
Account for the following:
1. Sulphur in vapour form exhibit paramagnetic behaviour
2. $SnC{l_4}$ is more covalent than $SnC{l_2}$
3. ${H_3}P{O_2}$ is stronger reducing agent than ${H_3}P{O_3}$
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: There may be many reasons for the behaviour of different elements and compounds. Sulphur exists as ${S_2}$ in vapour just like ${O_2}$ . $Sn$ has +4 and +2 oxidation states and more oxidation state means more polarizing power of the atom. In ${H_3}P{O_2}$ , two hydrogen atoms are bonded to phosphorus elements and in ${H_3}P{O_3}$ only one hydrogen is bonded with phosphorus element.
Complete step by step answer:
1. Here, we need to give reason why sulphur in vapour form exhibits paramagnetic behaviour. Sulphur is a multivalent non-metal which is abundant, tasteless and odourless. It is a bright yellow and crystalline solid at room temperature. Its vapour state, sulphur partly exists as ${S_2}$ molecule and has two unpaired electrons like ${O_2}$ in the antibonding pi-orbital. Hence, it exhibits paramagnetic behaviour.
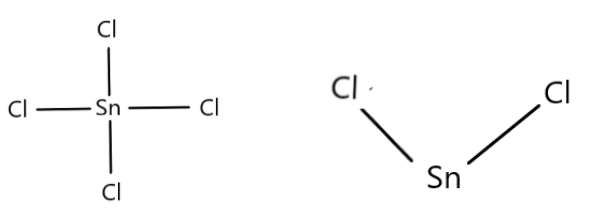
2. We need to justify that $SnC{l_4}$ is more covalent than $SnC{l_2}$ . $SnC{l_4}$ is also called Tin tetrachloride and $SnC{l_2}$ is called Tin Chloride dihydrate. Tin has atomic number 50 and oxidation states +2 and +4. $SnC{l_2}$ is a white crystalline solid ad a reducing agent. $SnC{l_4}$ is a colourless liquid which fumes in contact with air. The oxidation state of the central atom $Sn$ in $SnC{l_4}$ and $SnC{l_2}$ are +4 and +2 respectively. The +4 oxidation state of $Sn$ has higher polarising power which in turn increases the covalent character of bond formed between the central atom and other atoms.
3. ${H_3}P{O_2}$ is also called Hypophosphorous acid or phosphinic acid and is colourless with low melting point. ${H_3}P{O_3}$ is also called as Phosphorous acid and its organic derivatives are called Phosphonic acids. Reducing agents are those molecules that can donate electrons. The donating electrons are hydrogen atoms which are bonded to phosphorus atoms. In case of ${H_3}P{O_2}$ there are two hydrogen atoms bonded to P atom and in case of ${H_3}P{O_3}$ only one hydrogen is bonded to P atom. Therefore \[{H_3}P{O_2}\] will more readily donate electrons. Therefore, ${H_3}P{O_2}$ is stronger reducing agent than ${H_3}P{O_3}$ .
Note:
Here we have known that sulphur has paramagnetic behaviour in vapour form because of two unpaired electrons like oxygen. $SnC{l_4}$ is more covalent due to the higher oxidation state of $Sn$ which increases the polarizing power. Also, in \[{H_3}P{O_2}\] there are two hydrogen atoms bonded to P atom and in case of ${H_3}P{O_3}$ only one hydrogen is bonded to P atom and therefore \[{H_3}P{O_2}\] readily donates hydrogen atom and is a better reducing agent.
Complete step by step answer:
1. Here, we need to give reason why sulphur in vapour form exhibits paramagnetic behaviour. Sulphur is a multivalent non-metal which is abundant, tasteless and odourless. It is a bright yellow and crystalline solid at room temperature. Its vapour state, sulphur partly exists as ${S_2}$ molecule and has two unpaired electrons like ${O_2}$ in the antibonding pi-orbital. Hence, it exhibits paramagnetic behaviour.
2. We need to justify that $SnC{l_4}$ is more covalent than $SnC{l_2}$ . $SnC{l_4}$ is also called Tin tetrachloride and $SnC{l_2}$ is called Tin Chloride dihydrate. Tin has atomic number 50 and oxidation states +2 and +4. $SnC{l_2}$ is a white crystalline solid ad a reducing agent. $SnC{l_4}$ is a colourless liquid which fumes in contact with air. The oxidation state of the central atom $Sn$ in $SnC{l_4}$ and $SnC{l_2}$ are +4 and +2 respectively. The +4 oxidation state of $Sn$ has higher polarising power which in turn increases the covalent character of bond formed between the central atom and other atoms.

3. ${H_3}P{O_2}$ is also called Hypophosphorous acid or phosphinic acid and is colourless with low melting point. ${H_3}P{O_3}$ is also called as Phosphorous acid and its organic derivatives are called Phosphonic acids. Reducing agents are those molecules that can donate electrons. The donating electrons are hydrogen atoms which are bonded to phosphorus atoms. In case of ${H_3}P{O_2}$ there are two hydrogen atoms bonded to P atom and in case of ${H_3}P{O_3}$ only one hydrogen is bonded to P atom. Therefore \[{H_3}P{O_2}\] will more readily donate electrons. Therefore, ${H_3}P{O_2}$ is stronger reducing agent than ${H_3}P{O_3}$ .
Note:
Here we have known that sulphur has paramagnetic behaviour in vapour form because of two unpaired electrons like oxygen. $SnC{l_4}$ is more covalent due to the higher oxidation state of $Sn$ which increases the polarizing power. Also, in \[{H_3}P{O_2}\] there are two hydrogen atoms bonded to P atom and in case of ${H_3}P{O_3}$ only one hydrogen is bonded to P atom and therefore \[{H_3}P{O_2}\] readily donates hydrogen atom and is a better reducing agent.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




