
Alanine forms Zwitter ion which exists as:
(a)- $C{{H}_{3}}-\overset{\oplus N{{H}_{3}}}{\mathop{\overset{|}{\mathop{C}}\,}}\,-HCO{{O}^{-}}$ in acidic medium
(b)- $C{{H}_{3}}-\overset{\oplus N{{H}_{3}}}{\mathop{\overset{|}{\mathop{C}}\,}}\,-HCOOH$ in a medium of pH = 4
(c)- $C{{H}_{3}}-\underset{N{{H}_{2}}}{\mathop{\underset{|}{\mathop{C}}\,}}\,-HCO{{O}^{-}}$ in a medium of pH = 1
(d)- $C{{H}_{3}}-\underset{N{{H}_{2}}}{\mathop{\underset{|}{\mathop{C}}\,}}\,-HCO{{O}^{-}}$ in a medium of pH = 2
Answer
542.4k+ views
Hint:Alanine is a compound that belongs to amino acids which means the compound will have one amino group and one carboxylic acid group. Zwitter ion is formed when a proton travels within the molecule.
Complete step-by-step answer:We know that amino acids are those compounds in which the same molecule has one amino group, i.e., $(-N{{H}_{2}})$ and one carboxylic acid group, i.e., $(-COOH)$. On specifying alpha-amino acid means the amino group is on the alpha position of the carboxylic acid and alanine is an example of alpha-amino acid group. The molecular formula of alanine is ${{C}_{3}}{{H}_{7}}N{{O}_{2}}$. It is a compound of two carbon atoms in which the same carbon atom has an amine group as well as a carboxylic acid group. The structure of alanine is given below:
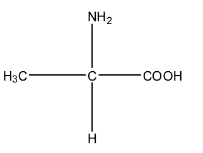
Zwitter ion is formed when a proton travels within the molecule. So, in alanine, the proton from the carboxylic acid group will shift to the amine group because the carboxylic acid has the tendency to release the proton, and amine being base has the tendency to accept the proton. The zwitter ion is formed in an acidic medium. The structure is given below:
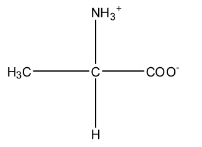
So, from the given options only option (a) resembles the structure of the zwitterion.
Therefore, the correct answer is an option (a).
Note: Zwitterion is only possible if the same molecule has both an electron donor and an electron acceptor. Alanine is a white powder whose molecular formula is 89.094 g/8mol.
Complete step-by-step answer:We know that amino acids are those compounds in which the same molecule has one amino group, i.e., $(-N{{H}_{2}})$ and one carboxylic acid group, i.e., $(-COOH)$. On specifying alpha-amino acid means the amino group is on the alpha position of the carboxylic acid and alanine is an example of alpha-amino acid group. The molecular formula of alanine is ${{C}_{3}}{{H}_{7}}N{{O}_{2}}$. It is a compound of two carbon atoms in which the same carbon atom has an amine group as well as a carboxylic acid group. The structure of alanine is given below:

Zwitter ion is formed when a proton travels within the molecule. So, in alanine, the proton from the carboxylic acid group will shift to the amine group because the carboxylic acid has the tendency to release the proton, and amine being base has the tendency to accept the proton. The zwitter ion is formed in an acidic medium. The structure is given below:

So, from the given options only option (a) resembles the structure of the zwitterion.
Therefore, the correct answer is an option (a).
Note: Zwitterion is only possible if the same molecule has both an electron donor and an electron acceptor. Alanine is a white powder whose molecular formula is 89.094 g/8mol.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




