
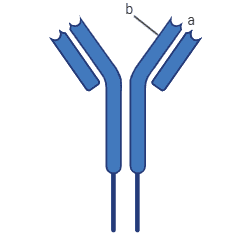
A. What does the above diagram illustrate?
B. Name the labeled a and b.
C. Name the types of cells that produce this molecule.

Answer
560.7k+ views
Hint:Human body has an immune system for the protection of our body from foreign antigens causing harm. To protect the human immune system produces antibodies that recognize the antigen and stimulate a response against it.
Complete answer:
Antibodies are glycoproteins resembling a Y-shaped molecule that has binding sites for antigen. These are produced by the B-lymphocytes. When B cells interact with any antigen it gets activated and produces two different cells known as B effector cells (also known as plasma cells) that produce specific antibodies; and memory B cells.
Plasma cells produce antibodies specific to the antigen recognized by the B cell. Antibodies are Y-shaped glycoprotein molecules having two binding sites for antigen with one stock known as the FC region. They constantly circulate through the body in the blood and reach the site of invasion by the pathogen. They bind to the pathogen and activate the defense mechanism that destroys the pathogen.
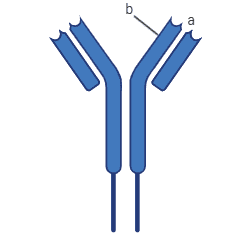
The diagram given above is of an antibody molecule. As we can see, it has two identical long heavy polypeptide chains and two identical short light polypeptide chains. Label ‘a’ in the diagram represents the variable region that is the antigen-binding site which varies in antibodies while label b represents the constant region of an antibody that is constant in all antibodies. As we discussed before these antigen molecules are produced by the white cells known as B-lymphocytes.
Note: Ab cell binds to antigen through a receptor called B cell receptor that resembles the structure of the antibody. The difference between these two is that the receptor on B cells are known as membrane-bound immunoglobulins while the antibodies are said to be secreted immunoglobulins.
Complete answer:
Antibodies are glycoproteins resembling a Y-shaped molecule that has binding sites for antigen. These are produced by the B-lymphocytes. When B cells interact with any antigen it gets activated and produces two different cells known as B effector cells (also known as plasma cells) that produce specific antibodies; and memory B cells.
Plasma cells produce antibodies specific to the antigen recognized by the B cell. Antibodies are Y-shaped glycoprotein molecules having two binding sites for antigen with one stock known as the FC region. They constantly circulate through the body in the blood and reach the site of invasion by the pathogen. They bind to the pathogen and activate the defense mechanism that destroys the pathogen.

The diagram given above is of an antibody molecule. As we can see, it has two identical long heavy polypeptide chains and two identical short light polypeptide chains. Label ‘a’ in the diagram represents the variable region that is the antigen-binding site which varies in antibodies while label b represents the constant region of an antibody that is constant in all antibodies. As we discussed before these antigen molecules are produced by the white cells known as B-lymphocytes.
Note: Ab cell binds to antigen through a receptor called B cell receptor that resembles the structure of the antibody. The difference between these two is that the receptor on B cells are known as membrane-bound immunoglobulins while the antibodies are said to be secreted immunoglobulins.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




