
Account for the following:
A. ${\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}$is more covalent than ${\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_3}$
B. Iron on reaction with ${\rm{HCl}}$ forms ${\rm{FeC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{2}}}$and not ${\rm{FeC}}{{\rm{l}}_3}$
C. The two ${\rm{O}} - {\rm{O}}$bond lengths in the ozone molecule are equal.
Answer
595.8k+ views
Hint: We know that the covalent character of a compound depends on the oxidation state of the central metal atom. Iron is a metal and ${\rm{HCl}}$ is an acid, so when both react, salt and hydrogen gas is formed and .Ozone is a molecule whose structure is bent and three oxygen atoms present in the molecule.
Complete step-by-step answer:
(i) We have to calculate the oxidation state of P in ${\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}$and${\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_3}$ to compare the covalent character of the two compounds. More the oxidation state of the central metal atom, greater the polarizing power which results in more covalent character of the bond formed between central metal atom and the other atoms.
Now, we calculate the oxidation state of P in${\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}$. The oxidation number of chlorine is -1 and the oxidation number of neutral compounds is zero.
Take x as the oxidation number of Phosphorus (P) in ${\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}$ .
$\begin{array}{c}x - 5 = 0\\x = 5\end{array}$
Similarly, calculate the oxidation state of P in${\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_3}$.
$\begin{array}{c}x - 3 = 0\\x = 3\end{array}$
So, in ${\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}$, oxidation state of P is more than ${\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_3}$. Hence, ${\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}$is more covalent than ${\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_3}$.
(ii) Now, we write the reaction of ${\rm{Fe}}$ and ${\rm{HCl}}$,
${\rm{Fe}} + {\rm{HCl}} \to {\rm{FeC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{2}}} + {{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}$
From the above reaction, we observed that hydrogen gas is evolved. The liberated ${{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}$undergoes reaction with oxygen to produce water molecules. The formation of water molecules reduces the oxidation of ferrous chloride to ferric chloride ${\rm{FeC}}{{\rm{l}}_3}$. Hence, ${\rm{FeC}}{{\rm{l}}_3}$ will not form.
(iii) We know that, in the molecule of ozone, one single bond and one double bond is present.
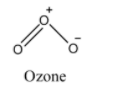
The oxygen atoms of ozone are arranged in such a way that it forms a bent structure. One terminal O atom makes a single bond to the central O atom and the other terminal O atom makes a double bond to the central O atom. The pi electrons of the double bond are delocalized over all the three O atoms in the molecule. Due to this, the bonds (double and single) are not pure and the bonds are resonance hybrids of single and double bonds respectively. So, the bond length of two O-O bonds is equal.
Note: (i) Between ${\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}$and ${\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_3}$, the oxidation state of ${\rm{P}}$ in ${\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}$ is greater than ${\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_3}$. This causes ${\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}$ having more covalent character than ${\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_3}$.
(ii) The ${\rm{FeC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{3}}}$ can be produced by reacting iron with stronger oxidizing agent such as chlorine.
(iii) The resonance effect observed in the ozone molecule results in an equal bond length of the two ${\rm{O}} - {\rm{O}}$ bonds. So, we can say that resonance affects the bond lengths of molecules.
Complete step-by-step answer:
(i) We have to calculate the oxidation state of P in ${\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}$and${\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_3}$ to compare the covalent character of the two compounds. More the oxidation state of the central metal atom, greater the polarizing power which results in more covalent character of the bond formed between central metal atom and the other atoms.
Now, we calculate the oxidation state of P in${\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}$. The oxidation number of chlorine is -1 and the oxidation number of neutral compounds is zero.
Take x as the oxidation number of Phosphorus (P) in ${\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}$ .
$\begin{array}{c}x - 5 = 0\\x = 5\end{array}$
Similarly, calculate the oxidation state of P in${\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_3}$.
$\begin{array}{c}x - 3 = 0\\x = 3\end{array}$
So, in ${\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}$, oxidation state of P is more than ${\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_3}$. Hence, ${\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}$is more covalent than ${\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_3}$.
(ii) Now, we write the reaction of ${\rm{Fe}}$ and ${\rm{HCl}}$,
${\rm{Fe}} + {\rm{HCl}} \to {\rm{FeC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{2}}} + {{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}$
From the above reaction, we observed that hydrogen gas is evolved. The liberated ${{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}$undergoes reaction with oxygen to produce water molecules. The formation of water molecules reduces the oxidation of ferrous chloride to ferric chloride ${\rm{FeC}}{{\rm{l}}_3}$. Hence, ${\rm{FeC}}{{\rm{l}}_3}$ will not form.
(iii) We know that, in the molecule of ozone, one single bond and one double bond is present.

The oxygen atoms of ozone are arranged in such a way that it forms a bent structure. One terminal O atom makes a single bond to the central O atom and the other terminal O atom makes a double bond to the central O atom. The pi electrons of the double bond are delocalized over all the three O atoms in the molecule. Due to this, the bonds (double and single) are not pure and the bonds are resonance hybrids of single and double bonds respectively. So, the bond length of two O-O bonds is equal.
Note: (i) Between ${\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}$and ${\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_3}$, the oxidation state of ${\rm{P}}$ in ${\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}$ is greater than ${\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_3}$. This causes ${\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{5}}}$ having more covalent character than ${\rm{PC}}{{\rm{l}}_3}$.
(ii) The ${\rm{FeC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{3}}}$ can be produced by reacting iron with stronger oxidizing agent such as chlorine.
(iii) The resonance effect observed in the ozone molecule results in an equal bond length of the two ${\rm{O}} - {\rm{O}}$ bonds. So, we can say that resonance affects the bond lengths of molecules.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




