
A typical dicotyledonous embryo consists of
a. Radicle only
b. Radicle, embryonic axis, cotyledons
c. Cotyledons only
d. Embryonic axis only
Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint: Flowering plants or angiosperms are divided into two groups based on the number of embryonic seed leaves or cotyledons. They are Monocots – plants with one cotyledon, and Dicots – plants with two seed leaves. A seed of a plant consists of three parts namely, the seed coat, embryo, and endosperm. The embryo is composed of different parts that will eventually form the plant.
Complete answer:
Dicotyledonous plants are plants that are known to have two embryonic seed leaves or cotyledons.
A dicotyledonous embryo consists of the following:
- An embryonic axis: It consists of three parts, namely, the plumule, radicle and hypocotyl.
- Two cotyledons
The seed is protected by a seed coat, which is divided into an outer coat called the Testa and an inner coat called the Tegmen.
The embryonic axis terminates in a radicle or the embryonic root. It is from this region, the root of the will develop. The root tip is covered with a root cap or calyptra.
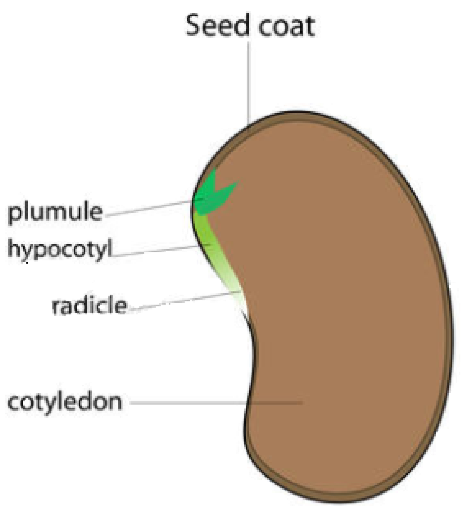
Fig: Structure of a dicotyledonous seed
The region of the embryo between the point of attachment of cotyledon and the below radicle is called hypocotyl.
Similarly, the region above the cotyledons is called the epicotyl. The epicotyl terminates in the plumule. This region is responsible for the growth of the stem. The plumule contains apical meristems.
Hence, the correct answer is option (B).
Additional information:
An embryo is that part of the seed that gives rise to a new plant. It is a multicellular structure. The embryo is formed by a process called fertilization where the male and female nuclei of the plant fuse to form a zygote. Going forward, the zygote forms the embryo, which remains protected by the seed. The seed, also, contains a structure called endosperm that acts as a food reserve for the embryo. The seed, if subjected to correct climatic conditions like optimum temperature, enough water, oxygen and minerals, germinates into a seedling. This seedling will eventually develop into an adult plant.
Note: A typical seed contains an embryo, which goes on to form a plant under proper environmental conditions. The embryo contains the miniature shoot, root and leaves. The basic structure of embryos in monocots and Dicots are the same. However, a few differences can be observed like the presence of additional structures like coleoptile, coleorhiza, scutellum in Monocots. These structures are absent in Dicots.
Complete answer:
Dicotyledonous plants are plants that are known to have two embryonic seed leaves or cotyledons.
A dicotyledonous embryo consists of the following:
- An embryonic axis: It consists of three parts, namely, the plumule, radicle and hypocotyl.
- Two cotyledons
The seed is protected by a seed coat, which is divided into an outer coat called the Testa and an inner coat called the Tegmen.
The embryonic axis terminates in a radicle or the embryonic root. It is from this region, the root of the will develop. The root tip is covered with a root cap or calyptra.

Fig: Structure of a dicotyledonous seed
The region of the embryo between the point of attachment of cotyledon and the below radicle is called hypocotyl.
Similarly, the region above the cotyledons is called the epicotyl. The epicotyl terminates in the plumule. This region is responsible for the growth of the stem. The plumule contains apical meristems.
Hence, the correct answer is option (B).
Additional information:
An embryo is that part of the seed that gives rise to a new plant. It is a multicellular structure. The embryo is formed by a process called fertilization where the male and female nuclei of the plant fuse to form a zygote. Going forward, the zygote forms the embryo, which remains protected by the seed. The seed, also, contains a structure called endosperm that acts as a food reserve for the embryo. The seed, if subjected to correct climatic conditions like optimum temperature, enough water, oxygen and minerals, germinates into a seedling. This seedling will eventually develop into an adult plant.
Note: A typical seed contains an embryo, which goes on to form a plant under proper environmental conditions. The embryo contains the miniature shoot, root and leaves. The basic structure of embryos in monocots and Dicots are the same. However, a few differences can be observed like the presence of additional structures like coleoptile, coleorhiza, scutellum in Monocots. These structures are absent in Dicots.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




