkanes are the monocyclic saturated hydrocarbons, a cycloalkanes consisting only of carbon and hydrogen atoms arranged in a structure containing a single ring. Cycloalkanes having one ring have a general formula ${C_n}{H_{2n}}$.
Some common examples of cycloalkane are cyclopropane, cyclobutane, cyclohexane .
The number of the carbon atoms present in the compound decides the structure of cycloalkanes.

The molecular formula for the above compounds is:
A. Cyclopropane: ${C_3}{H_6}$
B. Cyclobutane:${C_4}{H_8}$
C: Cyclohexane: ${C_6}{H_{12}}$
These molecules follow the general formula for Cyclic hydrocarbon which is ${C_n}{H_{2n}}$
The least possible value of this unit can be, $C{H_2} $
In the above picture we can observe that each structure of the carbon atom is $sp_3$ hybridized which means that each carbon makes form two carbon hydrogen bonds and two carbon-carbon bonds. This implies that each structure contains.
Hence Option B is correct.
Note:
An Alternate method to determine the answer is that These molecules follow the general formula for Cyclic hydrocarbon which is ${C_n}{H_{2n}}$
The least possible value of this unit can be, $C{H_2} $. Hence, the repeating unit must be a methylene group.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




