
What is a triplet codon?
(a)Fixed
(b)Degenerate
(c)Ambiguous
(d)Non-wobbly
Answer
601.2k+ views
Hint: Triplet codon is a sequence of three DNA or RNA nucleotides that code for a specific amino acid. Some amino acids are coded by more than one base triplet or codon. The full set of codons is called the genetic code.
Complete answer :Degeneracy of codons can be explained as the redundancy of the genetic code. It is shown as the multiplicity of three-base pair codon combinations that code for a particular amino acid. The degeneracy of the genetic code accounts for the existence of synonymous mutations.
Additional information:
Characteristics of the genetic code:
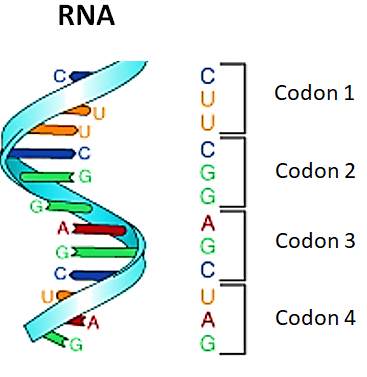
>Triplet nature: Codon is a set of three nucleotides that code for a particular amino acid. There are 64 codons used to code all 20 amino acids.
>Degeneracy: The triplet codon is degenerate means the same amino acid is coded by more than one base triplet. For example, GAA and GAG both specify glutamic acid and exhibit redundancy.
>Non-Overlapping: The genetic code is non overlapping means the same code is not used for two different codons. In other words, the adjacent codons do not overlap.
>Commaless: The genetic codes are comma free. There are no punctuations at the beginning and the end of the codon. In mRNA, the codon is read in a continuous fashion.
>Non-ambiguity: Genetic codes are specific i.e. one codon codes for only one amino acid.
>Start codon: AUG and GUG codes for Methionine (Met) and Valine (Val), respectively. They perform dual functions and also act as initiator codon.
>Stop codon: There are 3 codons that do not code for any amino acids hence they perform stop codon. They include UAG, UAA, UGA called nonsense codons.
So, the correct answer is ‘degenerate’.
Note: Codons are universal in nature such as from bacteria to human UUU is a code for Phenylalanine (phe).
-The genetic code is always read in a fixed direction, i.e., in the 5′ → 3′ direction.
-The nature of a codon was first revealed by Marshall Nirenberg and Heinrich J. Matthaei in 1961.
Complete answer :Degeneracy of codons can be explained as the redundancy of the genetic code. It is shown as the multiplicity of three-base pair codon combinations that code for a particular amino acid. The degeneracy of the genetic code accounts for the existence of synonymous mutations.
Additional information:
Characteristics of the genetic code:
>Triplet nature: Codon is a set of three nucleotides that code for a particular amino acid. There are 64 codons used to code all 20 amino acids.
>Degeneracy: The triplet codon is degenerate means the same amino acid is coded by more than one base triplet. For example, GAA and GAG both specify glutamic acid and exhibit redundancy.
>Non-Overlapping: The genetic code is non overlapping means the same code is not used for two different codons. In other words, the adjacent codons do not overlap.
>Commaless: The genetic codes are comma free. There are no punctuations at the beginning and the end of the codon. In mRNA, the codon is read in a continuous fashion.
>Non-ambiguity: Genetic codes are specific i.e. one codon codes for only one amino acid.
>Start codon: AUG and GUG codes for Methionine (Met) and Valine (Val), respectively. They perform dual functions and also act as initiator codon.
>Stop codon: There are 3 codons that do not code for any amino acids hence they perform stop codon. They include UAG, UAA, UGA called nonsense codons.
So, the correct answer is ‘degenerate’.
Note: Codons are universal in nature such as from bacteria to human UUU is a code for Phenylalanine (phe).
-The genetic code is always read in a fixed direction, i.e., in the 5′ → 3′ direction.
-The nature of a codon was first revealed by Marshall Nirenberg and Heinrich J. Matthaei in 1961.

Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

How is the angle of emergence e related to the angle class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between lanthanoids and actinoids class 12 chemistry CBSE

Derive Lens Makers formula for a convex lens class 12 physics CBSE

a Draw Labelled diagram of Standard Hydrogen Electrode class 12 chemistry CBSE




