
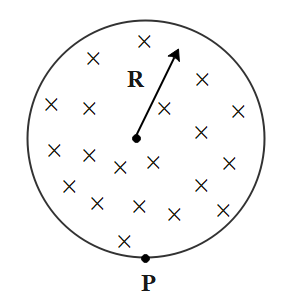
A uniform magnetic field of induction B is continued to a cylindrical region of radius R. The magnetic field is increasing at a constant rate of $\dfrac{{dB}}{{dt}}T{s^{ - 1}}$. An electron of charge e, placed at the point P on the periphery of the field experiences an acceleration:
A. $\dfrac{1}{2}\dfrac{{eR}}{m}\dfrac{{dB}}{{dt}}{\text{ toward left}}$
B. $\dfrac{1}{2}\dfrac{{eR}}{m}\dfrac{{dB}}{{dt}}{\text{ toward right}}$
C. $\dfrac{{eR}}{m}\dfrac{{dB}}{{dt}}{\text{ toward left}}$
D. zero

Answer
573k+ views
Hint: Induced emf is defined as the generation of a potential difference in a coil due to the changes in the magnetic flux through it. It is also known as the induced electromotive force, electromagnetic induction, and electromotive force induction.
Formula Used: $E = - N\dfrac{{d\phi }}{{dt}}$
Complete answer:
We know that the emf induced is defined as the negative rate of change of flux, and flux is defined as the dot product of magnetic field and area vector.
If we consider the cylindrical surface to be a ring of radius R to changing field.
$\int {Ed\vec l} = \dfrac{{d\phi }}{{dt}} = - A\dfrac{{dB}}{{dt}}$
Now, we know that the area of the circle is given as,
$A = \pi {R^2}$
$\eqalign{
& \Rightarrow E2\pi R = - \pi {R^2}\dfrac{{dB}}{{dt}} \cr
& \Rightarrow E = \dfrac{R}{2}\dfrac{{dB}}{{dt}} \cr} $
Force on an electron is given as,
F = qE = -eE
$ \Rightarrow F = - \dfrac{{eR}}{2}\dfrac{{dB}}{{dt}}$
As we know that, force is given by the formula,
F = ma Where ‘F’ is the force, ‘m’ is the mass of the object or the particle and ‘a’ is the acceleration.
Equating the formula of force with the above relation we get,
$\therefore a = \dfrac{1}{2}\dfrac{{eR}}{m}\dfrac{{dB}}{{dt}}$
Therefore, as the field is increasing while directed inside the paper so the current induced in the ring will be in the anticlockwise direction. Thus, the acceleration experienced by the electron on the periphery of the field will be in the left direction.
Hence, option (A) is the correct answer.
Note:
There are various applications of induced emf such as, it is used in generators, galvanometers and also in transformers. We know that the working of transformers is based on the principle of mutual induction. When the current in one coil induces emf in the other coil it is defined as the Mutual inductance.
Formula Used: $E = - N\dfrac{{d\phi }}{{dt}}$
Complete answer:
We know that the emf induced is defined as the negative rate of change of flux, and flux is defined as the dot product of magnetic field and area vector.
If we consider the cylindrical surface to be a ring of radius R to changing field.
$\int {Ed\vec l} = \dfrac{{d\phi }}{{dt}} = - A\dfrac{{dB}}{{dt}}$
Now, we know that the area of the circle is given as,
$A = \pi {R^2}$
$\eqalign{
& \Rightarrow E2\pi R = - \pi {R^2}\dfrac{{dB}}{{dt}} \cr
& \Rightarrow E = \dfrac{R}{2}\dfrac{{dB}}{{dt}} \cr} $
Force on an electron is given as,
F = qE = -eE
$ \Rightarrow F = - \dfrac{{eR}}{2}\dfrac{{dB}}{{dt}}$
As we know that, force is given by the formula,
F = ma Where ‘F’ is the force, ‘m’ is the mass of the object or the particle and ‘a’ is the acceleration.
Equating the formula of force with the above relation we get,
$\therefore a = \dfrac{1}{2}\dfrac{{eR}}{m}\dfrac{{dB}}{{dt}}$
Therefore, as the field is increasing while directed inside the paper so the current induced in the ring will be in the anticlockwise direction. Thus, the acceleration experienced by the electron on the periphery of the field will be in the left direction.
Hence, option (A) is the correct answer.
Note:
There are various applications of induced emf such as, it is used in generators, galvanometers and also in transformers. We know that the working of transformers is based on the principle of mutual induction. When the current in one coil induces emf in the other coil it is defined as the Mutual inductance.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




