
A vibratory motion is represented by$x = 2A\cos \omega t + A\cos \left( {\omega t + \dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right) + A\cos \left( {\omega t + \pi } \right) + \dfrac{A}{2}\cos \left( {\omega t + \dfrac{{3\pi }}{2}} \right)$. The resultant amplitude of the motion is
A. 9A/2
B. $\dfrac{{\sqrt 5 A}}{2}$
C. 5A/2
D. 2A
Answer
579.3k+ views
Hint: In this question, we need to determine the resultant amplitude of the vibratory motion which is represented by the given equation. For this, we will find the resultant vector by following the properties of the vectors.
Complete step by step answer:
We can solve it by a vector method using a phasor diagram. First we will find the resultant vectors along the x and the y axes and then apply the vector rule to determine the resultant of the amplitude of the given function.
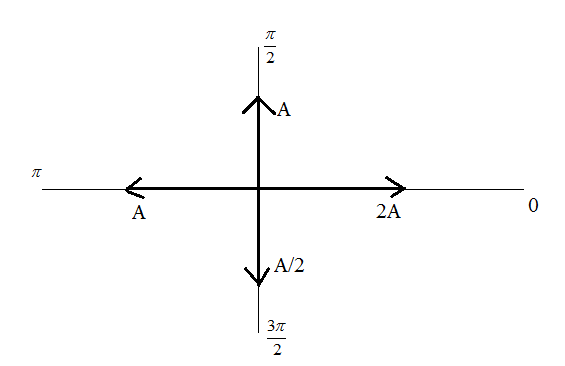
Resultant on horizontal axis is given as: \[2A - A = A\]and the resultant on vertical axis is given as: \[A - \left( {\dfrac{A}{2}} \right) = \dfrac{A}{2}\]
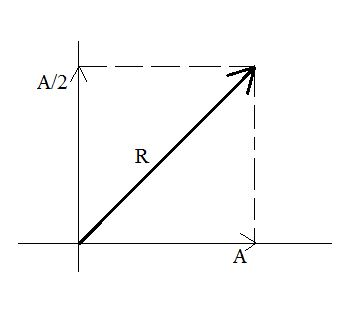
The resultant vector is given by parallelogram law as:
$
R = \sqrt {{A^2} + {B^2} + 2AB\cos \theta } \\
R = \sqrt {{A^2} + {B^2}} {\text{ }}\left[ {\theta = {{90}^ \circ } \Rightarrow \cos \theta = 0} \right] \\
$
So, the resultant amplitude is given as:
$
\sqrt {{A^2} + {{\left( {\dfrac{A}{2}} \right)}^2}} \\
= \sqrt {{A^2} + \dfrac{{{A^2}}}{4}} \\
= \sqrt {\dfrac{5}{4}A} \\
$
$
Amp = \sqrt {{A^2} + {{\left( {\dfrac{A}{2}} \right)}^2}} \\
= \sqrt {{A^2} + \dfrac{{{A^2}}}{4}} \\
= \sqrt {\dfrac{5}{4}{A^2}} \\
= \dfrac{{A\sqrt 5 }}{2} \\
$
Hence, the resultant amplitude of the vibratory motion which is defined by the equation $x = 2A\cos \omega t + A\cos \left( {\omega t + \dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right) + A\cos \left( {\omega t + \pi } \right) + \dfrac{A}{2}\cos \left( {\omega t + \dfrac{{3\pi }}{2}} \right)$
x= $\dfrac{{A\sqrt 5 }}{2}$.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
It should be noted down here that the vectors should not be added or subtracted like simple algebra, use vector addition methods always. Moreover, many times students got confused with the problem and carried out the simple arithmetic operations on the vector identities also, which led them to a wrong answer. Here, as all the vectors are displaced by certain factors of $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ and the angle between any two axes is $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ so, we have taken $\theta = \dfrac{\pi }{2}$.
Complete step by step answer:
We can solve it by a vector method using a phasor diagram. First we will find the resultant vectors along the x and the y axes and then apply the vector rule to determine the resultant of the amplitude of the given function.

Resultant on horizontal axis is given as: \[2A - A = A\]and the resultant on vertical axis is given as: \[A - \left( {\dfrac{A}{2}} \right) = \dfrac{A}{2}\]

The resultant vector is given by parallelogram law as:
$
R = \sqrt {{A^2} + {B^2} + 2AB\cos \theta } \\
R = \sqrt {{A^2} + {B^2}} {\text{ }}\left[ {\theta = {{90}^ \circ } \Rightarrow \cos \theta = 0} \right] \\
$
So, the resultant amplitude is given as:
$
\sqrt {{A^2} + {{\left( {\dfrac{A}{2}} \right)}^2}} \\
= \sqrt {{A^2} + \dfrac{{{A^2}}}{4}} \\
= \sqrt {\dfrac{5}{4}A} \\
$
$
Amp = \sqrt {{A^2} + {{\left( {\dfrac{A}{2}} \right)}^2}} \\
= \sqrt {{A^2} + \dfrac{{{A^2}}}{4}} \\
= \sqrt {\dfrac{5}{4}{A^2}} \\
= \dfrac{{A\sqrt 5 }}{2} \\
$
Hence, the resultant amplitude of the vibratory motion which is defined by the equation $x = 2A\cos \omega t + A\cos \left( {\omega t + \dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right) + A\cos \left( {\omega t + \pi } \right) + \dfrac{A}{2}\cos \left( {\omega t + \dfrac{{3\pi }}{2}} \right)$
x= $\dfrac{{A\sqrt 5 }}{2}$.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
It should be noted down here that the vectors should not be added or subtracted like simple algebra, use vector addition methods always. Moreover, many times students got confused with the problem and carried out the simple arithmetic operations on the vector identities also, which led them to a wrong answer. Here, as all the vectors are displaced by certain factors of $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ and the angle between any two axes is $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ so, we have taken $\theta = \dfrac{\pi }{2}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




