
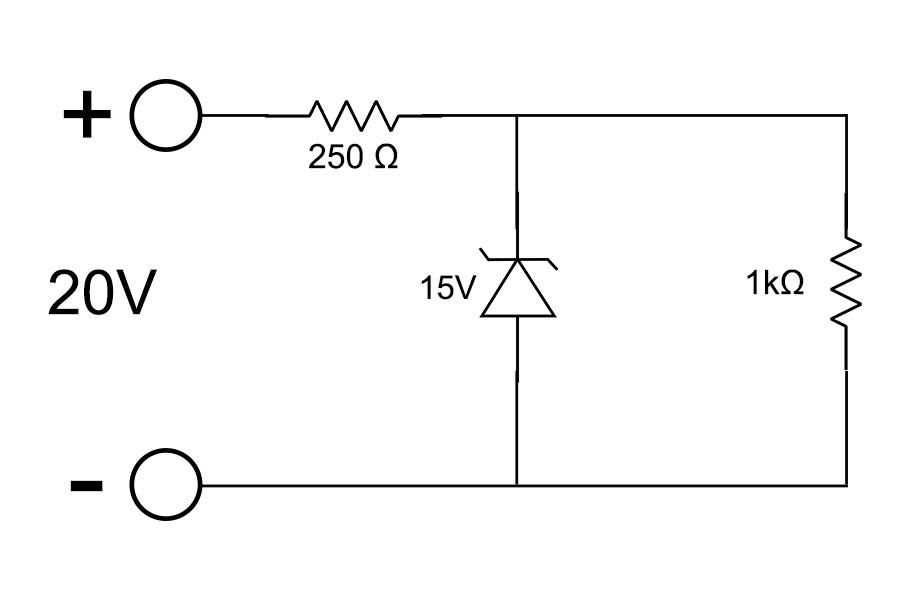
A Zener diode, having breakdown voltage equal to \[15\;{\rm{V}}\], is used in a voltage regulator circuit shown in figure. The current through the diode is
A. \[20\;{\rm{mA}}\]
B. \[5\;{\rm{mA}}\]
C. \[10\;{\rm{mA}}\]
D. \[15\;{\rm{mA}}\]

Answer
568.8k+ views
Hint: The above problem can be resolved using the meaning and fundamental concept of the Zener diode. In this problem, we are given an electrical circuit along which the resistors are kept at both sides of the Zener diode. Then the value of current flowing through the resistors are calculated, these values are then utilised to estimate the magnitude of current across the Zener diode, by taking the difference of current through the resistors.
Complete step by step answer:
Given:
The value of resistance is, \[{R_1} = 250\;\Omega \]
The value of another resistance is, \[{R_2} = 1\;{\rm{k\Omega }} = 1\;{\rm{k\Omega }} \times \dfrac{{1000\;\Omega }}{{1\;{\rm{k\Omega }}}} = 1000\;\Omega \].
The voltage through source is, \[{V_1} = 20\;{\rm{V}}\].
The voltage across the Zener diode is, \[{V_2} = 15\;\Omega \].
Then, the magnitude of current across the Zener diode through resistance \[{R_1}\] is,
\[{I_1} = \dfrac{{{V_2}}}{{{R_2}}}\]
Solve by substituting the values in above equation as,
\[\begin{array}{l}
{I_1} = \dfrac{{{V_2}}}{{{R_2}}}\\
{I_1} = \dfrac{{15\;{\rm{V}}}}{{1000\;\Omega }}\\
{I_1} = 0.015\;{\rm{A}} \times \dfrac{{1000\;mA}}{{1\;A}} = 15\;{\rm{mA}}\\
{I_1} = 15\;{\rm{mA}}
\end{array}\]
Further solving as,
\[\begin{array}{l}
{I_2} = \dfrac{{\left( {{V_1} - {V_2}} \right)}}{{{R_1}}}\\
{I_2} = \dfrac{{20\;{\rm{V}} - 15\;{\rm{V}}}}{{250\;\Omega }}\\
{I_2} = \dfrac{{5\;{\rm{V}}}}{{250\;\Omega }}\\
{I_2} = 0.02\;{\rm{A}} \times \dfrac{{1000\;{\rm{mA}}}}{{1\;{\rm{A}}}} = 20\;{\rm{A}}
\end{array}\]
Then the current through the Zener diode is,
\[\begin{array}{l}
{I_{zener}} = \left( {{I_2} - {I_1}} \right)\\
{I_{zener}} = \left( {20\;{\rm{mA}} - 15\;{\rm{mA}}} \right)\\
{I_{zener}} = 5\;{\rm{mA}}
\end{array}\]
Therefore, the magnitude of current through the Zener diode is \[5\;{\rm{mA}}\] and option (B) is correct.
Note:To resolve the given problem, one must know the formula for the voltage and current or commonly known as the equation of Ohm's law. Then from this information, we are handy with the current flowing, and this magnitude is utilised to draw out the magnitude of net current across the given diode. Moreover, the applications of Zener diodes are also needed to be taken into consideration to derive such relations. As this will also help to understand the various key concepts under the Zener diode.
Complete step by step answer:
Given:
The value of resistance is, \[{R_1} = 250\;\Omega \]
The value of another resistance is, \[{R_2} = 1\;{\rm{k\Omega }} = 1\;{\rm{k\Omega }} \times \dfrac{{1000\;\Omega }}{{1\;{\rm{k\Omega }}}} = 1000\;\Omega \].
The voltage through source is, \[{V_1} = 20\;{\rm{V}}\].
The voltage across the Zener diode is, \[{V_2} = 15\;\Omega \].
Then, the magnitude of current across the Zener diode through resistance \[{R_1}\] is,
\[{I_1} = \dfrac{{{V_2}}}{{{R_2}}}\]
Solve by substituting the values in above equation as,
\[\begin{array}{l}
{I_1} = \dfrac{{{V_2}}}{{{R_2}}}\\
{I_1} = \dfrac{{15\;{\rm{V}}}}{{1000\;\Omega }}\\
{I_1} = 0.015\;{\rm{A}} \times \dfrac{{1000\;mA}}{{1\;A}} = 15\;{\rm{mA}}\\
{I_1} = 15\;{\rm{mA}}
\end{array}\]
Further solving as,
\[\begin{array}{l}
{I_2} = \dfrac{{\left( {{V_1} - {V_2}} \right)}}{{{R_1}}}\\
{I_2} = \dfrac{{20\;{\rm{V}} - 15\;{\rm{V}}}}{{250\;\Omega }}\\
{I_2} = \dfrac{{5\;{\rm{V}}}}{{250\;\Omega }}\\
{I_2} = 0.02\;{\rm{A}} \times \dfrac{{1000\;{\rm{mA}}}}{{1\;{\rm{A}}}} = 20\;{\rm{A}}
\end{array}\]
Then the current through the Zener diode is,
\[\begin{array}{l}
{I_{zener}} = \left( {{I_2} - {I_1}} \right)\\
{I_{zener}} = \left( {20\;{\rm{mA}} - 15\;{\rm{mA}}} \right)\\
{I_{zener}} = 5\;{\rm{mA}}
\end{array}\]
Therefore, the magnitude of current through the Zener diode is \[5\;{\rm{mA}}\] and option (B) is correct.
Note:To resolve the given problem, one must know the formula for the voltage and current or commonly known as the equation of Ohm's law. Then from this information, we are handy with the current flowing, and this magnitude is utilised to draw out the magnitude of net current across the given diode. Moreover, the applications of Zener diodes are also needed to be taken into consideration to derive such relations. As this will also help to understand the various key concepts under the Zener diode.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




