
A tripeptide is written as glycine-alanine-glycine. The correct structure of the tripeptide is:
A.
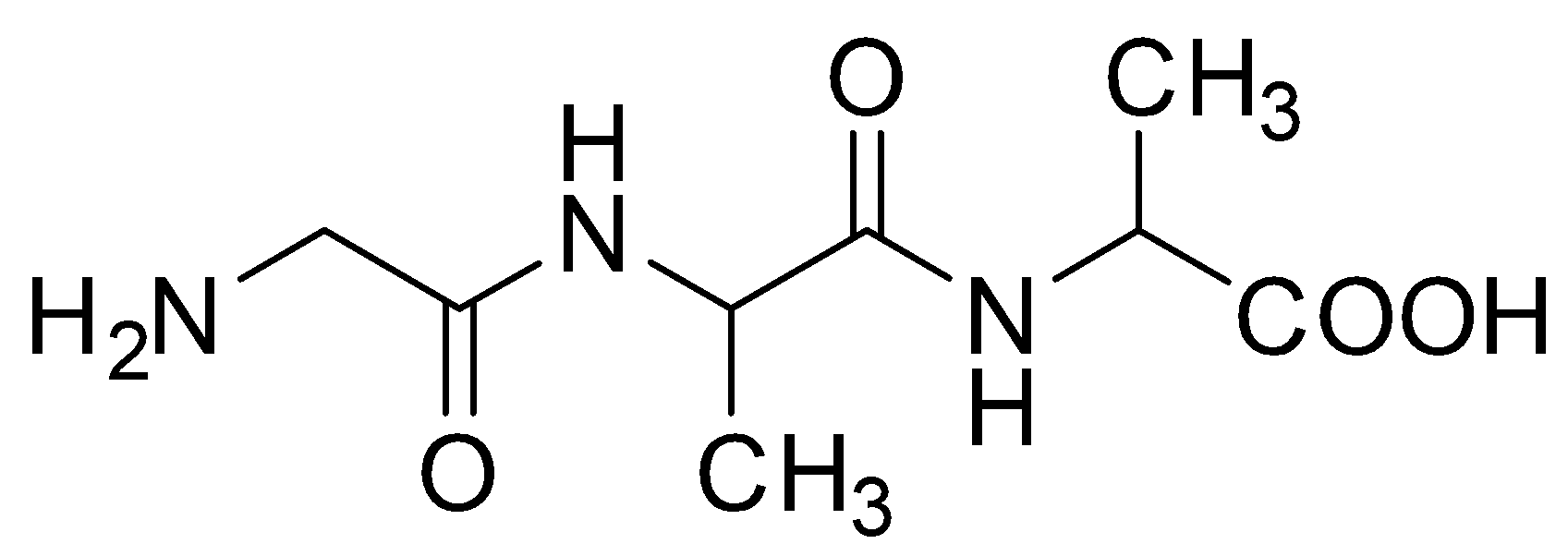 B.
B.
