
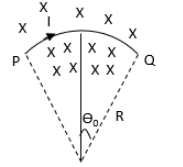
A wire carrying current \[I\] is ted between two points P and Q and is in the shape of a circular arc of radius \[R\] due to a uniform magnetic field \[B\] (perpendicular to the plane of paper, shown by xxx) in the vicinity of the wire. If the wire subtends an angle \[2{\theta _0}\] at the centre of the circle (of which it forms an arch) then the tension in the wire is:
A. \[IBR\]
B. \[\dfrac{{IBR}}{{\sin {\theta _0}}}\]
C. \[\dfrac{{IBR}}{{2\sin {\theta _0}}}\]
D. \[\dfrac{{IBR{\theta _0}}}{{\sin {\theta _0}}}\]

Answer
563.1k+ views
Hint: Use the formula for the magnetic force acting on the current carrying wire. This formula gives the relation between the magnetic field, length of the wire and current. Consider the small element of length of the wire and determine the magnetic force on this length. Apply Newton’s second law of motion in the vertical direction to the wire and determine the value of tension in the wire.
Formula used:
The magnetic force \[F\] acting on a wire is
\[F = BIL\] …… (1)
Here, \[B\] is a magnetic field, \[I\] is current flowing in the wire and \[L\] is the length of the wire.
Complete step by step answer:
We have given that the current \[I\] flows through a current carrying wire which is tied between the points P and Q in the shape of a circular arc of radius \[R\] and the angle subtended by the arc of wire at the centre of the circle is \[2{\theta _0}\].Let \[L\] be the length of the wire.Let us consider a small element \[dL\] on the length of the current carrying wire and let this small element subtends a small angle \[d{\theta _0}\] at the centre of the circle.Let us determine the magnetic force on this small element on the length of the wire.Substitute \[dL\] for \[L\] in equation (1).
\[F = BIdL\]
The direction of this magnetic force is acting radially outward from the centre of the arc.We can use the relation between the radius, length of arc and angle subtended at the centre.
\[2{\theta _0} = \dfrac{{dL}}{R}\]
Let us draw a free body diagram of the wire.
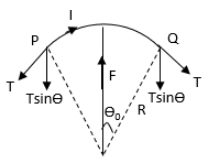
In the above free body diagram, \[T\] is the tension in the wire.Apply Newton’s second law of motion to the wire in vertical direction.
\[F = 2T\sin d{\theta _0}\]
Since the angle is very small, we can write
\[\sin d{\theta _0} = d{\theta _0}\]
Thus,
\[ \Rightarrow F = 2Td{\theta _0}\]
Substitute \[BIdL\] for \[F\] in the above equation.
\[BIdL = 2T{\theta _0}\]
\[ \Rightarrow BIdL = 2T\left( {\dfrac{{2{\theta _0}}}{2}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow BIdL = T\left( {2{\theta _0}} \right)\]
Substitute \[\dfrac{{dL}}{R}\] for \[2{\theta _0}\] in the above equation.
\[ \Rightarrow BIdL = T\left( {\dfrac{{dL}}{R}} \right)\]
\[ \therefore T = IBR\]
Therefore, the tension in the wire is \[IBR\].
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note:The students should keep in mind that the relation between angle, radius and arc length for the half of the angle subtended by the arc at the centre of the circle is the same for the whole angle subtended by the arc as the length of the wire and radius of the arc remains the same. Hence, we have replaced the whole angle subtended by the wire by the relation between the length of the small element and radius of the arc.
Formula used:
The magnetic force \[F\] acting on a wire is
\[F = BIL\] …… (1)
Here, \[B\] is a magnetic field, \[I\] is current flowing in the wire and \[L\] is the length of the wire.
Complete step by step answer:
We have given that the current \[I\] flows through a current carrying wire which is tied between the points P and Q in the shape of a circular arc of radius \[R\] and the angle subtended by the arc of wire at the centre of the circle is \[2{\theta _0}\].Let \[L\] be the length of the wire.Let us consider a small element \[dL\] on the length of the current carrying wire and let this small element subtends a small angle \[d{\theta _0}\] at the centre of the circle.Let us determine the magnetic force on this small element on the length of the wire.Substitute \[dL\] for \[L\] in equation (1).
\[F = BIdL\]
The direction of this magnetic force is acting radially outward from the centre of the arc.We can use the relation between the radius, length of arc and angle subtended at the centre.
\[2{\theta _0} = \dfrac{{dL}}{R}\]
Let us draw a free body diagram of the wire.

In the above free body diagram, \[T\] is the tension in the wire.Apply Newton’s second law of motion to the wire in vertical direction.
\[F = 2T\sin d{\theta _0}\]
Since the angle is very small, we can write
\[\sin d{\theta _0} = d{\theta _0}\]
Thus,
\[ \Rightarrow F = 2Td{\theta _0}\]
Substitute \[BIdL\] for \[F\] in the above equation.
\[BIdL = 2T{\theta _0}\]
\[ \Rightarrow BIdL = 2T\left( {\dfrac{{2{\theta _0}}}{2}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow BIdL = T\left( {2{\theta _0}} \right)\]
Substitute \[\dfrac{{dL}}{R}\] for \[2{\theta _0}\] in the above equation.
\[ \Rightarrow BIdL = T\left( {\dfrac{{dL}}{R}} \right)\]
\[ \therefore T = IBR\]
Therefore, the tension in the wire is \[IBR\].
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note:The students should keep in mind that the relation between angle, radius and arc length for the half of the angle subtended by the arc at the centre of the circle is the same for the whole angle subtended by the arc as the length of the wire and radius of the arc remains the same. Hence, we have replaced the whole angle subtended by the wire by the relation between the length of the small element and radius of the arc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




