
A vector of length l is turned through the angle $\theta $ about its tail. What is the magnitude change in the position vector of its head?
A. $l\cos (\theta /2)$
B. $2l\sin (\theta /2)$
C. $2l\cos (\theta /2)$
D. $l\sin (\theta /2)$.
Answer
609.3k+ views
Hint: In this question, we will use the concept of mathematical operations on vectors. Here we will use the parallelogram law of vector addition i.e. $R = \sqrt {{P^2} + {Q^2} + 2PQ\cos \theta } $.
Formula used: $R = \sqrt {{P^2} + {Q^2} + 2PQ\cos \theta } $.
Complete step-by-step solution -
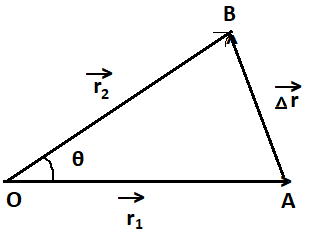
Given that, length of vector = l, angle inclined =$\theta $.
We have to find the magnitude change in the position of the vector.
We know that, if two vectors can be represented in both magnitude and direction by the two adjacent sides of a parallelogram drawn from a common point, ten their resultant is completely represented both in magnitude and direction by the diagonal of the parallelogram passing through that point.
According to the question, the vector is turned through the angle $\theta $ about its tail. So the magnitude of resultant will become $\overrightarrow {\vartriangle r} = \overrightarrow {{r_2}} - \overrightarrow {{r_1}} $, where ${r_1} = {r_2} = l$
Using the parallelogram law of vector addition,
The magnitude of resultant vector, $\vartriangle r = \sqrt {{r_1}^2 + {r_2}^2 - 2({r_1})({r_2})\cos \theta } $
$ \Rightarrow \vartriangle r = \sqrt {2{l^2} - 2{l^2}\cos \theta } $
Now taking common $2{l^2}$ from both sides, we get
$ \Rightarrow \vartriangle r = \sqrt {2{l^2}(1 - \cos \theta } )$
Using the identity, $(1 - \cos \theta ) = 2{\sin ^2}\dfrac{\theta }{2}$, we get
$
\Rightarrow \vartriangle r = l\sqrt {2\left( {2{{\sin }^2}\dfrac{\theta }{2}} \right)} \\
\Rightarrow \vartriangle r = 2l\sin \left( {\dfrac{\theta }{2}} \right). \\
$
Hence, we can see that the magnitude change in the position vector of its head = $2l\sin \left( {\dfrac{\theta }{2}} \right).$
Therefore, the correct answer is option (B).
Note: Whenever we ask such a question, first we have to remember the concept of addition of vectors. Then we will use that method to find out the magnitude of the resultant vector when the magnitude of two vectors is given and the angle inclined is also given. Through this we will get the answer.
Formula used: $R = \sqrt {{P^2} + {Q^2} + 2PQ\cos \theta } $.
Complete step-by-step solution -

Given that, length of vector = l, angle inclined =$\theta $.
We have to find the magnitude change in the position of the vector.
We know that, if two vectors can be represented in both magnitude and direction by the two adjacent sides of a parallelogram drawn from a common point, ten their resultant is completely represented both in magnitude and direction by the diagonal of the parallelogram passing through that point.
According to the question, the vector is turned through the angle $\theta $ about its tail. So the magnitude of resultant will become $\overrightarrow {\vartriangle r} = \overrightarrow {{r_2}} - \overrightarrow {{r_1}} $, where ${r_1} = {r_2} = l$
Using the parallelogram law of vector addition,
The magnitude of resultant vector, $\vartriangle r = \sqrt {{r_1}^2 + {r_2}^2 - 2({r_1})({r_2})\cos \theta } $
$ \Rightarrow \vartriangle r = \sqrt {2{l^2} - 2{l^2}\cos \theta } $
Now taking common $2{l^2}$ from both sides, we get
$ \Rightarrow \vartriangle r = \sqrt {2{l^2}(1 - \cos \theta } )$
Using the identity, $(1 - \cos \theta ) = 2{\sin ^2}\dfrac{\theta }{2}$, we get
$
\Rightarrow \vartriangle r = l\sqrt {2\left( {2{{\sin }^2}\dfrac{\theta }{2}} \right)} \\
\Rightarrow \vartriangle r = 2l\sin \left( {\dfrac{\theta }{2}} \right). \\
$
Hence, we can see that the magnitude change in the position vector of its head = $2l\sin \left( {\dfrac{\theta }{2}} \right).$
Therefore, the correct answer is option (B).
Note: Whenever we ask such a question, first we have to remember the concept of addition of vectors. Then we will use that method to find out the magnitude of the resultant vector when the magnitude of two vectors is given and the angle inclined is also given. Through this we will get the answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




