
Accessory buds occur at
(a) Stem tip
(b) Branch tip
(c) Leaf axil
(d) Side of axillary bud
Answer
600.3k+ views
Hint: Bud is a small growth on the stem that develops into a flower. Accessory buds as the name suggest are extra buds and also known as secondary buds.
Complete answer:
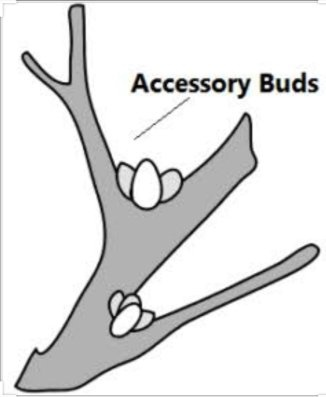
Accessory buds occur at the side of axillary buds. These buds may represent a source of new growth when the primary buds are damaged by frost or other factors. When the plant transitions from vegetative growth to flowering, axillary buds form and grow out in a basipetal wave from newly formed nodes near the shoot apex to the older basal nodes. These axillary meristems undergo a short vegetative phase before they undergo transition into reproductive development.
Additional Information:
The leaf makes an angle with the upper part of the stem. The angle made between the leaves and the upper part of the ste, is called the axil. The bud which is present at the axile is called the axillary bud. A bud is the young, immature, under developed, compact shoot. When the plant transitions from vegetative growth to flowering, axillary buds form and grow out in a basipetal wave from newly formed nodes near the shoot apex to the older basal nodes. These axillary meristems undergo a short vegetative phase before they undergo transition into reproductive development.
So the correct answer is, ‘Side of axillary bud’.
Notes:
1. The buds present on the shoots are of two types, terminal and axillary buds. Terminal buds are present at the tip of the shoot.
2. Axillary buds are morphologically visible at the cotyledonary node early during vegetative development of the plant.
3. Additional axillary buds are known as accessory buds, develop in the axils of cotyledons, repeating largely the development pattern of the primary shoot, resulting in numerous lateral shoots.
Complete answer:
Accessory buds occur at the side of axillary buds. These buds may represent a source of new growth when the primary buds are damaged by frost or other factors. When the plant transitions from vegetative growth to flowering, axillary buds form and grow out in a basipetal wave from newly formed nodes near the shoot apex to the older basal nodes. These axillary meristems undergo a short vegetative phase before they undergo transition into reproductive development.

Additional Information:
The leaf makes an angle with the upper part of the stem. The angle made between the leaves and the upper part of the ste, is called the axil. The bud which is present at the axile is called the axillary bud. A bud is the young, immature, under developed, compact shoot. When the plant transitions from vegetative growth to flowering, axillary buds form and grow out in a basipetal wave from newly formed nodes near the shoot apex to the older basal nodes. These axillary meristems undergo a short vegetative phase before they undergo transition into reproductive development.
So the correct answer is, ‘Side of axillary bud’.
Notes:
1. The buds present on the shoots are of two types, terminal and axillary buds. Terminal buds are present at the tip of the shoot.
2. Axillary buds are morphologically visible at the cotyledonary node early during vegetative development of the plant.
3. Additional axillary buds are known as accessory buds, develop in the axils of cotyledons, repeating largely the development pattern of the primary shoot, resulting in numerous lateral shoots.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




