
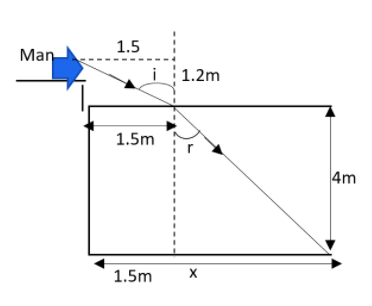
After a long day of driving a person takes a late-night swim in a motel swimming pool. When he goes to his room, he realizes that he has lost his room key in the pool. He borrows a strong flashlight and walks around the pool, by shining the light into it. The light falls on the key, which is placed on the bottom of the pool. When the flashlight is held $1.2m$ above the water surface and is directed at the surface a horizontal distance of $1.5m$ from the edge. If the water here is $4.0m$ deep, what will be the distance to the key from the edge of the pool?
$\begin{align}
& A.4.0m \\
& B.4.16m \\
& C.4.86m \\
& D.4.36m \\
\end{align}$

Answer
576.3k+ views
Hint: Snell’s law is the basis for solving this question. First of all find the angles using trigonometric relationships and Snell’s law. In the same way by taking the tangent of ${{\theta }_{b}}$, find the length from the edge of the pool. This will help you in answering this question.
Complete answer:
We are having the following diagram for light beams. Suppose an angle of ${{\theta }_{a}}$ and refract at an angle of ${{\theta }_{b}}$ with the normal as represented in the diagram.
As we all know, the index of refraction of air will be equivalent to $1$ and that of the water can be written as $1.33$. We can get the ${{\theta }_{a}}$ using the dimensions given. Let us apply Snell's law in this question for getting the value of ${{\theta }_{b}}$.
The value of ${{\theta }_{a}}$ can be written as,
$\begin{align}
& \tan {{\theta }_{a}}=\dfrac{1.5}{1.2} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\theta }_{a}}={{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{1.5}{1.2} \right) \\
& \therefore {{\theta }_{a}}=51.34{}^\circ \\
\end{align}$
Use the Snell’s law in the equation as,
${{n}_{a}}\sin \left( {{\theta }_{a}} \right)={{n}_{b}}\sin \left( {{\theta }_{b}} \right)$
Substituting the values in it will give,
\[\begin{align}
& 1\times \sin \left( 51.34{}^\circ \right)=1.33\times \sin \left( {{\theta }_{b}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \sin \left( {{\theta }_{b}} \right)=0.587 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\theta }_{b}}={{\sin }^{-1}}\left( 0.587 \right) \\
& \therefore {{\theta }_{b}}=35.94{}^\circ \\
\end{align}\]
Now from the triangle ABC we can write that,
\[\tan \left( {{\theta }_{b}} \right)=\dfrac{BC}{AB}\]
Where \[AB\] be the depth of the pool which is mentioned as,
\[AB=4m\]
Substituting the values in this equation will give,
\[\begin{align}
& \tan \left( 35.94 \right)=\dfrac{BC}{4} \\
& \Rightarrow BC=4\times 0.725 \\
& \Rightarrow BC=2.86m \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore the total length from the edge of the pool can be shown as,
\[L=1.5+2.86=4.36m\]
Therefore the answer has been obtained as option D.
Note:
Snell's law is basically an equation helpful in describing the connection between the angles of incidence and refraction, when we consider light or other waves passing through a boundary between various isotropic media like water, air or glass.
Complete answer:
We are having the following diagram for light beams. Suppose an angle of ${{\theta }_{a}}$ and refract at an angle of ${{\theta }_{b}}$ with the normal as represented in the diagram.
As we all know, the index of refraction of air will be equivalent to $1$ and that of the water can be written as $1.33$. We can get the ${{\theta }_{a}}$ using the dimensions given. Let us apply Snell's law in this question for getting the value of ${{\theta }_{b}}$.
The value of ${{\theta }_{a}}$ can be written as,
$\begin{align}
& \tan {{\theta }_{a}}=\dfrac{1.5}{1.2} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\theta }_{a}}={{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{1.5}{1.2} \right) \\
& \therefore {{\theta }_{a}}=51.34{}^\circ \\
\end{align}$
Use the Snell’s law in the equation as,
${{n}_{a}}\sin \left( {{\theta }_{a}} \right)={{n}_{b}}\sin \left( {{\theta }_{b}} \right)$
Substituting the values in it will give,
\[\begin{align}
& 1\times \sin \left( 51.34{}^\circ \right)=1.33\times \sin \left( {{\theta }_{b}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \sin \left( {{\theta }_{b}} \right)=0.587 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\theta }_{b}}={{\sin }^{-1}}\left( 0.587 \right) \\
& \therefore {{\theta }_{b}}=35.94{}^\circ \\
\end{align}\]
Now from the triangle ABC we can write that,
\[\tan \left( {{\theta }_{b}} \right)=\dfrac{BC}{AB}\]
Where \[AB\] be the depth of the pool which is mentioned as,
\[AB=4m\]
Substituting the values in this equation will give,
\[\begin{align}
& \tan \left( 35.94 \right)=\dfrac{BC}{4} \\
& \Rightarrow BC=4\times 0.725 \\
& \Rightarrow BC=2.86m \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore the total length from the edge of the pool can be shown as,
\[L=1.5+2.86=4.36m\]
Therefore the answer has been obtained as option D.
Note:
Snell's law is basically an equation helpful in describing the connection between the angles of incidence and refraction, when we consider light or other waves passing through a boundary between various isotropic media like water, air or glass.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




