
What is the allosteric inhibitor? Explain with an example.
Answer
504.3k+ views
Hint: The allosteric inhibitors affect the activity of the enzyme and do not lead to the formation of the enzyme-substrate complex. These inhibitors are proteins that are used to regulate the speed of the metabolic reaction.
Complete answer:
The enzymes are the biomolecules that react with the substrate and bring about the formation of the product. They alter the rate of forwarding reaction by lowering the activation energy. The enzymes have an active site at which only a specific substrate can bind. These active sites contain proteins that allow only the specific molecules to bring about chemical change.
Some molecules(effectors) resemble the substrate and binds at the allosteric site of the enzymes thereby altering the proteins at the active site. Due to this, the specific substrate is not able to bind at the active site as a result of which the enzyme activity is deactivated. This is known as allosteric inhibition and the molecule which binds the allosteric site is known as an allosteric inhibitor.
The best example of allosteric inhibition is the ATP molecule. When a lot of ATP molecule is available as a result of cellular respiration, it affects the enzyme and deactivates it as ATP is an unstable molecule. Another example is glucokinase is an effector which binds with the enzymes released by the pancreas. This mechanism is used in treating diabetes.
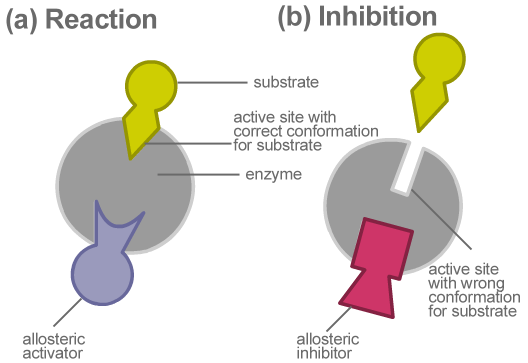
Note: The effector molecule can act as an inhibitor or the activator which can lead to conformational change in the active site. Another method of inhibition of enzyme activity is the competitive inhibition in two substrates compete for the particular active site. The binding of the wrong substrate brings about deactivating the enzyme activity.
Complete answer:
The enzymes are the biomolecules that react with the substrate and bring about the formation of the product. They alter the rate of forwarding reaction by lowering the activation energy. The enzymes have an active site at which only a specific substrate can bind. These active sites contain proteins that allow only the specific molecules to bring about chemical change.
Some molecules(effectors) resemble the substrate and binds at the allosteric site of the enzymes thereby altering the proteins at the active site. Due to this, the specific substrate is not able to bind at the active site as a result of which the enzyme activity is deactivated. This is known as allosteric inhibition and the molecule which binds the allosteric site is known as an allosteric inhibitor.
The best example of allosteric inhibition is the ATP molecule. When a lot of ATP molecule is available as a result of cellular respiration, it affects the enzyme and deactivates it as ATP is an unstable molecule. Another example is glucokinase is an effector which binds with the enzymes released by the pancreas. This mechanism is used in treating diabetes.

Note: The effector molecule can act as an inhibitor or the activator which can lead to conformational change in the active site. Another method of inhibition of enzyme activity is the competitive inhibition in two substrates compete for the particular active site. The binding of the wrong substrate brings about deactivating the enzyme activity.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




