
A well $3.5\ m$ in diameter and $20\ m$ deep is dug in a rectangular field $20\ m\times 14\ m$. The earth taken out spread evenly on the field. Find the level of the earth raised in the field.
Answer
597.9k+ views
Hint: First of all, we will consider earth dug as cylindrical shaped and then based on that we will find its volume i.e. $\text{Volume of cylinder or well dug}=\pi {{r}^{2}}h$ . Now, to find the rise in level of earth in remaining part we will first find the area of remaining part by taking difference area of well dug i.e. $\text{Area of base}=\pi {{r}^{2}}$ and rectangular field i.e. $\text{Area of field}=length\times breadth$ . Then, from that we will find the volume of the remaining field which must be equal to the volume of well dug, so we will equate them and from that we will find the value of rise in level of height.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In question we are given that a well of $3.5\ m$ diameter and $20\ m$ deep is dug in a rectangular field of $20\ m\times 14\ m$. Now, the mud which comes out while digging the well is spread out on the field due to which the level of field rises and we are asked to find the height of the field raised. Now, first of all we consider the well is in the shape of cylinder so, the diameter and depth of the well can be given as,
$\text{Diameter}\ D=3.5\ m$ . Figure of well is given as below:
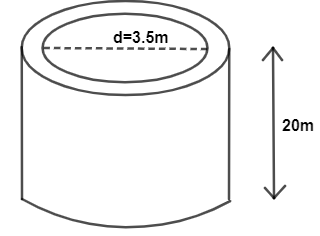
So, the radius will be, $\text{radius}\ r=\dfrac{3.5}{2}\ m$
$\text{depth}\ d=20\ m$
Now, volume of the earth dug or well, made can be given by the formula,
$\text{Volume of cylinder or well dug}=\pi {{r}^{2}}h$
Where, D is diameter, $\pi =3.14$ and h is depth.
On, substituting the values in expression we will get,
$\Rightarrow \text{Volume of cylinder or well dug}=3.14{{\left( \dfrac{3.5}{2} \right)}^{2}}20\ {{m}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{Volume of well dug}=192.422\ {{m}^{3}}$
Now, the dimensions of the rectangular field which was dug is given as, $20\ m\times 14\ m$ . So, figure is as given below:
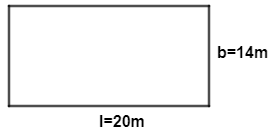
$\text{Area of field}=length\times breadth=20\ m\times 14\ m$
$\text{Area of field}=280\ {{m}^{2}}$ ……………..…………..(i)
Now, the area of well dug out is equal to the area of the base of well, which can be given as,
$\text{Area of base}=\pi {{r}^{2}}$
The base is in the form of a circle as shown in figure. So, on substituting the values we will get,
$\text{Area of base}=3.14{{\left( \dfrac{3.5}{2} \right)}^{2}}=9.62\ {{m}^{2}}$ ………………..……………(ii)
Now, the area of remaining part of the field can be given as,
$\text{Area of remaining part of field}=\text{Area of field}-\text{Area of base}$
On substituting the values from expression (i) and (ii) we will get,
$\text{Area of remaining part of field}=280-9.62\ =\ 270.38\ {{m}^{2}}$
Now, in question it is given that the field rises by some height so let the rise in height be h, and the volume of the raised field can be given as,
$\text{volume of raised field}=\text{Area of base }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ height}$
Now, area of remaining part of the field is equal to the area of base, so on substituting this value in expression we will get,
$\text{volume of raised field}=270.38\times \text{height}\ {{m}^{3}}$
Now, we know that volume of raised field is equal to the volume of field dug out, so this can be given mathematically as,
$\text{volume of raised field}=\text{Volume of well dug}$
$\Rightarrow 270.38\times \text{height}=192.422$
$\Rightarrow \text{height}=\dfrac{192.422}{270.38}=0.7117\ {{m}^{3}}$
Thus, the height of the rise in the level of the field is $0.7117\ {{m}^{3}}$.
