
A uniform solid sphere of mass $1kg$ and radius $10cm$ is kept stationary on a rough inclined plane by fixing a highly dense particle at $B$. Inclination of the plane is ${37^o}$ with horizontal and $AB$ is the diameter of the sphere which is parallel to the plane, as shown in the figure. Then,
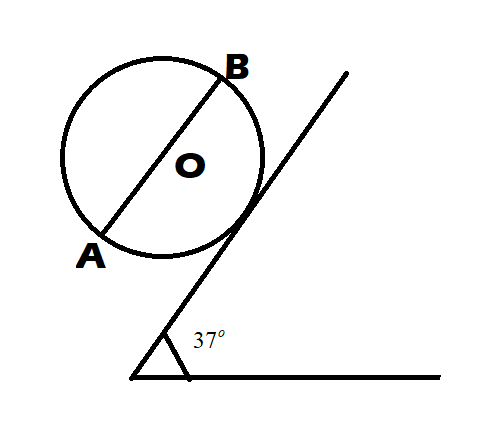
A. Mass of the particle fixes at $B$ is $4kg$
B. Mass of the particle fixes at $B$ is $3kg$
C. Minimum required coefficient of friction between sphere and the plane to keep in equilibrium is ${\mu _{\min }} = 0.75$
D. Minimum required coefficient of friction between sphere and the plane to keep in equilibrium is ${\mu _{\min }} = 0.5$

Answer
579.3k+ views
Hint: This is a great question as per standards. First we have to assume the mass of the particle. Then we have to make the free body diagram and mention all the forces. After than to obtain the limiting condition of friction, we have to find the forces along the normal and along the plane. Then we can just put them under the formula and then get the answer.
Complete step by step answer:
Firstly we have to sort out what we have got :
Mass of uniform solid sphere : $1kg$
Radius of uniform solid sphere : $10cm$
Inclination of the plane : ${37^o}$
Step1: We have to assume the mass of the particle as $m$. Now, it is most important to make the free body diagram of the system with all the forces mentioned so that we can work on the forces.
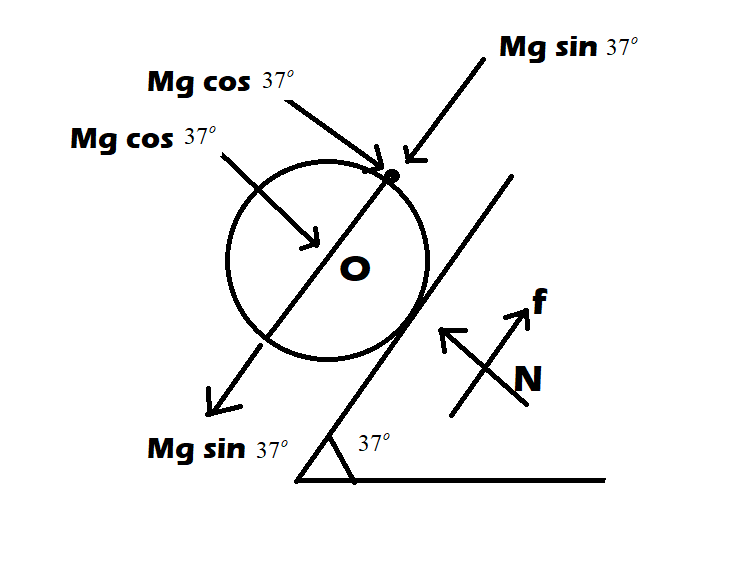
By the system we can observe that the given system is in a state of equilibrium, thus the net torque would be zero.
