
(a) What do you mean by food chain?
(b) Explain the food chain in grassland with an example.
(c) Explain the energy flow in an ecosystem with the help of a diagram.
Answer
567.3k+ views
Hint: The food chain in ecology is the collection of flows of matter and energy in the form of food from organism to organism. As more than one type of animal or plant is consumed by most animals, food chains intertwine locally into a food web.
Complete answer:
a.The food chain in ecology is the collection of flows of matter and energy in the form of food from organism to organism. As mo(a) The food chain is the sequence of populations or organisms that pass through an environment through food and its energy contained in it with members being the food of the sequence at a later stage at one stage.
b.In the food chain, the main source of food that uses chlorophyll pigment to absorb light energy from sunlight is the green plant (grass). The grasshopper (insect) is the main consumer, since they consume the green plant directly. Since the grasshopper is eaten by it the bird is the secondary buyer. The snake is the consumer who consumes more than one type of animal or plant that feeds on the egg.t species, food chains intertwine locally into a food web.
c.The food chains are responsible for relating the different organisms, these also give rise to different trophic levels of an ecosystem. The producers convert energy of the sun into the chemical energy and transfer it to other trophic levels. The primary consumers consume producers, which are called herbivores. The secondary consumers consume the primary consumers and this makes them carnivores. The tertiary consumers consume secondary consumers. Decomposers break down complex nutrients from all trophic levels to release nutrients. Thus, there is flow of energy from Sun ---> Producer ---> Herbivore ----> Carnivore ---> Decomposers.
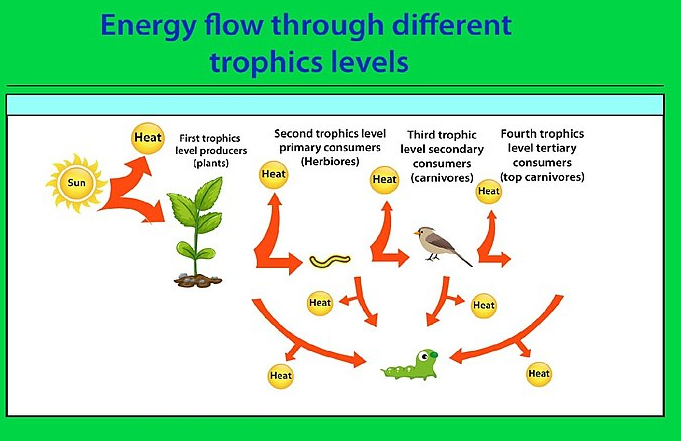
Note: Ten percent law- According to this law, only about ten per cent of the transferred energy is deposited during the transition of organic food energy from one trophic stage to the next higher level.
Complete answer:
a.The food chain in ecology is the collection of flows of matter and energy in the form of food from organism to organism. As mo(a) The food chain is the sequence of populations or organisms that pass through an environment through food and its energy contained in it with members being the food of the sequence at a later stage at one stage.
b.In the food chain, the main source of food that uses chlorophyll pigment to absorb light energy from sunlight is the green plant (grass). The grasshopper (insect) is the main consumer, since they consume the green plant directly. Since the grasshopper is eaten by it the bird is the secondary buyer. The snake is the consumer who consumes more than one type of animal or plant that feeds on the egg.t species, food chains intertwine locally into a food web.
c.The food chains are responsible for relating the different organisms, these also give rise to different trophic levels of an ecosystem. The producers convert energy of the sun into the chemical energy and transfer it to other trophic levels. The primary consumers consume producers, which are called herbivores. The secondary consumers consume the primary consumers and this makes them carnivores. The tertiary consumers consume secondary consumers. Decomposers break down complex nutrients from all trophic levels to release nutrients. Thus, there is flow of energy from Sun ---> Producer ---> Herbivore ----> Carnivore ---> Decomposers.

Note: Ten percent law- According to this law, only about ten per cent of the transferred energy is deposited during the transition of organic food energy from one trophic stage to the next higher level.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




