
Aestivation of petals in the flower of cotton is correctly shown in
A.

B.
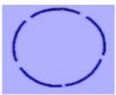
C.

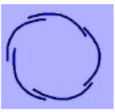
D.




Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint: Flower is considered as a reproductive organ of a plant. They facilitate reproduction by the production of seeds. The flower has mainly four parts: Petals and Sepals which constitute the vegetative parts of the flower; Stamen and Pistil which constitute the reproductive parts of plants.
Complete answer:
Different flowers vary with each other on the basis of the number of petals, the number of sepals, and their arrangement. The arrangement of either petals or sepals in the growing flower bud in relation to one another is called Aestivation. Aestivation is of the following types:
Valvate Aestivation is that in which petals do not overlap. There is only touching of margins with each other.
Twisted Aestivation is that in which petals or sepals overlap each other in a regular fashion in one direction.
Imbricate Aestivation is that in which petals or sepals overlap each other in an irregular fashion.
Quincuncial Aestivation is those in which petals and sepals are spirally arranged in such a way that two are exterior, two are interior, and the other has one edge exterior and one edge interior.
Vexillary Aestivation includes a single large petal or sepal which overlaps the lateral two petals or sepals (wings) which further overlap the two smallest petals or sepals (keel)
In the given question, option A represents Vexillary Aestivation seen in peas.
> Option B represents Valvate Aestivation seen in Mustard.
> Option C represents Imbricate Aestivation seen in Cassia.
> Option D represents Twisted Aestivation seen in Cotton.
So, the correct answer is Option (D).
Note: Phyllotaxy refers to the arrangement of leaves on the stem which includes Cyclic phyllotaxy and Spiral or Alternate or Acyclic phyllotaxy. Placentation is the arrangement of ovules in the ovary of the plant which may be Marginal, Basal, Apical, Parietal, Axial, Superficial, or Free Central.
Complete answer:
Different flowers vary with each other on the basis of the number of petals, the number of sepals, and their arrangement. The arrangement of either petals or sepals in the growing flower bud in relation to one another is called Aestivation. Aestivation is of the following types:
Valvate Aestivation is that in which petals do not overlap. There is only touching of margins with each other.
Twisted Aestivation is that in which petals or sepals overlap each other in a regular fashion in one direction.
Imbricate Aestivation is that in which petals or sepals overlap each other in an irregular fashion.
Quincuncial Aestivation is those in which petals and sepals are spirally arranged in such a way that two are exterior, two are interior, and the other has one edge exterior and one edge interior.
Vexillary Aestivation includes a single large petal or sepal which overlaps the lateral two petals or sepals (wings) which further overlap the two smallest petals or sepals (keel)
In the given question, option A represents Vexillary Aestivation seen in peas.
> Option B represents Valvate Aestivation seen in Mustard.
> Option C represents Imbricate Aestivation seen in Cassia.
> Option D represents Twisted Aestivation seen in Cotton.
So, the correct answer is Option (D).
Note: Phyllotaxy refers to the arrangement of leaves on the stem which includes Cyclic phyllotaxy and Spiral or Alternate or Acyclic phyllotaxy. Placentation is the arrangement of ovules in the ovary of the plant which may be Marginal, Basal, Apical, Parietal, Axial, Superficial, or Free Central.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