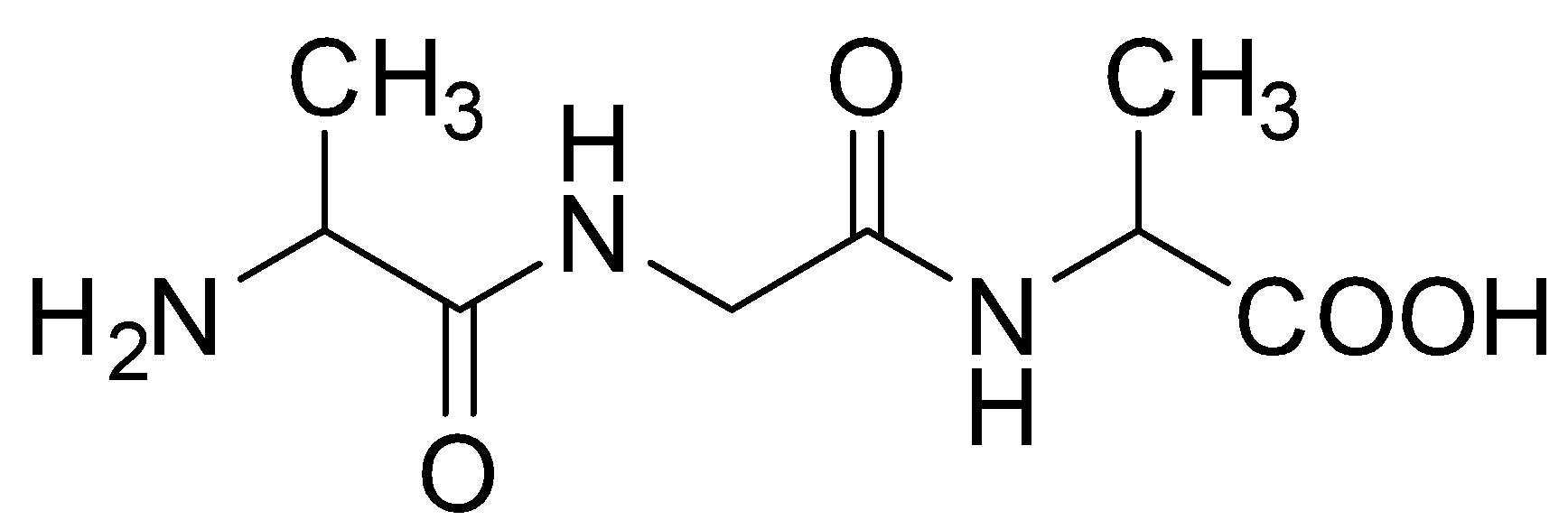 C.
C.
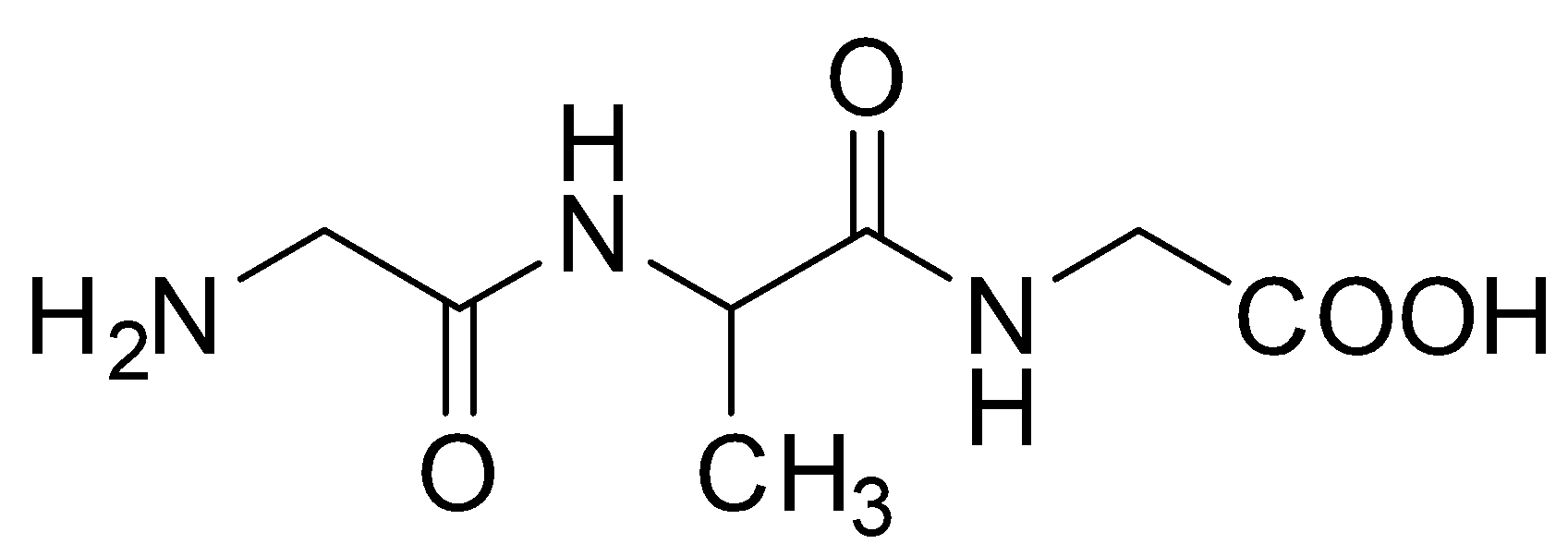 D.
