
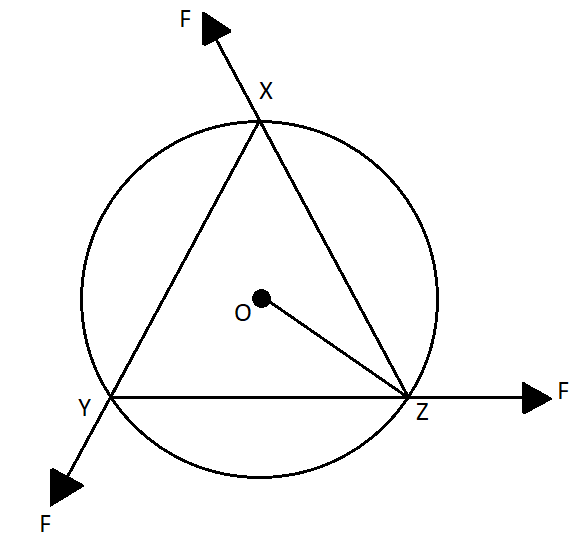
A uniform circular disc of mass $ 1.5kg $ and radius $ 0.5m $ is initially at rest on a horizontal frictionless surface. Three forces of equal magnitude $ 0.5N $ are applied simultaneously along the three sides of an equilateral triangle XYZ with its vertices on the perimeter of the disc (see figure). One second after applying the forces, the angular speed of the disc in $ rad{s^{ - 1}} $ is:
(A) 2
(B) 4
(C) 5
(D) 7

Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint We can equate the value of torque from the product of the component of force causing the torque and the radius and the product of the moment of inertia and we can also equate it from the angular acceleration. From there we can get the angular acceleration of the disc. From the equation of rotational kinematics, we can find the angular speed of the disc.
Formula Used: In the solution we will be using the following formula,
$\Rightarrow \tau = FR $
where $ \tau $ is the torque, $ F $ is the force and $ R $ is the radius of the disc
$\Rightarrow \tau = I\alpha $
where $ I $ is the moment of inertia and $ \alpha $ is the angular acceleration.
$\Rightarrow \omega = {\omega _o} + \alpha t $
where $ \omega $ is angular speed, $ {\omega _o} $ is initial angular speed and $ t $ is the time.
Complete step by step answer
From the figure we can see that there are three forces acting on the disc at the points X, Y and Z. All these three forces are acting in the anti clockwise direction. The force can be broken down to two components. We can see this in the diagram.
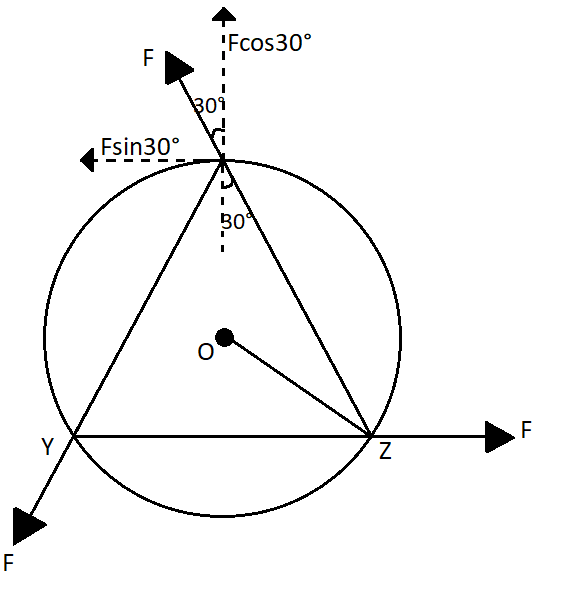
The triangle XYZ is an equilateral triangle. So each angle of the triangle is $ 60^\circ $. Therefore, we can break the force into its two components as in the diagram. The sine component of the force will cause the torque. So we can write the torque for one force as,
$\Rightarrow \tau = FR\sin 30^\circ $
There are three forces acting on the disc, so we get the total torque as,
$\Rightarrow \tau = 3FR\sin 30^\circ $
Now the torque can also be calculated as the product of the moment of inertia and the angular acceleration. So we have,
$\Rightarrow \tau = I\alpha $
Now, we can equate the two torques as,
$\Rightarrow I\alpha = 3FR\sin 30^\circ $
By taking the $ I $ to the RHS we get,
$\Rightarrow \alpha = \dfrac{{3FR\sin 30^\circ }}{I} $
For an uniform circular disc, $ I = \dfrac{{M{R^2}}}{2} $
Substituting and cancelling the $ R $ we get,
$\Rightarrow \alpha = \dfrac{{6F\sin 30^\circ }}{{MR}} $
In the question we are given that $ F = 0.5N $, $ R = 0.5m $ and $ M = 1.5kg $
The value of $ \sin 30 $ is $ \dfrac{1}{2} $. So substituting we get,
$\Rightarrow \alpha = \dfrac{{6 \times 0.5}}{{2 \times 1.5 \times 0.5}} $
On calculating we have,
$\Rightarrow \alpha = 2rad{s^{ - 2}} $
Now from the equation of rotational kinematics, we have
$\Rightarrow \omega = {\omega _o} + \alpha t $
Now the initial angular speed is 0 and the time is one second. So substituting we get,
$\Rightarrow \omega = 2 \times 1 $
So the angular speed is $ 2rad{s^{ - 1}} $.
