
A vector a has magnitude 5 units and points north east and another vector b has magnitude 5 units and points north west. Then the magnitude of the vector (a-b) is ?
1) 0
2) \[5\sqrt 2 \]
3) 10
4) 25
Answer
501.3k+ views
Hint: A vector is an object which has both magnitudes and direction and is usually represented by an arrow. Here, we are given \[\overrightarrow a = 5\] units which point north east and \[\overrightarrow b = 5\] units which point north west. And, we need to find the value of \[|\overrightarrow a - \overrightarrow b |\] . For this, we will draw the diagram first, and then we will get the value of vector a and vector b. Then, after using these values we can find the final output.
Complete answer:
Given that,
\[\overrightarrow a \] has magnitude 5 units and points north east and
\[\overrightarrow b \] has magnitude 5 units and points northwest.
According to the given information, we will draw a figure as below:
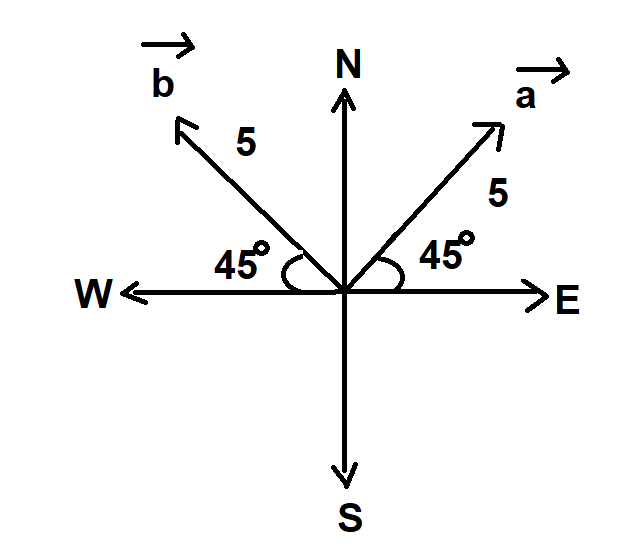
From the figure, we get,
\[\overrightarrow a = 5\cos {45^\circ }\widehat i + 5\sin {45^\circ }\widehat j\]
\[\therefore \overrightarrow a = 5(\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }})\widehat i + 5(\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }})\widehat j\]
\[\therefore \overrightarrow a = \dfrac{5}{{\sqrt 2 }}(\widehat i + \widehat j)\]
And,
\[\overrightarrow b = 5\cos {45^\circ }( - \widehat i) + 5\sin {45^\circ }\widehat j\]
\[\therefore \overrightarrow b = 5(\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }})( - \widehat i) + 5(\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }})\widehat j\]
\[\therefore \overrightarrow b = \dfrac{5}{{\sqrt 2 }}( - \widehat i + \widehat j)\]
We need to find the magnitude of vector (a-b), which is done as below:
\[\therefore \overrightarrow a - \overrightarrow b \]
\[ = \dfrac{5}{{\sqrt 2 }}(\widehat i + \widehat j) - \dfrac{5}{{\sqrt 2 }}( - \widehat i + \widehat j)\]
\[ = \dfrac{5}{{\sqrt 2 }}(\widehat i + \widehat j) - \dfrac{5}{{\sqrt 2 }}( - \widehat i + \widehat j)\]
\[ = \dfrac{5}{{\sqrt 2 }}\widehat i + \dfrac{5}{{\sqrt 2 }}\widehat j + \dfrac{5}{{\sqrt 2 }}\widehat i - \dfrac{5}{{\sqrt 2 }}\widehat j\]
\[ = \dfrac{5}{{\sqrt 2 }} \times 2\widehat i\]
\[ = 5\sqrt 2 \widehat i\]
\[\therefore |\overrightarrow a - \overrightarrow b | = 5\sqrt 2 \]
Another Method:
Given that,
\[|\overrightarrow a | = 5\] units and \[|\overrightarrow b | = 5\] units
\[\therefore |\overrightarrow a - \overrightarrow b |\]
\[ = \sqrt {|a{|^2} + |b{|^2} + 2|a||b|\cos \theta } \]
\[ = \sqrt {{5^2} + {5^2} + 2(5)(5)\cos {{90}^\circ }} \]
\[ = \sqrt {25 + 25 + 2(5)(5)(0)} \] \[(\because \cos {90^\circ } = 0)\]
\[ = \sqrt {25 + 25 + 2(5)(5)(0)} \]
\[ = \sqrt {25 + 25 + 0} \]
\[ = \sqrt {50 + 0} \]
\[ = \sqrt {50} \]
\[ = \sqrt {5 \times 5 \times 2} \]
\[ = 5\sqrt 2 \]
Hence, for the given \[\overrightarrow a = 5\] units which points north east and \[\overrightarrow b = 5\] units which points north west, then the value of \[|\overrightarrow a - \overrightarrow b | = 5\sqrt 2 \] .
