
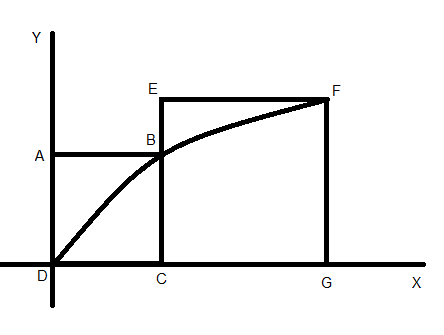
ABCD and EFGC are squares and the curve $y = k\sqrt x $ passed through the origin D and the points B and F. the ratio $\dfrac{{FG}}{{BC}}$ is –
A. $\dfrac{{\sqrt 5 + 1}}{2}$
B. $\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 + 1}}{2}$
C. $\dfrac{{\sqrt 5 + 1}}{4}$
D. $\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 + 1}}{4}$

Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: We can equate the sides of the squares. Then we can find the vertices of the squares that lies on the curve. Then we can substitute the points in the equation of the curve to get 2 equations. Then by solving the equations, we can obtain the vertices of the equation. Then by proper substituting we can find the required ratio.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have the expression of the curve as $y = k\sqrt x $ .
On squaring the equation if the curve, we get,
${y^2} = {k^2}x$
Now consider the square ABCD,
Let $AB = BC = a$ … (1)
So the point AB is given by (a,b)
On substituting this value in the equation of the curve, we get,
$ \Rightarrow {a^2} = {k^2}a$
On simplification, we get,
$ \Rightarrow a = {k^2}$ … (2)
Now consider the square EFGD,
Let $EF = FG = b$ … (3)
Then the point F can be represented as $\left( {FG,AB + EF} \right)$
On substituting the values, we get,
$F\left( {a + b,b} \right)$
On substituting this in the equation of the curve, we get,
$ \Rightarrow {b^2} = {k^2}\left( {a + b} \right)$
On substituting equation (2), we get,
$ \Rightarrow {b^2} = {k^2}\left( {{k^2} + b} \right)$
On expanding the bracket, we get,
$ \Rightarrow {b^2} = b{k^2} + {k^4}$
On rearranging, we get,
$ \Rightarrow {b^2} - b{k^2} - {k^4} = 0$
Now this is a quadratic equation of the form $a{x^2} + bx + c = 0$ . Then its solution is given by,
$x = \dfrac{{ - b \pm \sqrt {{b^2} - 4ac} }}{{2a}}$ .
On substituting the values, we get,
$ \Rightarrow b = \dfrac{{ - \left( { - {k^2}} \right) \pm \sqrt {{{\left( { - {k^2}} \right)}^2} - 4\left( { - {k^4}} \right)} }}{2}$
On simplification, we get,
$ \Rightarrow b = \dfrac{{{k^2} \pm \sqrt {{k^4} + 4{k^4}} }}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow b = \dfrac{{{k^2} \pm \sqrt {5{k^4}} }}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow b = \dfrac{{{k^2} \pm \sqrt 5 {k^2}}}{2}$
As the curve lies in the 1st quadrant, the value of b will be positive. So we reject the negative root,
$ \Rightarrow b = \dfrac{{{k^2} + \sqrt 5 {k^2}}}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow b = \dfrac{{{k^2}\left( {1 + \sqrt 5 } \right)}}{2}$ .. (4)
Now we need to find the ratio $\dfrac{{FG}}{{BC}}$ .
On substituting equation (3) and (1), we get,
$\dfrac{{FG}}{{BC}} = \dfrac{b}{a}$
On substituting equation (2) and (4), we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{FG}}{{BC}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{{k^2}\left( {1 + \sqrt 5 } \right)}}{2}}}{{{k^2}}}$
On simplification, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{FG}}{{BC}} = \dfrac{{\left( {1 + \sqrt 5 } \right)}}{2}$ .
