
(a) Write the mechanism of the following reaction:
$2\,{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{OH}}\mathop {\,\, \to }\limits^{{{\text{H}}^ + }} {\text{ C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}} - {\text{O}} - {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}$
(b) Write the equation involved in the acetylation of salicylic acid.
Answer
574.2k+ views
Hint: The ester can be prepared from the alcohol by protonation followed by ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}^2}$ attack of another molecule of alcohol and then deprotonation. Acetylation of salicylic acid takes place in presence of acetic anhydride and sulphuric acid.
Complete Step by step answer: (a)
Two molecules of propanol forms ethoxyethane in presence of acid. We have to determine the mechanism of the reaction.
The reaction is as follows:
$2\,{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{OH}}\mathop {\,\, \to }\limits^{{{\text{H}}^ + }} {\text{ C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}} - {\text{O}} - {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}$
The complete reaction is take palce in three steps:
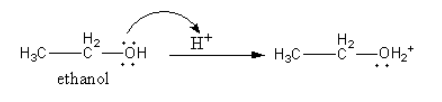
Step-1: Protonation of ethanol.
The oxygen atom of ethanol has lone pair so, it attacks on proton and get protonated so, a positive charge is generate on oxygen of ethanol.
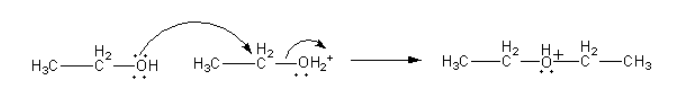
Step-2: ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}^2}$ attack of another molecule of ethanol.
The water molecule removes from the protonated ethanol simultaneously the oxygen atom of another ethanol molecule attacks from other side.
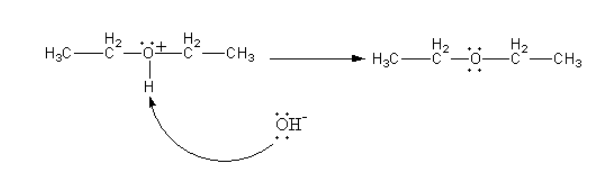
Step-3: Deprotonation from ether.
The hydroxyl ion of water molecules attacks on positively charged oxygen atoms to remove protons and give ether.
Therefore, the ester from alcohol is formed by protonation, ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}^2}$attack of second molecule of ethanol followed by deprotonation.
(b)
The equation involved in the acetylation of salicylic acid.
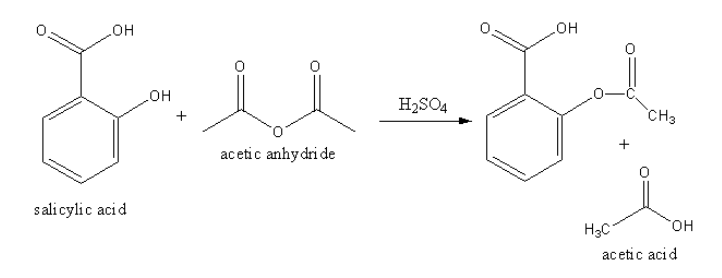
The acetylation of salicylic acid takes place in presence of strong acid like sulphuric acid.
The salicylic acid reacts with acetic anhydride in presence of sulphuric acid to form acetylated salicylic acid and acetic acid.
Note: The full name of ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}^2}$reaction is a bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction. The ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}^2}$reaction removal of a nucleophile and the attack of another nucleophile take place simultaneously. The compound with less steric hindrance will give the ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}^2}$ reaction faster.
Complete Step by step answer: (a)
Two molecules of propanol forms ethoxyethane in presence of acid. We have to determine the mechanism of the reaction.
The reaction is as follows:
$2\,{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{OH}}\mathop {\,\, \to }\limits^{{{\text{H}}^ + }} {\text{ C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}} - {\text{O}} - {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}$
The complete reaction is take palce in three steps:
Step-1: Protonation of ethanol.
The oxygen atom of ethanol has lone pair so, it attacks on proton and get protonated so, a positive charge is generate on oxygen of ethanol.

Step-2: ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}^2}$ attack of another molecule of ethanol.
The water molecule removes from the protonated ethanol simultaneously the oxygen atom of another ethanol molecule attacks from other side.

Step-3: Deprotonation from ether.
The hydroxyl ion of water molecules attacks on positively charged oxygen atoms to remove protons and give ether.

Therefore, the ester from alcohol is formed by protonation, ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}^2}$attack of second molecule of ethanol followed by deprotonation.
(b)
The equation involved in the acetylation of salicylic acid.

The acetylation of salicylic acid takes place in presence of strong acid like sulphuric acid.
The salicylic acid reacts with acetic anhydride in presence of sulphuric acid to form acetylated salicylic acid and acetic acid.
Note: The full name of ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}^2}$reaction is a bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction. The ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}^2}$reaction removal of a nucleophile and the attack of another nucleophile take place simultaneously. The compound with less steric hindrance will give the ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}^2}$ reaction faster.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




