
When acetic acid reacts with ethyl alcohol, we add concentrated ${H_2}S{O_4}$ it acts as ----and the process is called --------
Answer
507k+ views
Hint: The rate at which a carboxylic acid is esterified depends on one of the factors that is steric hindrance in the alcohol and the carboxylic acid, although the acidic strength of carboxylic acid plays a very minor role in the rate of ester formation. The reactivity of alcohol towards esterification increases from tertiary alcohol to primary alcohol.
Complete answer: When (acetic acid) carboxylic acids are heated with alcohols in the presence of concentrated ${H_2}S{O_4}$ esters are formed. The reaction is reversible in nature and thus known as esterification.
$C{{H}_{3}}COOH+HO{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}\xrightarrow{{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}}C{{H}_{3}}COO{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}+{{H}_{2}}O$
The esterification of carboxylic acids with alcohols is a kind of nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction. The mechanism of esterification includes the following steps:
First, a proton from the sulphuric acid attacks the carbonyl oxygen of carboxylic acid.
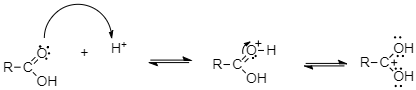
As a result of protonation, the carbonyl carbon gets activated and therefore it is readily attacked by the lone pairs of electrons on the oxygen of an alcohol to form the tetrahedral intermediate.
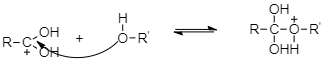
And then from the resulting intermediate, a proton shifts to OH group to form another tetrahedral intermediate. During this proton transfer, then –OH group gets converted into $ - O{H_2}^ + $ group.
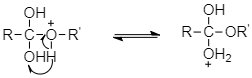
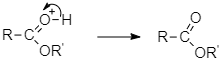
The intermediate obtained loses a water molecules to form protonated ester.
And at last the protonated ester loses a proton to form an ester.
Note:
The esterification of carboxylic acid with alcohol is a nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction.
Acetic acid or ethanoic acid is used in the manufacture of rayon, plastics, rubber and silk industries and esters have a nice smell and commonly used as fragrances, esters of benzoic acid are used in perfumery.
Complete answer: When (acetic acid) carboxylic acids are heated with alcohols in the presence of concentrated ${H_2}S{O_4}$ esters are formed. The reaction is reversible in nature and thus known as esterification.
$C{{H}_{3}}COOH+HO{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}\xrightarrow{{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}}C{{H}_{3}}COO{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}+{{H}_{2}}O$
The esterification of carboxylic acids with alcohols is a kind of nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction. The mechanism of esterification includes the following steps:
First, a proton from the sulphuric acid attacks the carbonyl oxygen of carboxylic acid.

As a result of protonation, the carbonyl carbon gets activated and therefore it is readily attacked by the lone pairs of electrons on the oxygen of an alcohol to form the tetrahedral intermediate.
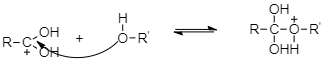
And then from the resulting intermediate, a proton shifts to OH group to form another tetrahedral intermediate. During this proton transfer, then –OH group gets converted into $ - O{H_2}^ + $ group.

The intermediate obtained loses a water molecules to form protonated ester.
And at last the protonated ester loses a proton to form an ester.

Note:
The esterification of carboxylic acid with alcohol is a nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction.
Acetic acid or ethanoic acid is used in the manufacture of rayon, plastics, rubber and silk industries and esters have a nice smell and commonly used as fragrances, esters of benzoic acid are used in perfumery.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




