
ABC is a triangle in which \[\angle B = 90^\circ \], BC = 48 cm and AB = 14 cm. A circle is inscribed in the triangle, whose center is O. Find the radius r of the in-circle.
(a). 4 cm
(b). 6 cm
(c). 7 cm
(d). 9 cm

Answer
530k+ views
Hint: Find the area of the triangle ABC using the formula \[\dfrac{1}{2}bh\] and find the area of the triangle using the radius of the incircle of the triangle. Equate both and find the radius of the incircle.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The incircle is the largest circle that can fit inside a triangle without crossing its sides. The center of the incircle is formed by the angle bisectors of the triangle.
The radii of the incircle are perpendicular to the sides of the triangle at the point of contact since they are tangents to the circle.
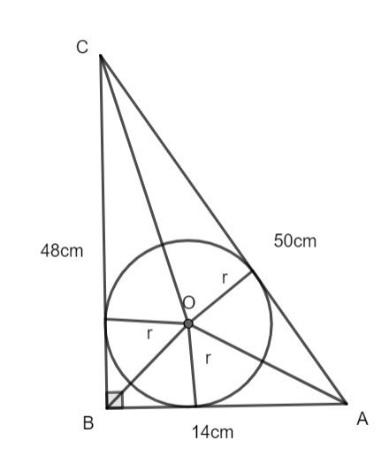
The two sides of the triangle ABC are given as follows:
AB = 14 cm
BC = 48 cm
Using the Pythagoras theorem, we find the third side.
\[A{C^2} = B{C^2} + A{B^2}\]
Hence, we have:
\[A{C^2} = {48^2} + {14^2}\]
\[A{C^2} = 2304 + 196\]
\[A{C^2} = 2500\]
\[AC = 50cm\]
Hence, the side AC is 50 cm long.
The area of the triangle is given as follows:
\[A = \dfrac{1}{2}bh\]
The area of triangle ABC is then given as follows:
\[A = \dfrac{1}{2}(48)(14)\]
\[A = 24 \times 14\]
\[A = 24 \times 14\]
\[A = 336c{m^2}............(1)\]
The area of the triangle can also be calculated using the radius of the incircle as follows:
\[A = \dfrac{1}{2}r(AB + BC + AC)\]
Then, we have:
\[A = \dfrac{1}{2}r(14 + 48 + 50)\]
\[A = \dfrac{1}{2}r(112)\]
\[A = 56r...............(2)\]
Equating equations (1) and (2), we have:
\[56r = 336\]
Solving for r, we have:
\[r = \dfrac{{336}}{{56}}\]
\[r = 6cm\]
Hence, option (b) is the correct answer.
Note: You can also find the radius of the incircle by using the property of the tangents, that is, the length of the tangents to the circle from an external point are equal
Complete step-by-step answer:
The incircle is the largest circle that can fit inside a triangle without crossing its sides. The center of the incircle is formed by the angle bisectors of the triangle.
The radii of the incircle are perpendicular to the sides of the triangle at the point of contact since they are tangents to the circle.

The two sides of the triangle ABC are given as follows:
AB = 14 cm
BC = 48 cm
Using the Pythagoras theorem, we find the third side.
\[A{C^2} = B{C^2} + A{B^2}\]
Hence, we have:
\[A{C^2} = {48^2} + {14^2}\]
\[A{C^2} = 2304 + 196\]
\[A{C^2} = 2500\]
\[AC = 50cm\]
Hence, the side AC is 50 cm long.
The area of the triangle is given as follows:
\[A = \dfrac{1}{2}bh\]
The area of triangle ABC is then given as follows:
\[A = \dfrac{1}{2}(48)(14)\]
\[A = 24 \times 14\]
\[A = 24 \times 14\]
\[A = 336c{m^2}............(1)\]
The area of the triangle can also be calculated using the radius of the incircle as follows:
\[A = \dfrac{1}{2}r(AB + BC + AC)\]
Then, we have:
\[A = \dfrac{1}{2}r(14 + 48 + 50)\]
\[A = \dfrac{1}{2}r(112)\]
\[A = 56r...............(2)\]
Equating equations (1) and (2), we have:
\[56r = 336\]
Solving for r, we have:
\[r = \dfrac{{336}}{{56}}\]
\[r = 6cm\]
Hence, option (b) is the correct answer.
Note: You can also find the radius of the incircle by using the property of the tangents, that is, the length of the tangents to the circle from an external point are equal
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE

State BPT theorem and prove it class 10 maths CBSE

A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

Find the area of the minor segment of a circle of radius class 10 maths CBSE

Write a letter to the editor of a newspaper explaining class 10 english CBSE

What is a "free hit" awarded for in limited-overs cricket?