Thus, the required ratio is, $\dfrac{{\left( {1 + \sqrt 5 } \right)}}{2}$ .
So, the correct answer is option A.
Note: We must square the equation of the curve for easy calculation. Calculating the square is easier than calculating the square root. The x coordinate of the point F must be taken as the sum of the length of the 2 squares as the x coordinate is the perpendicular distance of the point from the y axis. Similarly, the y coordinate is the perpendicular distance of the point from the x axis. We are taking the positive root of the variable b as we are dealing with the 1st quadrant. In that the x and y coordinates of a point will be always positive.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have the expression of the curve as $y = k\sqrt x $ .
On squaring the equation if the curve, we get,
${y^2} = {k^2}x$
Now consider the square ABCD,
Let $AB = BC = a$ … (1)
So the point AB is given by (a,b)
On substituting this value in the equation of the curve, we get,
$ \Rightarrow {a^2} = {k^2}a$
On simplification, we get,
$ \Rightarrow a = {k^2}$ … (2)
Now consider the square EFGD,
Let $EF = FG = b$ … (3)
Then the point F can be represented as $\left( {FG,AB + EF} \right)$
On substituting the values, we get,
$F\left( {a + b,b} \right)$
On substituting this in the equation of the curve, we get,
$ \Rightarrow {b^2} = {k^2}\left( {a + b} \right)$
On substituting equation (2), we get,
$ \Rightarrow {b^2} = {k^2}\left( {{k^2} + b} \right)$
On expanding the bracket, we get,
$ \Rightarrow {b^2} = b{k^2} + {k^4}$
On rearranging, we get,
$ \Rightarrow {b^2} - b{k^2} - {k^4} = 0$
Now this is a quadratic equation of the form $a{x^2} + bx + c = 0$ . Then its solution is given by,
$x = \dfrac{{ - b \pm \sqrt {{b^2} - 4ac} }}{{2a}}$ .
On substituting the values, we get,
$ \Rightarrow b = \dfrac{{ - \left( { - {k^2}} \right) \pm \sqrt {{{\left( { - {k^2}} \right)}^2} - 4\left( { - {k^4}} \right)} }}{2}$
On simplification, we get,
$ \Rightarrow b = \dfrac{{{k^2} \pm \sqrt {{k^4} + 4{k^4}} }}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow b = \dfrac{{{k^2} \pm \sqrt {5{k^4}} }}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow b = \dfrac{{{k^2} \pm \sqrt 5 {k^2}}}{2}$
As the curve lies in the 1st quadrant, the value of b will be positive. So we reject the negative root,
$ \Rightarrow b = \dfrac{{{k^2} + \sqrt 5 {k^2}}}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow b = \dfrac{{{k^2}\left( {1 + \sqrt 5 } \right)}}{2}$ .. (4)
Now we need to find the ratio $\dfrac{{FG}}{{BC}}$ .
On substituting equation (3) and (1), we get,
$\dfrac{{FG}}{{BC}} = \dfrac{b}{a}$
On substituting equation (2) and (4), we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{FG}}{{BC}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{{{k^2}\left( {1 + \sqrt 5 } \right)}}{2}}}{{{k^2}}}$
On simplification, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{FG}}{{BC}} = \dfrac{{\left( {1 + \sqrt 5 } \right)}}{2}$ .
Thus, the required ratio is, $\dfrac{{\left( {1 + \sqrt 5 } \right)}}{2}$ .
So, the correct answer is option A.
Note: We must square the equation of the curve for easy calculation. Calculating the square is easier than calculating the square root. The x coordinate of the point F must be taken as the sum of the length of the 2 squares as the x coordinate is the perpendicular distance of the point from the y axis. Similarly, the y coordinate is the perpendicular distance of the point from the x axis. We are taking the positive root of the variable b as we are dealing with the 1st quadrant. In that the x and y coordinates of a point will be always positive.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




