
What is the active region of the transistor?
A. Active region is that region in which emitter base junction is forward bias while collector base junction is also forward bias
B. Active region is that region in which emitter base junction is forward bias while collector base junction is reverse bias.
C. Active region is that region in which emitter base junction is reverse bias while collector base junction is reverse bias
D. Active region is that region in which emitter base junction is reverse bias while collector base junction is forward bias,
Answer
591k+ views
Hint: To solve the question, we must know that Active region of the transistor is the region in which the transistor behaves normally. A transistor in an active region behaves like an amplifier. To achieve amplifying action of the transistor its input and output junctions must be biased accordingly.
Complete answer:
A transistor is a three terminal device that has an emitter, base, and a collector. For a common base configuration, the input terminal is the emitter-base terminal and output terminal is the base-collector terminal. In the active region the emitter base (input region) junction is forward bias, and the base collector (output) junction is reverse bias.
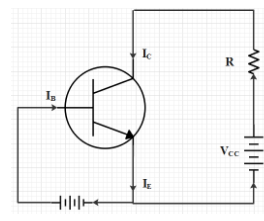
Now, we will look at the circuit in which a transistor is connected in common base configuration.
Then, the graph showing its active and saturation region will be,
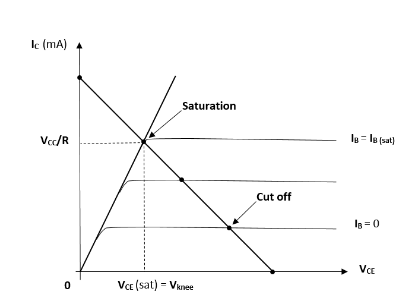
Active region is that region in which the emitter base junction is forward biased while the collector base junction is reverse biased.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Additional Information:
The transistor is in the cut off region when both E-B and B-C junctions are reverse biased and in the saturation region when both E-B and B-C junctions are reverse biased.
Note:
Students must remember that the active region of the transistor is the linear region between the cut off and saturation region in which amplifying action of the transistor is seen. In the cut off region the transistor acts as an off switch and in saturation region it behaves like an on switch.
Complete answer:
A transistor is a three terminal device that has an emitter, base, and a collector. For a common base configuration, the input terminal is the emitter-base terminal and output terminal is the base-collector terminal. In the active region the emitter base (input region) junction is forward bias, and the base collector (output) junction is reverse bias.
Now, we will look at the circuit in which a transistor is connected in common base configuration.

Then, the graph showing its active and saturation region will be,

Active region is that region in which the emitter base junction is forward biased while the collector base junction is reverse biased.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Additional Information:
The transistor is in the cut off region when both E-B and B-C junctions are reverse biased and in the saturation region when both E-B and B-C junctions are reverse biased.
Note:
Students must remember that the active region of the transistor is the linear region between the cut off and saturation region in which amplifying action of the transistor is seen. In the cut off region the transistor acts as an off switch and in saturation region it behaves like an on switch.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




