
All the vertices of a rhombus lie on a circle. Find the area of the rhombus, if the area of the circle is 1256$c{m^2}$.

Answer
529.5k+ views
Hint:Vertices of cyclic quadrilateral lie on a circle and for cyclic quadrilateral, sum of opposite angles is equal to ${180^0}$. Apply the properties of rhombus and find the relation between radius of circle and area of rhombus.
Complete step-by-step answer:
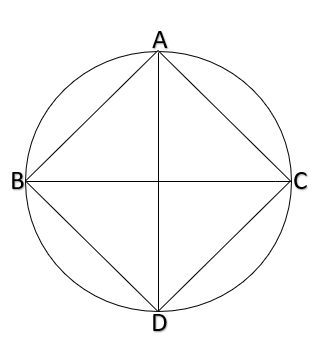
Since it is given rhombus is a cyclic quadrilateral.
Let ${d_1}{\text{ and }}{d_2}$be diagonals of rhombus
Sum of opposite angles = ${180^0}$
$\angle A + \angle C = {180^0}$
Also AB || CD
$
\Rightarrow \angle A + \angle B = {180^0} \\
\Rightarrow \angle B = \angle C \\
$
Now, as adjacent angles are equal, it is a square.
$\angle B = {90^0}$
$\angle B$is angle in semicircle
AC and BD are diameter of circle.
Now, Area of circle = 1256
$
\pi {r^2} = 1256 \\
{r^2} = \dfrac{{1256}}{{3.14}} \\
{r^2} = 400 \\
r = \sqrt {400} \\
r = 20cm \\
$
Diameter of circle = 2r = 40cm $ \Rightarrow {d_1} = {d_2} = 40cm$
$\therefore $Area of rhombus
$
= \dfrac{1}{2} \times {d_1} \times {d_2} \\
= \dfrac{1}{2} \times 40 \times 40 \\
= 800c{m^2} \\
\\
$
Note: A cyclic quadrilateral or inscribed quadrilateral is a quadrilateral whose vertices all lie on a single circle. This circle is called the circumcircle or circumscribed circle, and the vertices are said to be concyclic. Students must remember the formula for the area of some common geometrical figure such as circle and rhombus.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Since it is given rhombus is a cyclic quadrilateral.
Let ${d_1}{\text{ and }}{d_2}$be diagonals of rhombus
Sum of opposite angles = ${180^0}$
$\angle A + \angle C = {180^0}$
Also AB || CD
$
\Rightarrow \angle A + \angle B = {180^0} \\
\Rightarrow \angle B = \angle C \\
$
Now, as adjacent angles are equal, it is a square.
$\angle B = {90^0}$
$\angle B$is angle in semicircle
AC and BD are diameter of circle.
Now, Area of circle = 1256
$
\pi {r^2} = 1256 \\
{r^2} = \dfrac{{1256}}{{3.14}} \\
{r^2} = 400 \\
r = \sqrt {400} \\
r = 20cm \\
$
Diameter of circle = 2r = 40cm $ \Rightarrow {d_1} = {d_2} = 40cm$
$\therefore $Area of rhombus
$
= \dfrac{1}{2} \times {d_1} \times {d_2} \\
= \dfrac{1}{2} \times 40 \times 40 \\
= 800c{m^2} \\
\\
$
Note: A cyclic quadrilateral or inscribed quadrilateral is a quadrilateral whose vertices all lie on a single circle. This circle is called the circumcircle or circumscribed circle, and the vertices are said to be concyclic. Students must remember the formula for the area of some common geometrical figure such as circle and rhombus.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




