
Among cellulose, polyvinyl chloride, nylon, and natural rubber, the polymer in which the following intermolecular force of attraction is weakest?
A) Nylon
B) Polyvinyl chloride
C) Cellulose
D) Natural rubber
Answer
581.7k+ views
Hint: The polymers have the same intermolecular forces that we see in small molecules. There are various intermolecular forces between the polymers. Such as dispersion forces, hydrogen bonding, van der Waals’ forces of attraction, etc. The polymers may contain the heteroatoms which increase the dipole interaction.
Complete answer:
Rubber is a naturally occurring polymer. It is obtained as latex from rubber trees.
The natural rubber is a polymer of isoprene (2-methyl buta-1, 3-diene). The structure of the monomer is as below,
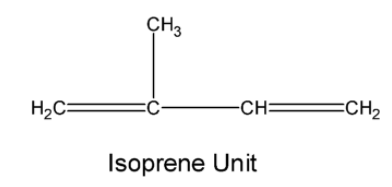
In natural rubber about 11,000 to 20,000 isoprene units are linked together in a chain-like arrangement as shown below:
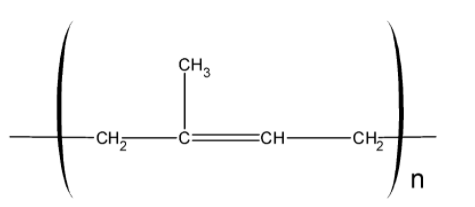
It may be noted that the natural rubber is a cis-1, 4-polyisoprene and has all cis configuration about the double bond as shown below,
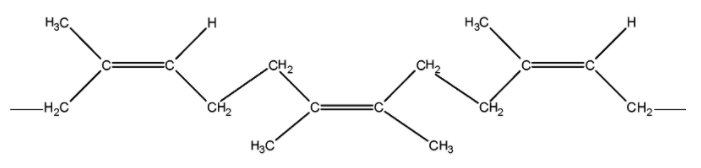
There are weak van der Waals forces and therefore, it is elastic and non-crystalline. It is a long flexible chain.
The natural rubber is made of the carbon C and hydrogen H atoms. It does not have the heteroatoms. Thus, the rubber rubber has a nonpolar $\text{ C}-\text{H }$ bond and has weak van der Waals forces of attraction.
On the other hand, the nylon has a polyamide $\text{ }-\text{CONH}-\text{ }$ linkage in the chain. Due to polyamide linkage, the nylon has a polar bond. These bonds result in the dipole interaction, even hydrogen bonding. One of the simplest nylons is nylon-6, 6.
The monomer unit of a Nylon 6, 6 is as shown below,
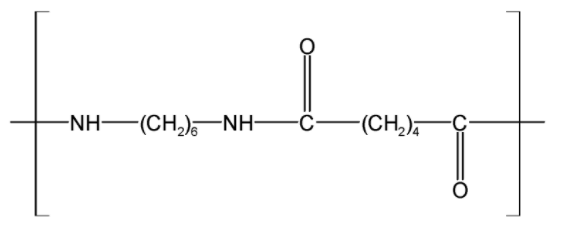
Similarly, the cellulose and polyvinyl chloride have the heteroatoms chlorine and oxygen in it. This results in a polar bond and thus increases the attraction between the monomeric units.
The natural rubber has the weakest force of attraction between the monomeric units.
Hence, (C) is the correct option.
Note:
Note that, the cis form of the natural rubber is elastic. However, the Trans configuration has a highly regular zig-zag structure, thus they fit together well. These are highly crystalline and non-elastic because of the strong packing of chains. The extended chain structure.
Complete answer:
Rubber is a naturally occurring polymer. It is obtained as latex from rubber trees.
The natural rubber is a polymer of isoprene (2-methyl buta-1, 3-diene). The structure of the monomer is as below,

In natural rubber about 11,000 to 20,000 isoprene units are linked together in a chain-like arrangement as shown below:

It may be noted that the natural rubber is a cis-1, 4-polyisoprene and has all cis configuration about the double bond as shown below,

There are weak van der Waals forces and therefore, it is elastic and non-crystalline. It is a long flexible chain.
The natural rubber is made of the carbon C and hydrogen H atoms. It does not have the heteroatoms. Thus, the rubber rubber has a nonpolar $\text{ C}-\text{H }$ bond and has weak van der Waals forces of attraction.
On the other hand, the nylon has a polyamide $\text{ }-\text{CONH}-\text{ }$ linkage in the chain. Due to polyamide linkage, the nylon has a polar bond. These bonds result in the dipole interaction, even hydrogen bonding. One of the simplest nylons is nylon-6, 6.
The monomer unit of a Nylon 6, 6 is as shown below,

Similarly, the cellulose and polyvinyl chloride have the heteroatoms chlorine and oxygen in it. This results in a polar bond and thus increases the attraction between the monomeric units.
The natural rubber has the weakest force of attraction between the monomeric units.
Hence, (C) is the correct option.
Note:
Note that, the cis form of the natural rubber is elastic. However, the Trans configuration has a highly regular zig-zag structure, thus they fit together well. These are highly crystalline and non-elastic because of the strong packing of chains. The extended chain structure.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




