
A trapezium is inscribed in the parabola \[{y^2} = 4x\], such that its diagonals pass through the point \[\left( {1,0} \right)\] and each has length \[\dfrac{{25}}{4}\]. If the area of the trapezium be \[P\], then \[4P\] is equal to
Answer
554.4k+ views
Hint:
Here, we will first draw a figure to show the given condition. We will then find the focal chord and the coordinates of the trapezium. Using this we will find the sides and the height of the trapezium. Then we will substitute these values in the formula of area of trapezium and hence, find the required value of \[4P\].
Formula Used:
Area of trapezium \[ABCD = \dfrac{1}{2} \times \] sum of parallel sides \[ \times \] height
Complete step by step solution:
First we will draw a parabola \[{y^2} = 4x\] which opens toward the positive side of the \[x\] axis.
Now, since, the trapezium is inscribed in this parabola, we will draw a trapezium such that its corners touch the parabola.
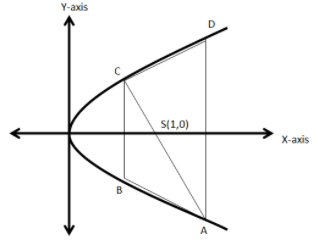
Now, let the focus of the trapezium be \[S\left( {1,0} \right)\] through which the diagonals of the trapezium passes and are of the length\[\dfrac{{25}}{4}\].
Now, let \[AS = x\] and, diagonal \[AC = \dfrac{{25}}{4}\]. Now we can write diagonal AC as a sum of AS and SC. So,
\[AS + SC = AC\]…………………………….\[\left( 1 \right)\]
Substituting \[AS = x\] and \[AC = \dfrac{{25}}{4}\] in the above equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow x + SC = \dfrac{{25}}{4}\]
Subtracting \[x\] from both the sides, we get
\[ \Rightarrow SC = \dfrac{{25}}{4} - x\]
Now taking reciprocal of equation \[\left( 1 \right)\], we can write it as:
\[\dfrac{1}{{AS}} + \dfrac{1}{{SC}} = \dfrac{1}{{AC}}\]……………………….\[\left( 2 \right)\]
Substituting \[SC = \dfrac{{25}}{4} - x\], \[AS = x\] and \[AC = 1\] in equation \[\left( 2 \right)\], we get
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{x} + \dfrac{1}{{\left( {\dfrac{{25}}{4} - x} \right)}} = \dfrac{1}{1}\]
Taking LCM on left hand side of the above equation, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\left( {\dfrac{{25}}{4} - x + x} \right)}}{{x\left( {\dfrac{{25}}{4} - x} \right)}} = 1\]
On cross multiplication, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{25}}{4} = \dfrac{{25}}{4}x - {x^2}\]
Taking LCM on RHS, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{25}}{4} = \dfrac{{25x - 4{x^2}}}{4}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 25 = 25x - 4{x^2}\]
Rewriting the above equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow 4{x^2} - 25x + 25 = 0\]
The above equation is a quadratic equation, so we will factorize the equation to get the value of \[x\].
Now, splitting the middle term, we get
\[ \Rightarrow 4{x^2} - 20x - 5x + 25 = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow 4x\left( {x - 5} \right) - 5\left( {x - 5} \right) = 0\]
Factoring out the common term, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {4x - 5} \right)\left( {x - 5} \right) = 0\]
Applying zero product property, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {4x - 5} \right) = 0\] or \[\left( {x - 5} \right) = 0\]
Hence,
\[x = \dfrac{5}{4}\] or \[x = 5\]
Now, since \[AC\] is the focal chord, hence, we can write,
\[AS = x = \left( {1 + {t^2}} \right)\]………………………..\[\left( 3 \right)\]
Now, substituting \[x = \dfrac{5}{4}\] in the above equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{5}{4} = \left( {1 + {t^2}} \right)\]
Subtracting 1 from both sides, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{5}{4} - 1 = {t^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{4} = {t^2}\]
Rewriting the above equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {\dfrac{1}{2}} \right)^2} = {t^2}\]
Taking square root on both sides, we get
\[ \Rightarrow t = \pm \dfrac{1}{2}\]
Substituting \[x = 5\] in equation \[\left( 3 \right)\], we get
\[ \Rightarrow 5 = \left( {1 + {t^2}} \right)\]
Subtracting 1 from both sides, we get
\[\begin{array}{l} \Rightarrow {t^2} = 4\\ \Rightarrow {t^2} = {\left( 2 \right)^2}\end{array}\]
Taking square root on both sides, we get
\[ \Rightarrow t = \pm 2\]
Now, we will find the coordinates of the trapezium \[ABCD\]
Substituting \[a = 1\] and \[t = \pm \dfrac{1}{2}\] in the coordinates of the trapezium \[ABCD\], we get
Coordinates of \[A\left( {a{t^2},2at} \right) = \left( {1 \times \dfrac{1}{4},2 \times 1 \times \dfrac{1}{2}} \right) = A\left( {\dfrac{1}{4},1} \right)\],
