
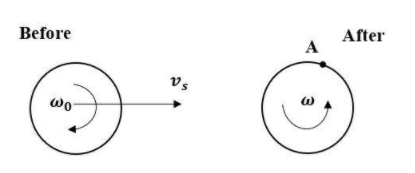
A uniform disc of mass M= 1 kg, radius R= 1m is moving towards right on smooth horizontal surface with velocity ${v}_{s} = 20 {m}/{s}$ and having velocity ${\omega}_{0}= 4 {rad}/{s}$ about the perpendicular axis outward the plane of disc passing through the center of disc. Suddenly the top point of the disc gets hinged about a fixed smooth axis. The angular velocity (in rad/s) of disc about new rotation axis is:

Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint: To solve this problem, first find the moment of inertia of disc. Then, using the relation between angular momentum, moment of inertia and angular velocity, find the value of angular momentum. Use the relation between torque and angular acceleration to find angular acceleration. Then, use the angular kinematic equation and substitute the values. This will give the angular velocity of the disc about the new rotation axis.
Complete answer:
Given: M= 1 kg
R= 1 m
${v}_{s} = 20 {m}/{s}$
${\omega}_{0}= 4 {rad}/{s}$
Moment of Inertia is given by,
$I= \dfrac {1}{2} M {R}^{2}$
Substituting the values in above equation we get,
$I= \dfrac {1}{2}\times 1 \times {1}^{2}$
$\therefore I= \dfrac {1}{2}$
Thus, the moment of inertia of the disc is $\dfrac {1}{2}{kg}/{{m}^{2}}$.
We know, angular momentum is given by,
$L= I \omega$
Substituting values in above equation we get,
$L = \dfrac {1}{2} \times 4$
$\therefore L = 2{{kg}/{{m}^{2}}}/{s}$.
But, we know, torque is equal to the change in angular momentum.
$\therefore \tau= 2Nm$
But, we also know, $\tau= I \alpha$
$\therefore 2= \dfrac {1}{2} \alpha$
$\therefore \alpha= 4 {{rad}/{s}^{2}}$
From angular kinematics we know,
${\omega}_{2}= {\omega}_{1} + \alpha t$
But, $v = \dfrac {r}{t}$
$\therefore { \omega}_{2}= {\omega}_{1}+ \alpha \dfrac {r}{v}$
Now, substituting the values in above equation we get,
$ { \omega}_{2}= 0.2 {rad}/{s}$
Hence, the angular velocity of the disc about the new rotation axis is 0.2 rad/s.
Note:
Students should know all the angular or rotational kinematic equations. They should also know the proper application of those equations. To choose the rotational kinematic equation, figure out which variables are given in the question and which are asked.
Example: $\omega ={\omega}_{0} +\alpha t$
If any three variables of these are given, then you can use this relation to find the fourth variable.
Complete answer:
Given: M= 1 kg
R= 1 m
${v}_{s} = 20 {m}/{s}$
${\omega}_{0}= 4 {rad}/{s}$
Moment of Inertia is given by,
$I= \dfrac {1}{2} M {R}^{2}$
Substituting the values in above equation we get,
$I= \dfrac {1}{2}\times 1 \times {1}^{2}$
$\therefore I= \dfrac {1}{2}$
Thus, the moment of inertia of the disc is $\dfrac {1}{2}{kg}/{{m}^{2}}$.
We know, angular momentum is given by,
$L= I \omega$
Substituting values in above equation we get,
$L = \dfrac {1}{2} \times 4$
$\therefore L = 2{{kg}/{{m}^{2}}}/{s}$.
But, we know, torque is equal to the change in angular momentum.
$\therefore \tau= 2Nm$
But, we also know, $\tau= I \alpha$
$\therefore 2= \dfrac {1}{2} \alpha$
$\therefore \alpha= 4 {{rad}/{s}^{2}}$
From angular kinematics we know,
${\omega}_{2}= {\omega}_{1} + \alpha t$
But, $v = \dfrac {r}{t}$
$\therefore { \omega}_{2}= {\omega}_{1}+ \alpha \dfrac {r}{v}$
Now, substituting the values in above equation we get,
$ { \omega}_{2}= 0.2 {rad}/{s}$
Hence, the angular velocity of the disc about the new rotation axis is 0.2 rad/s.
Note:
Students should know all the angular or rotational kinematic equations. They should also know the proper application of those equations. To choose the rotational kinematic equation, figure out which variables are given in the question and which are asked.
Example: $\omega ={\omega}_{0} +\alpha t$
If any three variables of these are given, then you can use this relation to find the fourth variable.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