Step 2: Therefore, we have to equate all the torque acting on the system. Taking torque of point $A$ of all the forces acting on system:
$
(Mg\sin {37^o})R + (mg\sin {37^o})R = (mg\cos {37^o})R \\
\Rightarrow (1 \times 10 \times \dfrac{3}{5}) + (m \times 10 \times \dfrac{3}{5}) = (m \times 10 \times \dfrac{4}{5}) \\
\Rightarrow 6 + 6m = 8m \\
\Rightarrow 2m = 6 \\
\Rightarrow m = 3kg \\
$
Therefore the mass is $3kg$
Step 3: The friction force between the sphere and the plane is static in nature so:
Forces along the normal would be :-
$
\Rightarrow N = Mg\cos {37^o} + mg\cos {37^o} \\
\Rightarrow N = 1 \times 10 \times \dfrac{4}{5} + 3 \times 10 \times \dfrac{4}{5} \\
\Rightarrow N = (8 + 24)N \\
\Rightarrow N = 32N \\
$
And the forces along the plane would be:-
$
f = Mg\sin {37^o} + mg\sin {37^o} \\
\Rightarrow f = 1 \times 10 \times \dfrac{3}{5} + 3 \times 10 \times \dfrac{3}{5} \\
\Rightarrow f = (6 + 18)N \\
\Rightarrow f = 24N \\
$
Therefore by the formula of ${\mu _{\min }}$ we will get:
$
{\mu _{\min }} = \dfrac{f}{N} \\
\Rightarrow {\mu _{\min }} = \dfrac{{24}}{{32}} \\
\Rightarrow {\mu _{\min }} = 0.75 \\
$
Hence, the value of ${\mu _{\min }} = 0.75$
Therefore, the correct options would be B and C
Note:- The forces along the plane and normal should be calculated considering the direction. If the forces go against each other the difference should take place whereas in the same direction they should be summed.
Complete step by step answer:
Firstly we have to sort out what we have got :
Mass of uniform solid sphere : $1kg$
Radius of uniform solid sphere : $10cm$
Inclination of the plane : ${37^o}$
Step1: We have to assume the mass of the particle as $m$. Now, it is most important to make the free body diagram of the system with all the forces mentioned so that we can work on the forces.

By the system we can observe that the given system is in a state of equilibrium, thus the net torque would be zero.
Step 2: Therefore, we have to equate all the torque acting on the system. Taking torque of point $A$ of all the forces acting on system:
$
(Mg\sin {37^o})R + (mg\sin {37^o})R = (mg\cos {37^o})R \\
\Rightarrow (1 \times 10 \times \dfrac{3}{5}) + (m \times 10 \times \dfrac{3}{5}) = (m \times 10 \times \dfrac{4}{5}) \\
\Rightarrow 6 + 6m = 8m \\
\Rightarrow 2m = 6 \\
\Rightarrow m = 3kg \\
$
Therefore the mass is $3kg$
Step 3: The friction force between the sphere and the plane is static in nature so:
Forces along the normal would be :-
$
\Rightarrow N = Mg\cos {37^o} + mg\cos {37^o} \\
\Rightarrow N = 1 \times 10 \times \dfrac{4}{5} + 3 \times 10 \times \dfrac{4}{5} \\
\Rightarrow N = (8 + 24)N \\
\Rightarrow N = 32N \\
$
And the forces along the plane would be:-
$
f = Mg\sin {37^o} + mg\sin {37^o} \\
\Rightarrow f = 1 \times 10 \times \dfrac{3}{5} + 3 \times 10 \times \dfrac{3}{5} \\
\Rightarrow f = (6 + 18)N \\
\Rightarrow f = 24N \\
$
Therefore by the formula of ${\mu _{\min }}$ we will get:
$
{\mu _{\min }} = \dfrac{f}{N} \\
\Rightarrow {\mu _{\min }} = \dfrac{{24}}{{32}} \\
\Rightarrow {\mu _{\min }} = 0.75 \\
$
Hence, the value of ${\mu _{\min }} = 0.75$
Therefore, the correct options would be B and C
Note:- The forces along the plane and normal should be calculated considering the direction. If the forces go against each other the difference should take place whereas in the same direction they should be summed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




