
A uniform solid right circular cone of base radius r is joined to a uniform solid hemisphere of radius r and of the same density, as shown. The center of mass of the composite solid lies at the center of the base of the cone. The height of cone is
$A.$ 1.5r
$B.$ $\sqrt 3 $r
$C.$ 3r
$D.$ $2\sqrt 3 $r

Answer
521.3k+ views
HINT- The center of mass of a body or a system of bodies is a mean position of the total weight of the body where the resultant of the forces applied is considered to be acted upon such that forces, momentum and energy are conserved. The body or system of bodies is balanced around the center of mass and the average of the weighted position coordinates defines its coordinates.
Now from the question, we have
The figure is shown below-
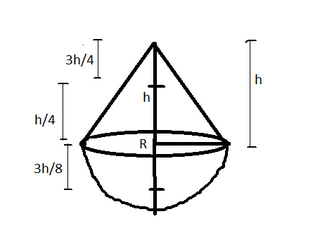
Volume of cone = $\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {r^3}h$
Mass of cone, ${m_1} = \rho \times \dfrac{1}{3}\pi {r^2}h$
Mass of hemisphere, ${m_2} = \rho \times \dfrac{1}{2} \times \dfrac{4}{3}\pi {r^3}$ = $\rho \times \dfrac{2}{3}\pi {r^3}$
Now, $Y = \dfrac{{{m_1}{y_1} + {m_2}{y_2}}}{{{m_1} + {m_2}}}$
$0 = \dfrac{{\rho \times \dfrac{1}{3}\pi {r^2}h \times \dfrac{h}{4} + \rho \times \dfrac{2}{3}\pi {r^3}( - \dfrac{{3r}}{8})}}{{\rho \times \dfrac{1}{3}\pi {r^2}h + \rho \times \dfrac{2}{3}\pi {r^3}}}$
Or, $\rho \times \dfrac{1}{3}\pi {r^2}[\dfrac{{{h^2}}}{4} - 2r \times \dfrac{{3r}}{8}] = 0$
Or $\dfrac{{{h^2}}}{4} - \dfrac{{3{r^2}}}{4} = 0$ or $h = \sqrt 3 r$
Therefore, the correct option is $B.$
NOTE- More about center of mass-
The center of mass of a distribution of mass in space is the unique point where the weighted relative position of the distributed mass sums zero. This is the point to which a force may be applied to cause a linear acceleration without an angular acceleration. Calculations in mechanics are often simplified when formulated with respect to the center of mass. It is a hypothetical point where the entire mass of an object may be assumed to be concentrated to visualize its motion. In other words, the center of mass is the particle equivalent of a given object for application of Newton’s laws of motion.
In case of a single rigid body, the center of mass is fixed in relation to the body, and if the body has uniform density, it will be located at the centroid. The center of mass may be located outside the physical body, as is sometimes the case for hollow or open-shaped objects, such as horseshoe. In case of a distribution of separate bodies, such as the planets of the Solar System, the center of mass may not correspond to the position of any individual member of the system.
Now from the question, we have
The figure is shown below-

Volume of cone = $\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {r^3}h$
Mass of cone, ${m_1} = \rho \times \dfrac{1}{3}\pi {r^2}h$
Mass of hemisphere, ${m_2} = \rho \times \dfrac{1}{2} \times \dfrac{4}{3}\pi {r^3}$ = $\rho \times \dfrac{2}{3}\pi {r^3}$
Now, $Y = \dfrac{{{m_1}{y_1} + {m_2}{y_2}}}{{{m_1} + {m_2}}}$
$0 = \dfrac{{\rho \times \dfrac{1}{3}\pi {r^2}h \times \dfrac{h}{4} + \rho \times \dfrac{2}{3}\pi {r^3}( - \dfrac{{3r}}{8})}}{{\rho \times \dfrac{1}{3}\pi {r^2}h + \rho \times \dfrac{2}{3}\pi {r^3}}}$
Or, $\rho \times \dfrac{1}{3}\pi {r^2}[\dfrac{{{h^2}}}{4} - 2r \times \dfrac{{3r}}{8}] = 0$
Or $\dfrac{{{h^2}}}{4} - \dfrac{{3{r^2}}}{4} = 0$ or $h = \sqrt 3 r$
Therefore, the correct option is $B.$
NOTE- More about center of mass-
The center of mass of a distribution of mass in space is the unique point where the weighted relative position of the distributed mass sums zero. This is the point to which a force may be applied to cause a linear acceleration without an angular acceleration. Calculations in mechanics are often simplified when formulated with respect to the center of mass. It is a hypothetical point where the entire mass of an object may be assumed to be concentrated to visualize its motion. In other words, the center of mass is the particle equivalent of a given object for application of Newton’s laws of motion.
In case of a single rigid body, the center of mass is fixed in relation to the body, and if the body has uniform density, it will be located at the centroid. The center of mass may be located outside the physical body, as is sometimes the case for hollow or open-shaped objects, such as horseshoe. In case of a distribution of separate bodies, such as the planets of the Solar System, the center of mass may not correspond to the position of any individual member of the system.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




