
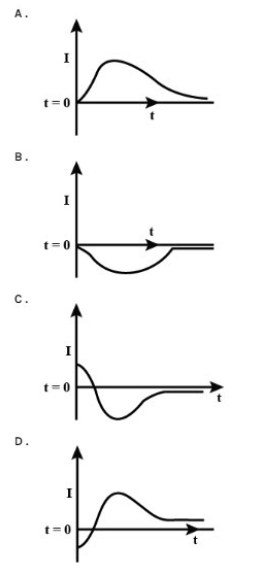
A very long solenoid of radius R is carrying current I(t)=kte-αt(k>0), as a function of time (t≥0). counter clockwise current is taken to be positive. A circular conducting coil of radius 2Ris placed in the equatorial plane of the solenoid and concentric with the solenoid. The current induced in the outer coil is correctly depicted, as a function of time, by?

Answer
594.9k+ views
Hint: As we all know that mutual inductance tells us about the relation between flux and current It tells us about the relation between the flux of object 2 and the current of object 1 and self inductance tells us about the flux of object 1 with respect to the current of object 2.
Formula used: $I(t) = kt{e^{ - \alpha t}}$
Complete step by step answer:
We can see that the current $I$ is the function of time. Since from the given curves, it can be seen that the current is zero at a point of time and also the initial value of the current is zero.
We all know that the flux change in the ring is due to the current inside the solenoid.Therefore, the flux through the ring is given by,
$\eqalign{
& {\phi _2} = M{i_1} \cr
& {\phi _2} = Mkt{e^{ - \alpha t}} \cr} $
Here, ${\phi _2}$is the flux of a ring and ${i_1}$ is the current through the solenoid and $M$ is the mutual inductance. Now we can say that due to change in flux inside the ring an emf is also generated inside the ring. So we can say that the value of emf is given by,
$emf = - \dfrac{{d{\phi _2}}}{{dt}}$…… (I)
We will substitute ${\phi _2} = Mkt{e^{ - \alpha t}}$in equation (I) to find the value of emf.
$\eqalign{
& emf = - \dfrac{{d\left( {Mkt{e^{ - \alpha t}}} \right)}}{{dt}} \cr
& emf = - Mk\left( {1 - \alpha t} \right){e^{ - \alpha t}} \cr} $
Now we all know that current generated inside the ring is given by,
${i_2} = \dfrac{{emf}}{R}$…… (II)
We will now substitute the value of $emf = - Mk\left( {1 - \alpha t} \right){e^{ - \alpha t}}$to find the value of current through coil that is ${i_2}$. Therefore, it becomes,
${i_2} = \dfrac{{ - Mk\left( {1 - \alpha t} \right){e^{ - \alpha t}}}}{R}$
When the value of $t$ becomes $t = \dfrac{1}{\alpha }$ then at that point the current becomes,
$\eqalign{
& {i_2} = \dfrac{{ - Mk\left( {1 - \alpha \times \dfrac{1}{\alpha }} \right){e^{ - \alpha t}}}}{R} \cr
& {i_2} = 0 \cr} $
Now at $t = 0$, we can find the initial value of current. So we will put $t = 0$ and it becomes,
$\eqalign{
& {i_2} = \dfrac{{ - Mk\left( {1 - \alpha \times 0} \right){e^{ - \alpha \times 0}}}}{R} \cr
& {i_2} = \dfrac{{ - Mk}}{R} \cr} $
So we can come to the point that, on seeing the behaviour of current a $t = 0$ and $t = \dfrac{1}{\alpha }$
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
In option (D), the initial value of the current is negative and it is also zero somewhere in the time axis.
Additional Information:
We know that when the current passes through the solenoid it generates the magnetic field inside the solenoid. And as the magnetic lines of force also crosses the ring of radius $2R$, it generates a change in flux inside the ring.
Note:
We know that the relation between magnetic field and current is determined by the Biot savart law. The constant current generated by the magnetic field is given by the biot savart law. It gives the relation between the magnetic field and current magnitude, length, direction and proximity.
Formula used: $I(t) = kt{e^{ - \alpha t}}$
Complete step by step answer:
We can see that the current $I$ is the function of time. Since from the given curves, it can be seen that the current is zero at a point of time and also the initial value of the current is zero.
We all know that the flux change in the ring is due to the current inside the solenoid.Therefore, the flux through the ring is given by,
$\eqalign{
& {\phi _2} = M{i_1} \cr
& {\phi _2} = Mkt{e^{ - \alpha t}} \cr} $
Here, ${\phi _2}$is the flux of a ring and ${i_1}$ is the current through the solenoid and $M$ is the mutual inductance. Now we can say that due to change in flux inside the ring an emf is also generated inside the ring. So we can say that the value of emf is given by,
$emf = - \dfrac{{d{\phi _2}}}{{dt}}$…… (I)
We will substitute ${\phi _2} = Mkt{e^{ - \alpha t}}$in equation (I) to find the value of emf.
$\eqalign{
& emf = - \dfrac{{d\left( {Mkt{e^{ - \alpha t}}} \right)}}{{dt}} \cr
& emf = - Mk\left( {1 - \alpha t} \right){e^{ - \alpha t}} \cr} $
Now we all know that current generated inside the ring is given by,
${i_2} = \dfrac{{emf}}{R}$…… (II)
We will now substitute the value of $emf = - Mk\left( {1 - \alpha t} \right){e^{ - \alpha t}}$to find the value of current through coil that is ${i_2}$. Therefore, it becomes,
${i_2} = \dfrac{{ - Mk\left( {1 - \alpha t} \right){e^{ - \alpha t}}}}{R}$
When the value of $t$ becomes $t = \dfrac{1}{\alpha }$ then at that point the current becomes,
$\eqalign{
& {i_2} = \dfrac{{ - Mk\left( {1 - \alpha \times \dfrac{1}{\alpha }} \right){e^{ - \alpha t}}}}{R} \cr
& {i_2} = 0 \cr} $
Now at $t = 0$, we can find the initial value of current. So we will put $t = 0$ and it becomes,
$\eqalign{
& {i_2} = \dfrac{{ - Mk\left( {1 - \alpha \times 0} \right){e^{ - \alpha \times 0}}}}{R} \cr
& {i_2} = \dfrac{{ - Mk}}{R} \cr} $
So we can come to the point that, on seeing the behaviour of current a $t = 0$ and $t = \dfrac{1}{\alpha }$
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
In option (D), the initial value of the current is negative and it is also zero somewhere in the time axis.
Additional Information:
We know that when the current passes through the solenoid it generates the magnetic field inside the solenoid. And as the magnetic lines of force also crosses the ring of radius $2R$, it generates a change in flux inside the ring.
Note:
We know that the relation between magnetic field and current is determined by the Biot savart law. The constant current generated by the magnetic field is given by the biot savart law. It gives the relation between the magnetic field and current magnitude, length, direction and proximity.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