Coordinates of \[D\left( {a{t^2},2at} \right) = \left( {1 \times \dfrac{1}{4},2 \times 1 \times \dfrac{{ - 1}}{2}} \right) = A\left( {\dfrac{1}{4}, - 1} \right)\]
Coordinates of \[B\left( {\dfrac{a}{{{t^2}}},\dfrac{{2a}}{t}} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{1}{{\dfrac{1}{4}}},\dfrac{{2 \times 1}}{{\dfrac{1}{2}}}} \right) = \left( {4,4} \right)\]
Coordinates of \[C\left( {\dfrac{a}{{{t^2}}},\dfrac{{2a}}{t}} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{1}{{\dfrac{1}{4}}},\dfrac{{2 \times 1}}{{\dfrac{{ - 1}}{2}}}} \right) = \left( {4, - 4} \right)\]
Now, by distance formula, \[\sqrt {{{\left( {{x_2} - {x_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_2} - {y_1}} \right)}^2}} \], we get
Distance of \[AD = \sqrt {{{\left( {\dfrac{1}{4} - \dfrac{1}{4}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( { - 1 - 1} \right)}^2}} = \sqrt 4 = 2{\rm{ units}}\]
Distance of \[BC = \sqrt {{{\left( {4 - 4} \right)}^2} + {{\left( { - 4 - 4} \right)}^2}} = \sqrt {64} = 8{\rm{ units}}\]
$\therefore $ Height of the trapezium or Distance between the lines \[AD\] and \[BC = 4 - \dfrac{1}{4} = \dfrac{{15}}{4}{\rm{ units}}\]
Now, according to the question, the area of the trapezium is \[P\]
As we know,
Area of trapezium \[ABCD = \dfrac{1}{2} \times \]sum of parallel sides\[ \times \]height
\[ \Rightarrow P = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {2 + 8} \right)\left( {\dfrac{{15}}{4}} \right)\]
Adding the terms in the bracket, we get
\[ \Rightarrow P = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 10 \times \left( {\dfrac{{15}}{4}} \right) = 5 \times \dfrac{{15}}{4}\]
Multiplying the terms, we get
\[ \Rightarrow P = \dfrac{{75}}{4}\]
$\therefore 4P=4\times \dfrac{75}{4}=75$ square units.
Therefore, if the area of the trapezium is \[P\], then \[4P\] is equal to 75 square units.
Note:
A parabola is a curve having a focus and a directrix, such that each point on parabola is at equal distance from them. Whereas, a trapezium is a quadrilateral which has one pair of its opposite sides parallel. Now, in this question, a trapezium is inscribed in a parabola. Hence, we will draw the largest possible trapezium which can be drawn inside a parabola to solve this question.
Here, we will first draw a figure to show the given condition. We will then find the focal chord and the coordinates of the trapezium. Using this we will find the sides and the height of the trapezium. Then we will substitute these values in the formula of area of trapezium and hence, find the required value of \[4P\].
Formula Used:
Area of trapezium \[ABCD = \dfrac{1}{2} \times \] sum of parallel sides \[ \times \] height
Complete step by step solution:
First we will draw a parabola \[{y^2} = 4x\] which opens toward the positive side of the \[x\] axis.
Now, since, the trapezium is inscribed in this parabola, we will draw a trapezium such that its corners touch the parabola.

Now, let the focus of the trapezium be \[S\left( {1,0} \right)\] through which the diagonals of the trapezium passes and are of the length\[\dfrac{{25}}{4}\].
Now, let \[AS = x\] and, diagonal \[AC = \dfrac{{25}}{4}\]. Now we can write diagonal AC as a sum of AS and SC. So,
\[AS + SC = AC\]…………………………….\[\left( 1 \right)\]
Substituting \[AS = x\] and \[AC = \dfrac{{25}}{4}\] in the above equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow x + SC = \dfrac{{25}}{4}\]
Subtracting \[x\] from both the sides, we get
\[ \Rightarrow SC = \dfrac{{25}}{4} - x\]
Now taking reciprocal of equation \[\left( 1 \right)\], we can write it as:
\[\dfrac{1}{{AS}} + \dfrac{1}{{SC}} = \dfrac{1}{{AC}}\]……………………….\[\left( 2 \right)\]
Substituting \[SC = \dfrac{{25}}{4} - x\], \[AS = x\] and \[AC = 1\] in equation \[\left( 2 \right)\], we get
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{x} + \dfrac{1}{{\left( {\dfrac{{25}}{4} - x} \right)}} = \dfrac{1}{1}\]
Taking LCM on left hand side of the above equation, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\left( {\dfrac{{25}}{4} - x + x} \right)}}{{x\left( {\dfrac{{25}}{4} - x} \right)}} = 1\]
On cross multiplication, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{25}}{4} = \dfrac{{25}}{4}x - {x^2}\]
Taking LCM on RHS, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{25}}{4} = \dfrac{{25x - 4{x^2}}}{4}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 25 = 25x - 4{x^2}\]
Rewriting the above equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow 4{x^2} - 25x + 25 = 0\]
The above equation is a quadratic equation, so we will factorize the equation to get the value of \[x\].
