
ABCD is a square in the figure, find x.
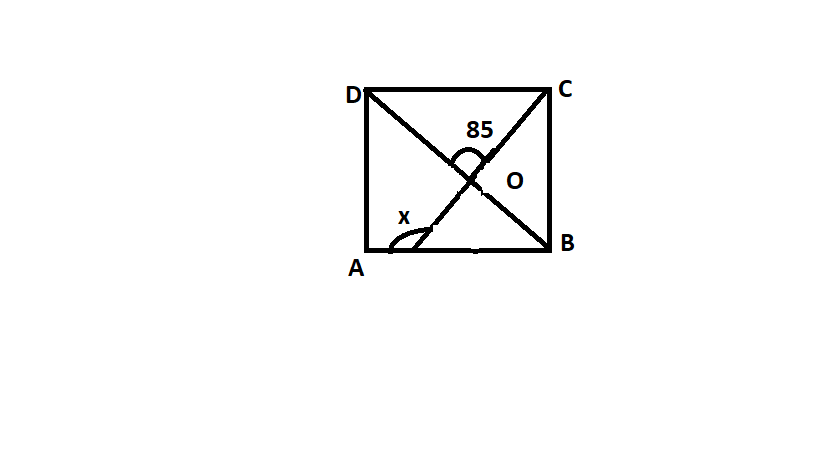
${\text{A}}{\text{. 15}}{0^ \circ }$
${\text{B}}{\text{. 13}}{0^ \circ }$
${\text{C}}{\text{. 12}}{0^ \circ }$
${\text{D}}{\text{.}}$ None of these

Answer
622.5k+ views
Hint: For a square, each angle is equal to 90 degrees, and the diagonals make an equal angle at every corner, use this to solve the question.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given a square ABCD.
Using the figure shown below-
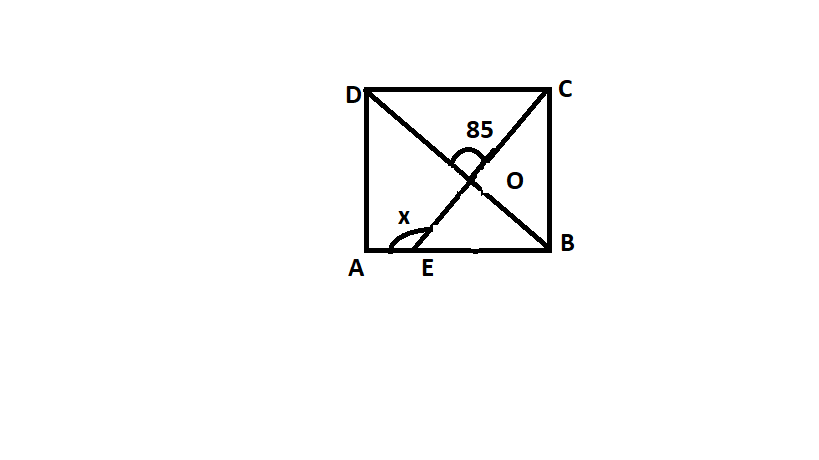
We have in triangle ABD,
AB = AD (sides of a square)
So, $\angle ADB = \angle ABD$
Now $\angle A = {90^ \circ }$ {angles of square are equal to 90 degrees}
Also, $\angle ADB = \angle ABD = \dfrac{{\angle A}}{2} = {45^ \circ }$
Now in triangle OEB
$\angle OEB + {85^ \circ } + {45^ \circ } = {180^ \circ }$ (By angle sum property)
$
\angle OEB + {130^ \circ } = {180^ \circ } \\
\therefore \angle OEB = {50^ \circ } \\
$
Now, we can say, $x + \angle OEB = {180^ \circ }$ {Angles on a straight line}
$x = {180^ \circ } - \angle OEB = {130^ \circ }$.
Therefore, the value of x is 130 degrees.
Hence, the correct option is ${\text{B}}{\text{. 13}}{0^ \circ }$.
Note: Whenever such types of questions appear, then use the property of square to find the value of x. As mentioned in the question, all sides of square are equal, so AB = AD, so the angles $\angle ADB = \angle ABD = \dfrac{{\angle A}}{2} = {45^ \circ }$, then in triangle OEB, by using angle sum property find the value of angle OEB. And then find the value of x by using the concept of angles on a straight line.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given a square ABCD.
Using the figure shown below-

We have in triangle ABD,
AB = AD (sides of a square)
So, $\angle ADB = \angle ABD$
Now $\angle A = {90^ \circ }$ {angles of square are equal to 90 degrees}
Also, $\angle ADB = \angle ABD = \dfrac{{\angle A}}{2} = {45^ \circ }$
Now in triangle OEB
$\angle OEB + {85^ \circ } + {45^ \circ } = {180^ \circ }$ (By angle sum property)
$
\angle OEB + {130^ \circ } = {180^ \circ } \\
\therefore \angle OEB = {50^ \circ } \\
$
Now, we can say, $x + \angle OEB = {180^ \circ }$ {Angles on a straight line}
$x = {180^ \circ } - \angle OEB = {130^ \circ }$.
Therefore, the value of x is 130 degrees.
Hence, the correct option is ${\text{B}}{\text{. 13}}{0^ \circ }$.
Note: Whenever such types of questions appear, then use the property of square to find the value of x. As mentioned in the question, all sides of square are equal, so AB = AD, so the angles $\angle ADB = \angle ABD = \dfrac{{\angle A}}{2} = {45^ \circ }$, then in triangle OEB, by using angle sum property find the value of angle OEB. And then find the value of x by using the concept of angles on a straight line.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What are gulf countries and why they are called Gulf class 8 social science CBSE

Name the states through which the Tropic of Cancer class 8 social science CBSE

What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Advantages and disadvantages of science

The pH of the gastric juices released during digestion class 8 biology CBSE