Note: Here, by considering the volume of well dug equal to the volume of remaining field we have find the height of the level raised, but many a times student forget to do this and instead of that they directly find the answer by considering length as height and breadth as $14m$, and find the answer by substituting in expression $\text{Area of remaining part of field}=\text{Area of field}-\text{Area of base}$. Where, the area of the remaining field is $h\ m\times 14\ m$. On substituting the values, we will get, value of height as $h=19.31\ m$, which is wrong and students must take care of such things while solving the problem.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In question we are given that a well of $3.5\ m$ diameter and $20\ m$ deep is dug in a rectangular field of $20\ m\times 14\ m$. Now, the mud which comes out while digging the well is spread out on the field due to which the level of field rises and we are asked to find the height of the field raised. Now, first of all we consider the well is in the shape of cylinder so, the diameter and depth of the well can be given as,
$\text{Diameter}\ D=3.5\ m$ . Figure of well is given as below:

So, the radius will be, $\text{radius}\ r=\dfrac{3.5}{2}\ m$
$\text{depth}\ d=20\ m$
Now, volume of the earth dug or well, made can be given by the formula,
$\text{Volume of cylinder or well dug}=\pi {{r}^{2}}h$
Where, D is diameter, $\pi =3.14$ and h is depth.
On, substituting the values in expression we will get,
$\Rightarrow \text{Volume of cylinder or well dug}=3.14{{\left( \dfrac{3.5}{2} \right)}^{2}}20\ {{m}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{Volume of well dug}=192.422\ {{m}^{3}}$
Now, the dimensions of the rectangular field which was dug is given as, $20\ m\times 14\ m$ . So, figure is as given below:

$\text{Area of field}=length\times breadth=20\ m\times 14\ m$
$\text{Area of field}=280\ {{m}^{2}}$ ……………..…………..(i)
Now, the area of well dug out is equal to the area of the base of well, which can be given as,
$\text{Area of base}=\pi {{r}^{2}}$
The base is in the form of a circle as shown in figure. So, on substituting the values we will get,
$\text{Area of base}=3.14{{\left( \dfrac{3.5}{2} \right)}^{2}}=9.62\ {{m}^{2}}$ ………………..……………(ii)
Now, the area of remaining part of the field can be given as,
$\text{Area of remaining part of field}=\text{Area of field}-\text{Area of base}$
On substituting the values from expression (i) and (ii) we will get,
$\text{Area of remaining part of field}=280-9.62\ =\ 270.38\ {{m}^{2}}$
Now, in question it is given that the field rises by some height so let the rise in height be h, and the volume of the raised field can be given as,
$\text{volume of raised field}=\text{Area of base }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ height}$
Now, area of remaining part of the field is equal to the area of base, so on substituting this value in expression we will get,
$\text{volume of raised field}=270.38\times \text{height}\ {{m}^{3}}$
Now, we know that volume of raised field is equal to the volume of field dug out, so this can be given mathematically as,
$\text{volume of raised field}=\text{Volume of well dug}$
$\Rightarrow 270.38\times \text{height}=192.422$
$\Rightarrow \text{height}=\dfrac{192.422}{270.38}=0.7117\ {{m}^{3}}$
Thus, the height of the rise in the level of the field is $0.7117\ {{m}^{3}}$.
Note: Here, by considering the volume of well dug equal to the volume of remaining field we have find the height of the level raised, but many a times student forget to do this and instead of that they directly find the answer by considering length as height and breadth as $14m$, and find the answer by substituting in expression $\text{Area of remaining part of field}=\text{Area of field}-\text{Area of base}$. Where, the area of the remaining field is $h\ m\times 14\ m$. On substituting the values, we will get, value of height as $h=19.31\ m$, which is wrong and students must take care of such things while solving the problem.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




