
According to Maxwell electromagnetic theory, through which path an electron should fall into the nucleus in Rutherford's atomic model:
A.Circular
B.Spiral
C.Zig-zag
D.Straight line
Answer
566.7k+ views
Hint: Another name for Rutherford’s atomic model is called the planetary model of an atom where the electrons revolve around the nucleus much like planets around the sun. Diagram for the Rutherford atomic model is as shown below:
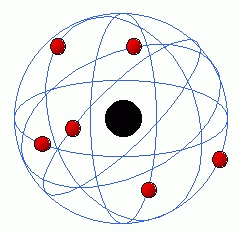
Complete answer:
Rutherford's model described the atom as a little, dense, charged core called a nucleus, during which nearly all the mass is concentrated, around which the sunshine, negative constituents, called electrons, circulate in a way, very like planets revolving round the Sun. consistent with the model electron’s speed will keep reducing because the electron keeps giving off energy by emitting electromagnetic waves and also the radius of its rotation will keep decreasing and it'll soon crash into the nucleus. If the radius is continuously decreasing the electron should follow a spiral path consistent with Maxwell's theory.
Hence the correct option is B.
Note:
The Rutherford model formulated the “plum-pudding” atomic model of English physicist Sir J.J. Thomson, during which the electrons were embedded during charged atoms like plums in an exceedingly pudding. Based wholly on classical physics, the Rutherford model itself was superseded during some years by the Bohr atomic model, which incorporated some early theory
Maxwell discovered a speed up to the speed of sunshine from a purely theoretical argument supporting experimental determinations of forces between currents in wires and forces between electrostatic charges. This within the end led to the conclusion that light might be a radiation, which there must be other such waves with different wavelengths. Hertz detected other waves having much longer wavelengths, experimentally, and this led on to radio, tv, radar, etc.

Complete answer:
Rutherford's model described the atom as a little, dense, charged core called a nucleus, during which nearly all the mass is concentrated, around which the sunshine, negative constituents, called electrons, circulate in a way, very like planets revolving round the Sun. consistent with the model electron’s speed will keep reducing because the electron keeps giving off energy by emitting electromagnetic waves and also the radius of its rotation will keep decreasing and it'll soon crash into the nucleus. If the radius is continuously decreasing the electron should follow a spiral path consistent with Maxwell's theory.
Hence the correct option is B.
Note:
The Rutherford model formulated the “plum-pudding” atomic model of English physicist Sir J.J. Thomson, during which the electrons were embedded during charged atoms like plums in an exceedingly pudding. Based wholly on classical physics, the Rutherford model itself was superseded during some years by the Bohr atomic model, which incorporated some early theory
Maxwell discovered a speed up to the speed of sunshine from a purely theoretical argument supporting experimental determinations of forces between currents in wires and forces between electrostatic charges. This within the end led to the conclusion that light might be a radiation, which there must be other such waves with different wavelengths. Hertz detected other waves having much longer wavelengths, experimentally, and this led on to radio, tv, radar, etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




