
Aldol condensation does not occur between:
A. two different aldehydes
B.an aldehyde and an ester
C. an aldehyde and ketones
D. two different ketones
Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: In a condensation reaction, when the reactants join together it forms a product, a small molecule is lost. In the case of aldol condensation, small molecule water is lost. In this reaction, a beta-hydroxy ketone or aldehyde is formed.
Complete step by step answer:
-Aldol condensation is a condensation reaction of organic chemistry, where an enolate ion or enol attacks the carbonyl group of another aldehyde or ketone and generates a beta-hydroxy ketone or beta hydroxy aldehyde.
-This condensation reaction can be possible in between two ketones, or aldehyde, or between one aldehyde and one ketone. In this condensation, the important condition is the compound must have beta hydrogen. If any compound does not have any beta hydrogen, it cannot perform an aldol reaction.
-In the case of the mix, aldol condensations were two different aldehydes or two different ketones or one ketone and one aldehyde took part. In this mix aldol, if both reactants pose beta hydrogen then a mixture of products is formed. And if only one reactant possesses the beta hydrogen then a pure condensed compound will form.
-The beta hydrogen-containing reactant forms the enolate ion or the enol. Which acts as a nucleophile.
-Then the enolate attacks the carbonyl group and forms a condense product.
-Then the alkoxy group accepts the proton and forms a beta-hydroxy carbonyl compound.
The reaction steps are shown below,
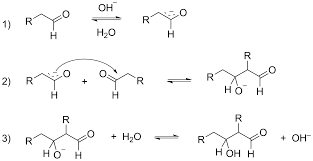
This aldol reaction is possible in between two different aldehydes, an aldehyde, and ketones two different ketones
But not in between an aldehyde and an ester because the electrophilicity of the carbonyl group of the ester is very low, that nucleophilic attack of the enolate ion will not be favored.
So, the correct option is B.
Note:
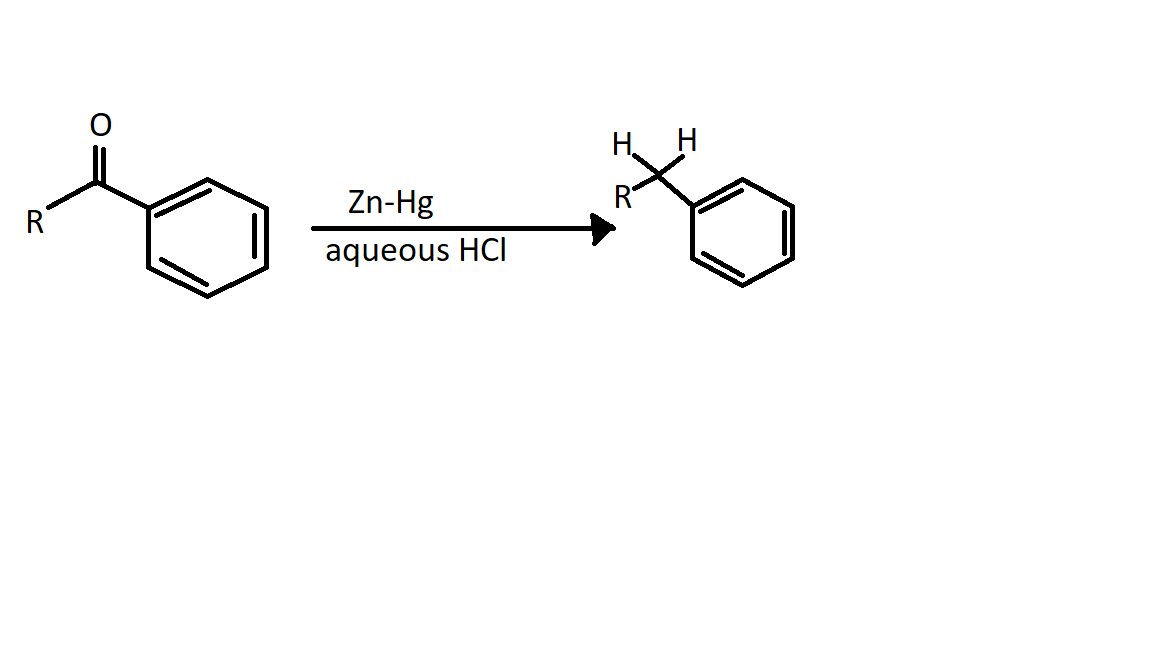
The Clemmensen reduction got its name from a Danish chemist, Erik Christian Clemmensen. The Clemmensen reduction is a reaction that is performed to reduce carbonyl compounds such as aldehydes or ketones to hydrocarbons that are alkanes using concentrated hydrochloric acid and zinc amalgam.
Complete step by step answer:
-Aldol condensation is a condensation reaction of organic chemistry, where an enolate ion or enol attacks the carbonyl group of another aldehyde or ketone and generates a beta-hydroxy ketone or beta hydroxy aldehyde.
-This condensation reaction can be possible in between two ketones, or aldehyde, or between one aldehyde and one ketone. In this condensation, the important condition is the compound must have beta hydrogen. If any compound does not have any beta hydrogen, it cannot perform an aldol reaction.
-In the case of the mix, aldol condensations were two different aldehydes or two different ketones or one ketone and one aldehyde took part. In this mix aldol, if both reactants pose beta hydrogen then a mixture of products is formed. And if only one reactant possesses the beta hydrogen then a pure condensed compound will form.
-The beta hydrogen-containing reactant forms the enolate ion or the enol. Which acts as a nucleophile.
-Then the enolate attacks the carbonyl group and forms a condense product.
-Then the alkoxy group accepts the proton and forms a beta-hydroxy carbonyl compound.
The reaction steps are shown below,

This aldol reaction is possible in between two different aldehydes, an aldehyde, and ketones two different ketones
But not in between an aldehyde and an ester because the electrophilicity of the carbonyl group of the ester is very low, that nucleophilic attack of the enolate ion will not be favored.
So, the correct option is B.
Note:
The Clemmensen reduction got its name from a Danish chemist, Erik Christian Clemmensen. The Clemmensen reduction is a reaction that is performed to reduce carbonyl compounds such as aldehydes or ketones to hydrocarbons that are alkanes using concentrated hydrochloric acid and zinc amalgam.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