Note:
Vector algebra studies the algebra of vector quantities. There are two types of physical quantities, scalars and vectors. The scalar quantity has only magnitude, whereas the vector quantity has both magnitude and direction. The magnitude of the vector is represented as |V|. Two vectors are said to be equal if they have equal magnitudes and equal direction. We also perform arithmetic operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication on vectors. But, in the case of multiplication, vectors have two terminologies, such as dot product and cross product.
Complete answer:
Given that,
\[\overrightarrow a \] has magnitude 5 units and points north east and
\[\overrightarrow b \] has magnitude 5 units and points northwest.
According to the given information, we will draw a figure as below:

From the figure, we get,
\[\overrightarrow a = 5\cos {45^\circ }\widehat i + 5\sin {45^\circ }\widehat j\]
\[\therefore \overrightarrow a = 5(\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }})\widehat i + 5(\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }})\widehat j\]
\[\therefore \overrightarrow a = \dfrac{5}{{\sqrt 2 }}(\widehat i + \widehat j)\]
And,
\[\overrightarrow b = 5\cos {45^\circ }( - \widehat i) + 5\sin {45^\circ }\widehat j\]
\[\therefore \overrightarrow b = 5(\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }})( - \widehat i) + 5(\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }})\widehat j\]
\[\therefore \overrightarrow b = \dfrac{5}{{\sqrt 2 }}( - \widehat i + \widehat j)\]
We need to find the magnitude of vector (a-b), which is done as below:
\[\therefore \overrightarrow a - \overrightarrow b \]
\[ = \dfrac{5}{{\sqrt 2 }}(\widehat i + \widehat j) - \dfrac{5}{{\sqrt 2 }}( - \widehat i + \widehat j)\]
\[ = \dfrac{5}{{\sqrt 2 }}(\widehat i + \widehat j) - \dfrac{5}{{\sqrt 2 }}( - \widehat i + \widehat j)\]
\[ = \dfrac{5}{{\sqrt 2 }}\widehat i + \dfrac{5}{{\sqrt 2 }}\widehat j + \dfrac{5}{{\sqrt 2 }}\widehat i - \dfrac{5}{{\sqrt 2 }}\widehat j\]
\[ = \dfrac{5}{{\sqrt 2 }} \times 2\widehat i\]
\[ = 5\sqrt 2 \widehat i\]
\[\therefore |\overrightarrow a - \overrightarrow b | = 5\sqrt 2 \]
Another Method:
Given that,
\[|\overrightarrow a | = 5\] units and \[|\overrightarrow b | = 5\] units
\[\therefore |\overrightarrow a - \overrightarrow b |\]
\[ = \sqrt {|a{|^2} + |b{|^2} + 2|a||b|\cos \theta } \]
\[ = \sqrt {{5^2} + {5^2} + 2(5)(5)\cos {{90}^\circ }} \]
\[ = \sqrt {25 + 25 + 2(5)(5)(0)} \] \[(\because \cos {90^\circ } = 0)\]
\[ = \sqrt {25 + 25 + 2(5)(5)(0)} \]
\[ = \sqrt {25 + 25 + 0} \]
\[ = \sqrt {50 + 0} \]
\[ = \sqrt {50} \]
\[ = \sqrt {5 \times 5 \times 2} \]
\[ = 5\sqrt 2 \]
Hence, for the given \[\overrightarrow a = 5\] units which points north east and \[\overrightarrow b = 5\] units which points north west, then the value of \[|\overrightarrow a - \overrightarrow b | = 5\sqrt 2 \] .
Note:
Vector algebra studies the algebra of vector quantities. There are two types of physical quantities, scalars and vectors. The scalar quantity has only magnitude, whereas the vector quantity has both magnitude and direction. The magnitude of the vector is represented as |V|. Two vectors are said to be equal if they have equal magnitudes and equal direction. We also perform arithmetic operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication on vectors. But, in the case of multiplication, vectors have two terminologies, such as dot product and cross product.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




