
A uniform steel rod of length \[1m\] and area of cross section $20c{{m}^{2}}$ is hanging from a fixed support. Find the increase in length of the rod. $\left( {{Y}_{\text{steel}}}=2.0\times {{10}^{11}}N{{m}^{-2}},\text{ }{{\rho }_{\text{steel}}}=7.85\times {{10}^{3}}Kg{{m}^{-3}} \right)$
$\begin{align}
& \text{A}\text{. }1.923\times {{10}^{-5}}cm \\
& \text{B}\text{. }2.923\times {{10}^{-5}}cm \\
& \text{C}\text{. }1.123\times {{10}^{-5}}cm \\
& \text{D}\text{. }3.123\times {{10}^{-5}}cm \\
\end{align}$
Answer
590.1k+ views
Hint: When a rod is hanged from a fixed point, the weight of the rod causes it to elongate. Hooke's law is used to determine the elongation in rod and the calculus of variations can be used to find the taper which can minimize the elongation.
Formula used:
$\Delta L=\dfrac{\rho g{{L}^{2}}}{2Y}$
Complete step by step answer:
When a rod is hung through the ceiling, extension in the length of the rod will be due to self-weight which is distributed all along its length. The extension in the length of the rod is half of the extension produced when the same rod is connected to the ceiling and force $F$ is applied to the other end. We use Hooke's law to find the extension in the rod length.
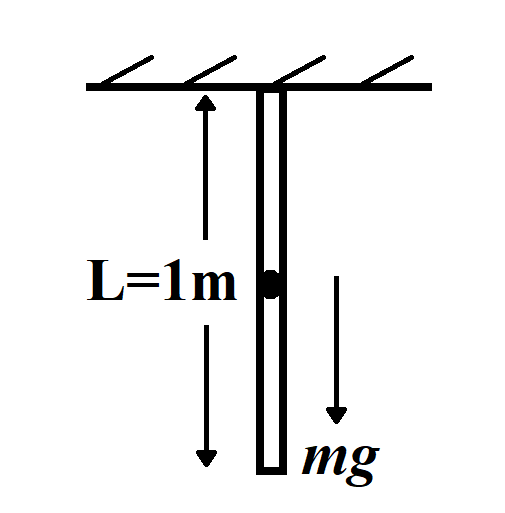
Weight of steel rod $W=mg$
Using the formula, $\text{density = }\dfrac{\text{mass}}{\text{volume}}$
We get, $\rho =\dfrac{m}{AL}$
Where,
$m$ is the mass of the rod
$A$ is the cross sectional area of rod
$L$ is the length of the rod
$W=mg=\rho ALg$
Elongation in the length of the rod due to its own weight would be half of the elongation due to point load,
Let the elongation in length of rod be:
\[\Delta L=\dfrac{WL}{2AY}\]
Or,
$\Delta L=\dfrac{\rho g{{L}^{2}}}{2Y}$
Putting the values,
$\begin{align}
& {{\rho }_{\text{steel}}}=7.85\times {{10}^{3}}N{{m}^{-2}} \\
& L=1m \\
& A=20c{{m}^{2}} \\
& {{Y}_{\text{steel}}}={{10}^{11}}N{{m}^{-2}} \\
\end{align}$
We get,
$\Delta L=\dfrac{7.85\times {{10}^{3}}\times g\times {{\left( 1 \right)}^{2}}}{2\times {{10}^{11}}}$
Put,
$g=9.8m{{s}^{-2}}$
$\begin{align}
& \Delta L=\dfrac{7.85\times {{10}^{3}}\times 9.8\times 1}{2\times 2\times {{10}^{11}}}=\dfrac{76.93\times {{10}^{3}}}{4\times {{10}^{11}}} \\
& \Delta L=19.23\times {{10}^{-8}}m \\
& \Delta L=1.923\times {{10}^{-5}}cm \\
\end{align}$
Elongation in length of steel rod is $1.923\times {{10}^{-5}}cm$
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note:
In order to taper a heavy rod, it should be hanged vertically, to minimize the elongation due to its own weight plus a load at its lower end. Hooke's law can be used to determine the elongation in the rod.
While doing calculations, prefer to take all the terms in SI units to avoid calculation error.
Formula used:
$\Delta L=\dfrac{\rho g{{L}^{2}}}{2Y}$
Complete step by step answer:
When a rod is hung through the ceiling, extension in the length of the rod will be due to self-weight which is distributed all along its length. The extension in the length of the rod is half of the extension produced when the same rod is connected to the ceiling and force $F$ is applied to the other end. We use Hooke's law to find the extension in the rod length.

Weight of steel rod $W=mg$
Using the formula, $\text{density = }\dfrac{\text{mass}}{\text{volume}}$
We get, $\rho =\dfrac{m}{AL}$
Where,
$m$ is the mass of the rod
$A$ is the cross sectional area of rod
$L$ is the length of the rod
$W=mg=\rho ALg$
Elongation in the length of the rod due to its own weight would be half of the elongation due to point load,
Let the elongation in length of rod be:
\[\Delta L=\dfrac{WL}{2AY}\]
Or,
$\Delta L=\dfrac{\rho g{{L}^{2}}}{2Y}$
Putting the values,
$\begin{align}
& {{\rho }_{\text{steel}}}=7.85\times {{10}^{3}}N{{m}^{-2}} \\
& L=1m \\
& A=20c{{m}^{2}} \\
& {{Y}_{\text{steel}}}={{10}^{11}}N{{m}^{-2}} \\
\end{align}$
We get,
$\Delta L=\dfrac{7.85\times {{10}^{3}}\times g\times {{\left( 1 \right)}^{2}}}{2\times {{10}^{11}}}$
Put,
$g=9.8m{{s}^{-2}}$
$\begin{align}
& \Delta L=\dfrac{7.85\times {{10}^{3}}\times 9.8\times 1}{2\times 2\times {{10}^{11}}}=\dfrac{76.93\times {{10}^{3}}}{4\times {{10}^{11}}} \\
& \Delta L=19.23\times {{10}^{-8}}m \\
& \Delta L=1.923\times {{10}^{-5}}cm \\
\end{align}$
Elongation in length of steel rod is $1.923\times {{10}^{-5}}cm$
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note:
In order to taper a heavy rod, it should be hanged vertically, to minimize the elongation due to its own weight plus a load at its lower end. Hooke's law can be used to determine the elongation in the rod.
While doing calculations, prefer to take all the terms in SI units to avoid calculation error.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




