
Acetamide is heated with bromine and sodium hydroxide solution.
Answer
595.8k+ views
Hint: Acetamide contains amide as a functional group. When acetamide reacts with bromine and NaOH solution, it will give a carbon-nitrogen rearrangement. This reaction was given by Scientist named Hoffman.
Complete step by step answer:
Basically when an amide is treated with bromine in an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide and bromine, degradation of amide takes place and that leads to the formation of primary amines. This reaction involves degradation of amide and this reaction is popularly known as Hoffmann’s bromamide degradation reaction. The primary amine thus which is formed from the reaction contains one carbon less than the number of carbon atoms in that amide.
\[\mathop {C{H_3}CON{H_2}}\limits_{Ethanamide} + 2B{r_2} + 4NaOH \to \mathop {C{H_2}N{H_2}}\limits_{{\text{Methyl amine}}} + N{a_2}C{O_3} + 2NaBr + 2{H_2}O\]
This is Hoffmann’s bromamide reaction or Hoffmann’s degradation reaction.
Let us see the mechanism of Hoffmann’s bromamide reaction. We can see that we obtain methyl amine from ethanamide. The mechanism of this reaction is as below.
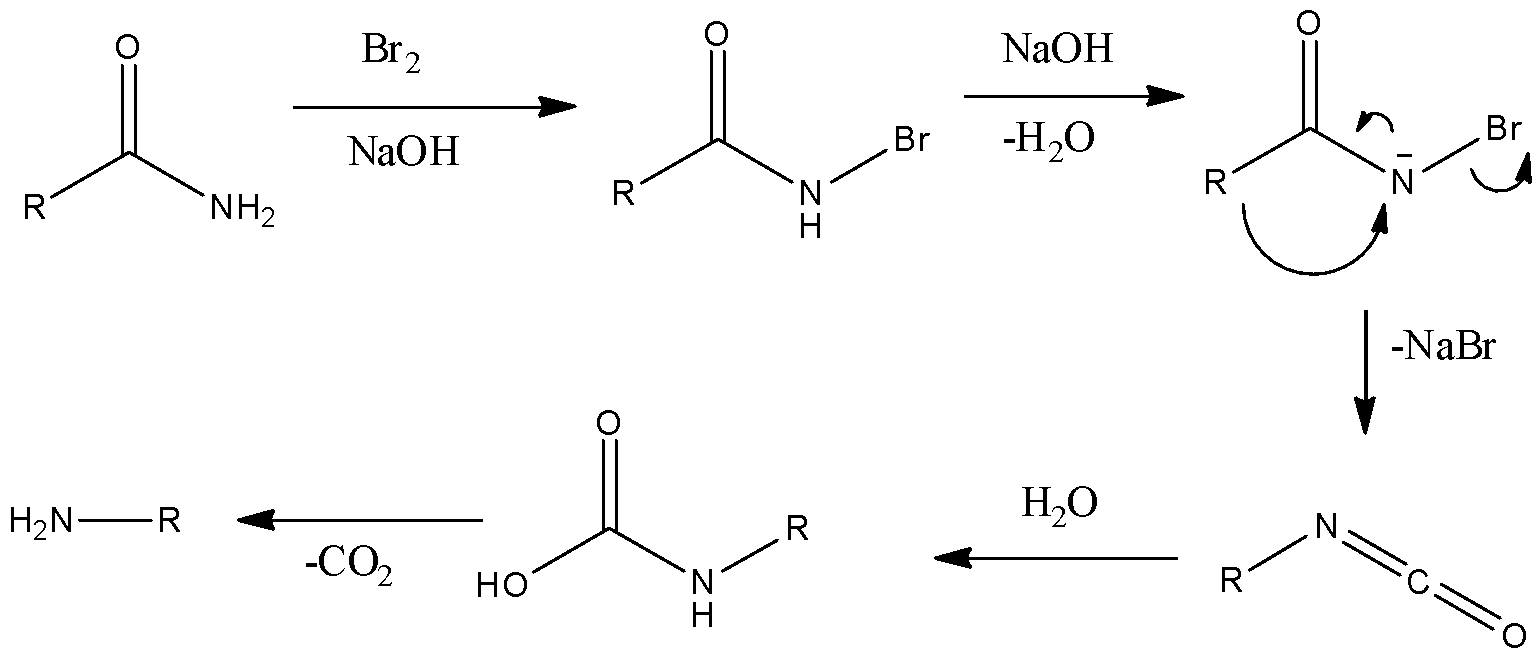
- Initially, hydrogen of amide is substituted by bromine atom in basic conditions. Then the proton gets removed and rearrangement occurs there resulting into the formation of isocyanate.
- Here, we can see that the intermediate formed is called isocyanate. Isocyanate on hydrolysis gives a derivative which can easily give carbon dioxide gas and results in a primary amine.
Applications of Hoffmann Bromamide Reaction are as below.
- Aliphatic & Aromatic amides are converted into aliphatic and aromatic amines, respectively.
- In the preparations of anthranilic acid from phthalimide.
- Nicotinic acid is converted into 3-Amino pyridine.
Note: Remember that the resultant amine has a carbon atom less than the number of carbons there in the amide. This occurs because the carbonyl carbon of the amide functional group is lost in the form of carbon dioxide.
Complete step by step answer:
Basically when an amide is treated with bromine in an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide and bromine, degradation of amide takes place and that leads to the formation of primary amines. This reaction involves degradation of amide and this reaction is popularly known as Hoffmann’s bromamide degradation reaction. The primary amine thus which is formed from the reaction contains one carbon less than the number of carbon atoms in that amide.
\[\mathop {C{H_3}CON{H_2}}\limits_{Ethanamide} + 2B{r_2} + 4NaOH \to \mathop {C{H_2}N{H_2}}\limits_{{\text{Methyl amine}}} + N{a_2}C{O_3} + 2NaBr + 2{H_2}O\]
This is Hoffmann’s bromamide reaction or Hoffmann’s degradation reaction.
Let us see the mechanism of Hoffmann’s bromamide reaction. We can see that we obtain methyl amine from ethanamide. The mechanism of this reaction is as below.

- Initially, hydrogen of amide is substituted by bromine atom in basic conditions. Then the proton gets removed and rearrangement occurs there resulting into the formation of isocyanate.
- Here, we can see that the intermediate formed is called isocyanate. Isocyanate on hydrolysis gives a derivative which can easily give carbon dioxide gas and results in a primary amine.
Applications of Hoffmann Bromamide Reaction are as below.
- Aliphatic & Aromatic amides are converted into aliphatic and aromatic amines, respectively.
- In the preparations of anthranilic acid from phthalimide.
- Nicotinic acid is converted into 3-Amino pyridine.
Note: Remember that the resultant amine has a carbon atom less than the number of carbons there in the amide. This occurs because the carbonyl carbon of the amide functional group is lost in the form of carbon dioxide.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE

Define Vant Hoff factor How is it related to the degree class 12 chemistry CBSE