D.
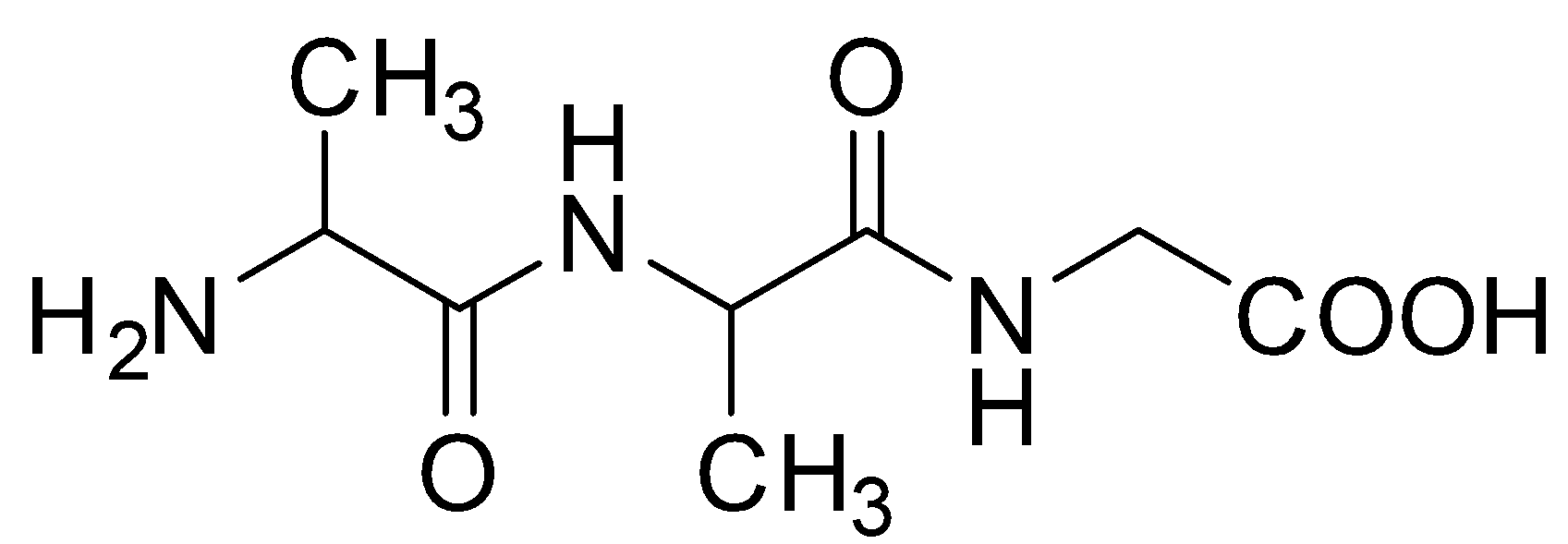




Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint:Amino acid is an organic molecule consisting of two functional groups, one basic part and another one is acidic. Amino acid can combine together to form a polypeptide or protein .They are the structural unit of proteins.
Complete step by step answer:
-To get the solution of the above mentioned question we have to first understand what amino acids and proteins are and what is peptide bond?
-Protein is a naturally occurring, extremely complex substance that consists of amino acid residue joined by peptide bonds. Proteins are present in all living organisms and include many essential biological compounds such as enzymes, hormones and antibodies.
-Amino acids are the structural unit of protein and consist of two parts one is acidic in nature and other is basic. The simplest amino acid is glycine and its structure may be written as $N{H_2} - C{H_2} - COOH$
-Basic group is the amino group $ - N{H_2}$ and the acidic group is the carboxyl group $ - COOH$ and an organic R group that is unique to each amino acid is also attached to it.
