
A wave is represented as \[\varepsilon =10\sin ({{10}^{8}}+6\sin 1250t)\]. Then the modulating index is –
A) 10
B) 1250
C) 1000
D) 6
Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: The modulating index is the ratio of the amplitude of the modulating wave to the amplitude of the carrier wave. We can find the amplitudes of both these waves very easily from the given wave equation which is the resultant wave after modulation.
Complete answer:
We know that most of the signals which we come across today are modulated to avoid the loss of the signal during its propagation through the large noisy atmosphere. The speciality of modulation is that the modulated wave or the signal which is to be carried from one place to another does not lose its identity when it is modulated with the carrier wave.
We can see a wave which is to be modulated as –
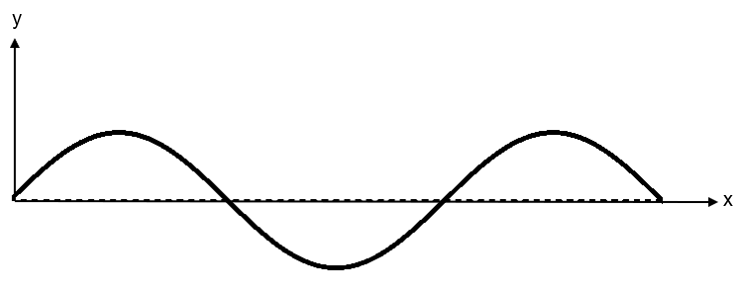
The equation of the wave is –
\[{{y}_{m}}={{a}_{m}}\sin (2\pi {{f}_{m}}t)\text{ --(1)}\]
The carrier wave is given as –
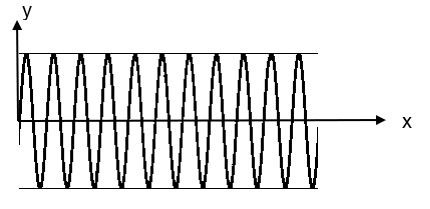
The equation of the wave is –
\[{{y}_{c}}={{a}_{c}}\sin (2\pi {{f}_{c}}t)\text{ --(2)}\]
From (1) and (2), we can derive the equation of the amplitude modulated wave as –
\[\begin{align}
& y={{y}_{m}}\sin \omega t+{{y}_{c}} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }y=[{{a}_{m}}\sin (2\pi {{f}_{m}}t)+{{a}_{c}}]\sin (2\pi {{f}_{c}}t) \\
\end{align}\]
This is because the modulated wave is embedded inside the carrier wave. So the modulating index can derived from the above equation as –
\[y=[1+\dfrac{{{a}_{m}}}{{{a}_{c}}}\sin (2\pi {{f}_{m}}t)]\sin (2\pi {{f}_{c}}t)\text{ --(3)}\]
We can compare the given equation and (3) to find the modulating index of the given wave.
The given wave equation is –
\[\varepsilon =10\sin ({{10}^{8}}+6\sin 1250t)\]
\[\Rightarrow \text{ }\varepsilon ={{10}^{9}}\sin \omega t(1+6\sin 1250t)\]
Comparing (3) with the above equation gives that 6 is the modulating index of the given amplitude modulated wave.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note:
The wave can be either modulated in amplitude or frequency. We can recognise them from the equation involved in the modulated wave. The frequency modulated waves are much more advantageous than the amplitude modulated waves.
Complete answer:
We know that most of the signals which we come across today are modulated to avoid the loss of the signal during its propagation through the large noisy atmosphere. The speciality of modulation is that the modulated wave or the signal which is to be carried from one place to another does not lose its identity when it is modulated with the carrier wave.
We can see a wave which is to be modulated as –

The equation of the wave is –
\[{{y}_{m}}={{a}_{m}}\sin (2\pi {{f}_{m}}t)\text{ --(1)}\]
The carrier wave is given as –

The equation of the wave is –
\[{{y}_{c}}={{a}_{c}}\sin (2\pi {{f}_{c}}t)\text{ --(2)}\]
From (1) and (2), we can derive the equation of the amplitude modulated wave as –
\[\begin{align}
& y={{y}_{m}}\sin \omega t+{{y}_{c}} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{ }y=[{{a}_{m}}\sin (2\pi {{f}_{m}}t)+{{a}_{c}}]\sin (2\pi {{f}_{c}}t) \\
\end{align}\]
This is because the modulated wave is embedded inside the carrier wave. So the modulating index can derived from the above equation as –
\[y=[1+\dfrac{{{a}_{m}}}{{{a}_{c}}}\sin (2\pi {{f}_{m}}t)]\sin (2\pi {{f}_{c}}t)\text{ --(3)}\]
We can compare the given equation and (3) to find the modulating index of the given wave.
The given wave equation is –
\[\varepsilon =10\sin ({{10}^{8}}+6\sin 1250t)\]
\[\Rightarrow \text{ }\varepsilon ={{10}^{9}}\sin \omega t(1+6\sin 1250t)\]
Comparing (3) with the above equation gives that 6 is the modulating index of the given amplitude modulated wave.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note:
The wave can be either modulated in amplitude or frequency. We can recognise them from the equation involved in the modulated wave. The frequency modulated waves are much more advantageous than the amplitude modulated waves.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