So the correct answer is option A.
Note
The torque on any body is the force that is needed to rotate the body about any axis. Like the way force causes linear acceleration in a body, similarly, the torque causes angular acceleration. The SI unit of torque is given as, Newton-meter.
Formula Used: In the solution we will be using the following formula,
$\Rightarrow \tau = FR $
where $ \tau $ is the torque, $ F $ is the force and $ R $ is the radius of the disc
$\Rightarrow \tau = I\alpha $
where $ I $ is the moment of inertia and $ \alpha $ is the angular acceleration.
$\Rightarrow \omega = {\omega _o} + \alpha t $
where $ \omega $ is angular speed, $ {\omega _o} $ is initial angular speed and $ t $ is the time.
Complete step by step answer
From the figure we can see that there are three forces acting on the disc at the points X, Y and Z. All these three forces are acting in the anti clockwise direction. The force can be broken down to two components. We can see this in the diagram.

The triangle XYZ is an equilateral triangle. So each angle of the triangle is $ 60^\circ $. Therefore, we can break the force into its two components as in the diagram. The sine component of the force will cause the torque. So we can write the torque for one force as,
$\Rightarrow \tau = FR\sin 30^\circ $
There are three forces acting on the disc, so we get the total torque as,
$\Rightarrow \tau = 3FR\sin 30^\circ $
Now the torque can also be calculated as the product of the moment of inertia and the angular acceleration. So we have,
$\Rightarrow \tau = I\alpha $
Now, we can equate the two torques as,
$\Rightarrow I\alpha = 3FR\sin 30^\circ $
By taking the $ I $ to the RHS we get,
$\Rightarrow \alpha = \dfrac{{3FR\sin 30^\circ }}{I} $
For an uniform circular disc, $ I = \dfrac{{M{R^2}}}{2} $
Substituting and cancelling the $ R $ we get,
$\Rightarrow \alpha = \dfrac{{6F\sin 30^\circ }}{{MR}} $
In the question we are given that $ F = 0.5N $, $ R = 0.5m $ and $ M = 1.5kg $
The value of $ \sin 30 $ is $ \dfrac{1}{2} $. So substituting we get,
$\Rightarrow \alpha = \dfrac{{6 \times 0.5}}{{2 \times 1.5 \times 0.5}} $
On calculating we have,
$\Rightarrow \alpha = 2rad{s^{ - 2}} $
Now from the equation of rotational kinematics, we have
$\Rightarrow \omega = {\omega _o} + \alpha t $
Now the initial angular speed is 0 and the time is one second. So substituting we get,
$\Rightarrow \omega = 2 \times 1 $
So the angular speed is $ 2rad{s^{ - 1}} $.
So the correct answer is option A.
Note
The torque on any body is the force that is needed to rotate the body about any axis. Like the way force causes linear acceleration in a body, similarly, the torque causes angular acceleration. The SI unit of torque is given as, Newton-meter.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