-There are total $20$ amino acids are present in which $9$ are essential amino acids, that is they must be consumed in the diet and remaining $11$ are non-essential amino acids, that is they can be made by the human body. They all have both acidic and basic groups differing in R which is unique.
-A peptide bond is a chemical bond formed between two molecules when the carboxyl group of one molecule reacts with the amino group of the other molecule releasing a molecule of water .Polypeptides or proteins are chains of amino acids held together by peptide bonds.
-Now coming to the solution part, as we know glycine structure $COOH - C{H_2} - N{H_2}$ and the structure of alanine may be written as $N{H_2} - CH\left( {C{H_3}} \right) - COOH$
-Then when glycine and alanine combine together remove water molecule, reaction may be written as $N{H_2} - C{H_2} - COOH + N{H_2} - CH\left( {C{H_3}} \right) - COOH$ $ = N{H_2} - C{H_2} - CONH - CH\left( {C{H_2}} \right) - COOH$
-Then again in above chain when glycine is added then the reaction comes like this,
$N{H_2} - C{H_2} - CONH - CH\left( {C{H_2}} \right) - COOH$ +$N{H_2} - C{H_2} - COOH$=$N{H_2} - C{H_2} - CONH - CH\left( {C{H_2}} \right) - CONH - C{H_2} - COOH$
Hence, option C is the correct answer.
Note:
-All natural occurring amino acids are levorotatory, that is L isomers .The alpha carbon is a chiral carbon atom except glycine which has two chemical equivalent hydrogen .
-Alanine is a sugar in the DNA and the RNA structures.
-Alanine has an affinity of Thiamine whereas Glycine is an amino acid which is considered as the building block for protein
Complete step by step answer:
-To get the solution of the above mentioned question we have to first understand what amino acids and proteins are and what is peptide bond?
-Protein is a naturally occurring, extremely complex substance that consists of amino acid residue joined by peptide bonds. Proteins are present in all living organisms and include many essential biological compounds such as enzymes, hormones and antibodies.
-Amino acids are the structural unit of protein and consist of two parts one is acidic in nature and other is basic. The simplest amino acid is glycine and its structure may be written as $N{H_2} - C{H_2} - COOH$
-Basic group is the amino group $ - N{H_2}$ and the acidic group is the carboxyl group $ - COOH$ and an organic R group that is unique to each amino acid is also attached to it.
-There are total $20$ amino acids are present in which $9$ are essential amino acids, that is they must be consumed in the diet and remaining $11$ are non-essential amino acids, that is they can be made by the human body. They all have both acidic and basic groups differing in R which is unique.
-A peptide bond is a chemical bond formed between two molecules when the carboxyl group of one molecule reacts with the amino group of the other molecule releasing a molecule of water .Polypeptides or proteins are chains of amino acids held together by peptide bonds.
-Now coming to the solution part, as we know glycine structure $COOH - C{H_2} - N{H_2}$ and the structure of alanine may be written as $N{H_2} - CH\left( {C{H_3}} \right) - COOH$
-Then when glycine and alanine combine together remove water molecule, reaction may be written as $N{H_2} - C{H_2} - COOH + N{H_2} - CH\left( {C{H_3}} \right) - COOH$ $ = N{H_2} - C{H_2} - CONH - CH\left( {C{H_2}} \right) - COOH$
-Then again in above chain when glycine is added then the reaction comes like this,
$N{H_2} - C{H_2} - CONH - CH\left( {C{H_2}} \right) - COOH$ +$N{H_2} - C{H_2} - COOH$=$N{H_2} - C{H_2} - CONH - CH\left( {C{H_2}} \right) - CONH - C{H_2} - COOH$
Hence, option C is the correct answer.
Note:
-All natural occurring amino acids are levorotatory, that is L isomers .The alpha carbon is a chiral carbon atom except glycine which has two chemical equivalent hydrogen .
-Alanine is a sugar in the DNA and the RNA structures.
-Alanine has an affinity of Thiamine whereas Glycine is an amino acid which is considered as the building block for protein
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




