
What is the aminoacid sequence in the polypeptide segment translated from the mRNA base sequence of AGU-UUU-UCC-GGG-UCG.
(a) serine-phenylalanine-serine-glycine-serine
(b) serine-serine-phenylalanine-glycine-serine
(c) Phenylalanine-serine-serine-glycine-serine
(d) serine-glycine-serine-phenylalanine-serine
Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: 61 codons code for 20 amino acids and 3 codons does not code for any amino acid so they are called stop codons. Each codon is a triplet.
Complete step by step answer:
The set of rules used by living cells for the translation of information present within genetic material in the coded form into amino acids is called genetic code. Each codon is a triplet. One codon codes for only one amino acid. The amino acids for the codons sequence AGU-UUU-UCC-gGG-UCG
Which is translated from mRNA are serine-phenylalanine-serine-glycine-serine.
Additional information:
- The codon that codes for amino acids are triplets. In total there are 64 codons and out of 64 codons, 61 codons code for amino acids, and the remaining 3 codons do not code for any of the amino acids so they are called step codons.
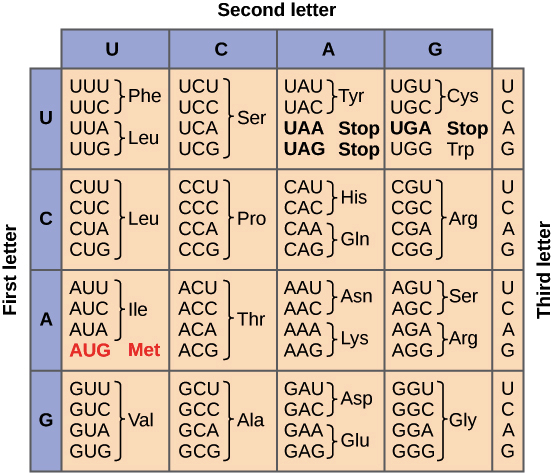
- Genetic code is unambiguous or specific because one codon codes only for one amino acid.
- Genetic code is degenerate because some amino acids are coded by more than one codon.
- The list of 20 amino acids that codons code for are Phenylalanine (Phe), Leucine (Leu), Isoleucine (Ile), Methionine (Met), Serine (Ser), Valine (Val), Proline (Pro), Threonine (Thr), Alanine (Ala), Tyrosine (Tyr), Histidine (His), Glutamine (Gln), Glutamine (Gln), Lysine (Lys), Aspartic acid (Asp), Glutamic acid (Glu), Cysteine (Cys), Tryptophan (Trp), Arginine (Arg), Glycine (Gly).
- The genetic code is nearly universal from bacteria to human beings.
So, the correct answer is ‘serine-phenylalanine-serine-glycine-serine’.
Note:
- The three stop codons present in the genetic code are UAA, UAG, and UGA.
- The codon AUG codes for methionine it is called as initiator codon.
- If any alterations in this triplet code due to mutations it leads to genetic disorders.
Complete step by step answer:
The set of rules used by living cells for the translation of information present within genetic material in the coded form into amino acids is called genetic code. Each codon is a triplet. One codon codes for only one amino acid. The amino acids for the codons sequence AGU-UUU-UCC-gGG-UCG
Which is translated from mRNA are serine-phenylalanine-serine-glycine-serine.
Additional information:
- The codon that codes for amino acids are triplets. In total there are 64 codons and out of 64 codons, 61 codons code for amino acids, and the remaining 3 codons do not code for any of the amino acids so they are called step codons.

- Genetic code is unambiguous or specific because one codon codes only for one amino acid.
- Genetic code is degenerate because some amino acids are coded by more than one codon.
- The list of 20 amino acids that codons code for are Phenylalanine (Phe), Leucine (Leu), Isoleucine (Ile), Methionine (Met), Serine (Ser), Valine (Val), Proline (Pro), Threonine (Thr), Alanine (Ala), Tyrosine (Tyr), Histidine (His), Glutamine (Gln), Glutamine (Gln), Lysine (Lys), Aspartic acid (Asp), Glutamic acid (Glu), Cysteine (Cys), Tryptophan (Trp), Arginine (Arg), Glycine (Gly).
- The genetic code is nearly universal from bacteria to human beings.
So, the correct answer is ‘serine-phenylalanine-serine-glycine-serine’.
Note:
- The three stop codons present in the genetic code are UAA, UAG, and UGA.
- The codon AUG codes for methionine it is called as initiator codon.
- If any alterations in this triplet code due to mutations it leads to genetic disorders.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




