
Among cellulose, polyvinyl chloride (P V C), nylon and natural rubber, the polymer in which intermolecular forces of attraction are weakest is:
A. Nylon
B. (P V C)
C. Natural rubber
D. Cellulose
Answer
581.7k+ views
Hint: Intermolecular forces are of different types. Such as hydrogen bonding, dipole-dipole interaction and Van Der Waals forces. Among them, the Vander Walls’s forces of attraction are the weakest.
Complete step by step answer:
Comparison between intermolecular forces of attraction among cellulose, poly-vinyl chloride (P V C), nylon and natural rubber.
Let us first understand about intermolecular forces.
Intermolecular forces are the forces which mediate interaction between atoms or ions. There are three major types of intermolecular interactions which come into play. They are as follows:
A. Dipole-dipole interaction
B. London dispersion force
C. Hydrogen bonds
The first two are sometimes collectively referred to as the Van Der Waals force.
The order of strength of the intermolecular forces are as follows:
Hydrogen Bonding >> Dipole-dipole interaction >> Van Der Waals force
If we analyze the four polymers given in the question, we see that Nylon has intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
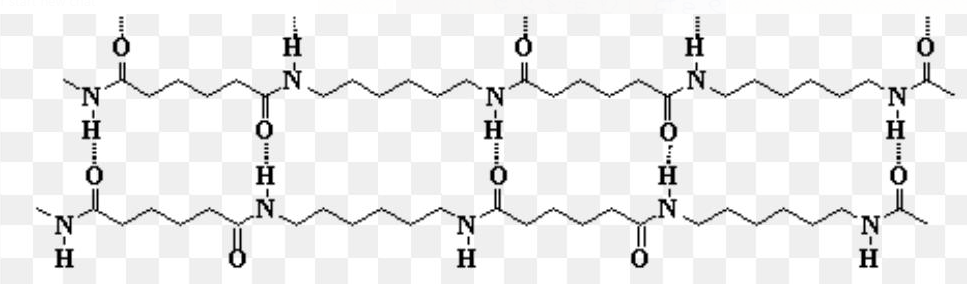
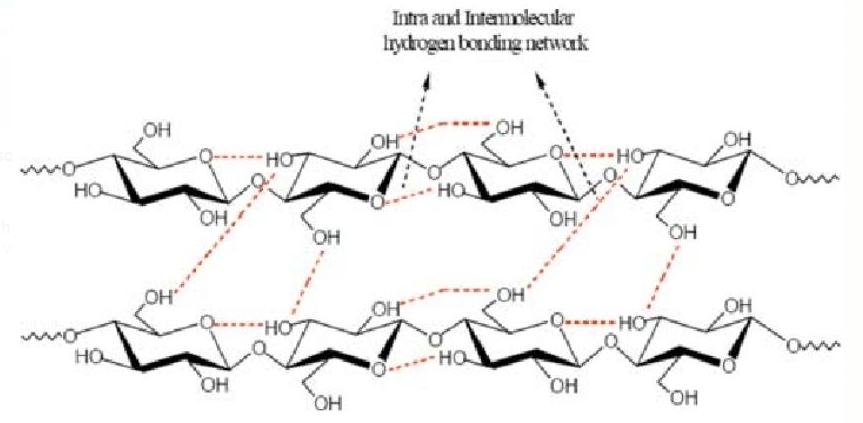
Cellulose too have intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
While poly vinyl chloride (P V C) has dipole-dipole interaction.

However, in case of natural rubber which is an elastomer, the interactions involved are a weak Van Der Waals force of attraction.
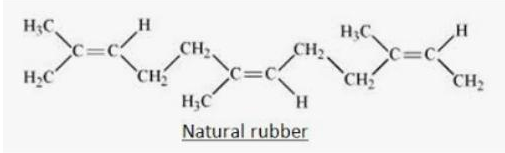
Looking into the order of strength of intermolecular forces we get natural rubber to have the weakest force of attraction.
Thus, the correct option is (D).
Note:
Students should note that intermolecular and intramolecular forces are two different kinds. The former exists between the molecules/atoms/ions while the latter holds the atoms together in a molecule. Intra-molecular forces are stronger than intermolecular forces.
Complete step by step answer:
Comparison between intermolecular forces of attraction among cellulose, poly-vinyl chloride (P V C), nylon and natural rubber.
Let us first understand about intermolecular forces.
Intermolecular forces are the forces which mediate interaction between atoms or ions. There are three major types of intermolecular interactions which come into play. They are as follows:
A. Dipole-dipole interaction
B. London dispersion force
C. Hydrogen bonds
The first two are sometimes collectively referred to as the Van Der Waals force.
The order of strength of the intermolecular forces are as follows:
Hydrogen Bonding >> Dipole-dipole interaction >> Van Der Waals force
If we analyze the four polymers given in the question, we see that Nylon has intermolecular hydrogen bonding.

Cellulose too have intermolecular hydrogen bonding.

While poly vinyl chloride (P V C) has dipole-dipole interaction.

However, in case of natural rubber which is an elastomer, the interactions involved are a weak Van Der Waals force of attraction.

Looking into the order of strength of intermolecular forces we get natural rubber to have the weakest force of attraction.
Thus, the correct option is (D).
Note:
Students should note that intermolecular and intramolecular forces are two different kinds. The former exists between the molecules/atoms/ions while the latter holds the atoms together in a molecule. Intra-molecular forces are stronger than intermolecular forces.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




