
a) Write the characteristics of nuclear force.
b) Draw a plot of potential energy of pairs of nucleons as a function of their separation. Write two important conclusions that can be drawn from the graph.
Answer
598.8k+ views
- Hint: In a structure of atoms nuclear force simply acts between neutron and proton. It simply keeps neutrons and protons together in the nucleus of an atom.
Potential energy of pairs of nucleons is minimum at 0.8 cm. Before 0.8 cm it decreases and after 0.8 cm it increases. According to it we can draw a plot of potential energy of pairs of nucleons as a function of their separation.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Nucleus of an atom consists of protons and neutrons, called nucleons. To bound these nucleons in a small distance, a force acts between nucleons, which is called nuclear force. This force is much stronger than electromagnetic and gravitational forces. As the separation between nucleons increases, force becomes negligible. This force is not represented by any formula.
Part (a)
Some characteristics of nuclear forces are as follows:
a) Nuclear forces are short ranged. They are most effective only up to a distance of order of femtometre (fm) or less. Where 1fm = $10^{-15}$ meter. Nuclear forces become negligible at a distance of fm. This distance is called nuclear range.
b) Nuclear forces are much stronger than electromagnetic and gravitational force in nuclear range.
c) Nuclear forces are independent of charge. This means the force between two protons (p-p), two neutrons (n-n) or proton-neutron (n-p) is the same.
d) Nuclear forces are not determined by the distance between nucleons, this means force are not central in nature
Part (b)
Potential energy as the function separation between two nucleons is plotted below.
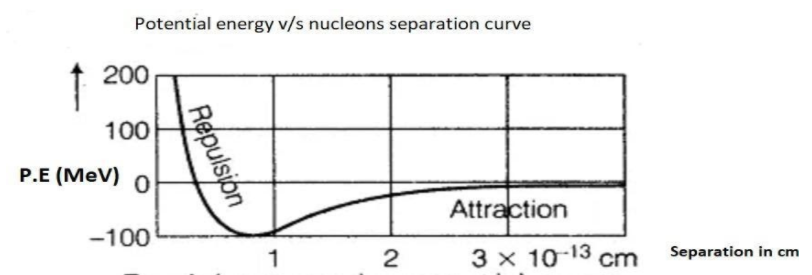
From this graph two important conclusion are drawn:
1. Nuclear force is a short range force.
2. Nuclear force is attractive in nature when separation between nucleons is more than 1 fm and repulsive in nature when separation is less than 1 fm.
Note: Thus, nuclear forces are strong forces in nuclear range. Nuclear range is of the order of radius of the nucleus. This force is responsible for keeping bounded nucleons in the nucleus.
Potential energy of pairs of nucleons is minimum at 0.8 cm. Before 0.8 cm it decreases and after 0.8 cm it increases. According to it we can draw a plot of potential energy of pairs of nucleons as a function of their separation.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Nucleus of an atom consists of protons and neutrons, called nucleons. To bound these nucleons in a small distance, a force acts between nucleons, which is called nuclear force. This force is much stronger than electromagnetic and gravitational forces. As the separation between nucleons increases, force becomes negligible. This force is not represented by any formula.
Part (a)
Some characteristics of nuclear forces are as follows:
a) Nuclear forces are short ranged. They are most effective only up to a distance of order of femtometre (fm) or less. Where 1fm = $10^{-15}$ meter. Nuclear forces become negligible at a distance of fm. This distance is called nuclear range.
b) Nuclear forces are much stronger than electromagnetic and gravitational force in nuclear range.
c) Nuclear forces are independent of charge. This means the force between two protons (p-p), two neutrons (n-n) or proton-neutron (n-p) is the same.
d) Nuclear forces are not determined by the distance between nucleons, this means force are not central in nature
Part (b)
Potential energy as the function separation between two nucleons is plotted below.

From this graph two important conclusion are drawn:
1. Nuclear force is a short range force.
2. Nuclear force is attractive in nature when separation between nucleons is more than 1 fm and repulsive in nature when separation is less than 1 fm.
Note: Thus, nuclear forces are strong forces in nuclear range. Nuclear range is of the order of radius of the nucleus. This force is responsible for keeping bounded nucleons in the nucleus.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