Now, splitting the middle term, we get
\[ \Rightarrow 4{x^2} - 20x - 5x + 25 = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow 4x\left( {x - 5} \right) - 5\left( {x - 5} \right) = 0\]
Factoring out the common term, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {4x - 5} \right)\left( {x - 5} \right) = 0\]
Applying zero product property, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {4x - 5} \right) = 0\] or \[\left( {x - 5} \right) = 0\]
Hence,
\[x = \dfrac{5}{4}\] or \[x = 5\]
Now, since \[AC\] is the focal chord, hence, we can write,
\[AS = x = \left( {1 + {t^2}} \right)\]………………………..\[\left( 3 \right)\]
Now, substituting \[x = \dfrac{5}{4}\] in the above equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{5}{4} = \left( {1 + {t^2}} \right)\]
Subtracting 1 from both sides, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{5}{4} - 1 = {t^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{4} = {t^2}\]
Rewriting the above equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {\dfrac{1}{2}} \right)^2} = {t^2}\]
Taking square root on both sides, we get
\[ \Rightarrow t = \pm \dfrac{1}{2}\]
Substituting \[x = 5\] in equation \[\left( 3 \right)\], we get
\[ \Rightarrow 5 = \left( {1 + {t^2}} \right)\]
Subtracting 1 from both sides, we get
\[\begin{array}{l} \Rightarrow {t^2} = 4\\ \Rightarrow {t^2} = {\left( 2 \right)^2}\end{array}\]
Taking square root on both sides, we get
\[ \Rightarrow t = \pm 2\]
Now, we will find the coordinates of the trapezium \[ABCD\]
Substituting \[a = 1\] and \[t = \pm \dfrac{1}{2}\] in the coordinates of the trapezium \[ABCD\], we get
Coordinates of \[A\left( {a{t^2},2at} \right) = \left( {1 \times \dfrac{1}{4},2 \times 1 \times \dfrac{1}{2}} \right) = A\left( {\dfrac{1}{4},1} \right)\],
Coordinates of \[D\left( {a{t^2},2at} \right) = \left( {1 \times \dfrac{1}{4},2 \times 1 \times \dfrac{{ - 1}}{2}} \right) = A\left( {\dfrac{1}{4}, - 1} \right)\]
Coordinates of \[B\left( {\dfrac{a}{{{t^2}}},\dfrac{{2a}}{t}} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{1}{{\dfrac{1}{4}}},\dfrac{{2 \times 1}}{{\dfrac{1}{2}}}} \right) = \left( {4,4} \right)\]
Coordinates of \[C\left( {\dfrac{a}{{{t^2}}},\dfrac{{2a}}{t}} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{1}{{\dfrac{1}{4}}},\dfrac{{2 \times 1}}{{\dfrac{{ - 1}}{2}}}} \right) = \left( {4, - 4} \right)\]
Now, by distance formula, \[\sqrt {{{\left( {{x_2} - {x_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_2} - {y_1}} \right)}^2}} \], we get
Distance of \[AD = \sqrt {{{\left( {\dfrac{1}{4} - \dfrac{1}{4}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( { - 1 - 1} \right)}^2}} = \sqrt 4 = 2{\rm{ units}}\]
Distance of \[BC = \sqrt {{{\left( {4 - 4} \right)}^2} + {{\left( { - 4 - 4} \right)}^2}} = \sqrt {64} = 8{\rm{ units}}\]
$\therefore $ Height of the trapezium or Distance between the lines \[AD\] and \[BC = 4 - \dfrac{1}{4} = \dfrac{{15}}{4}{\rm{ units}}\]
Now, according to the question, the area of the trapezium is \[P\]
As we know,
Area of trapezium \[ABCD = \dfrac{1}{2} \times \]sum of parallel sides\[ \times \]height
\[ \Rightarrow P = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {2 + 8} \right)\left( {\dfrac{{15}}{4}} \right)\]
Adding the terms in the bracket, we get
\[ \Rightarrow P = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 10 \times \left( {\dfrac{{15}}{4}} \right) = 5 \times \dfrac{{15}}{4}\]
Multiplying the terms, we get
\[ \Rightarrow P = \dfrac{{75}}{4}\]
$\therefore 4P=4\times \dfrac{75}{4}=75$ square units.
Therefore, if the area of the trapezium is \[P\], then \[4P\] is equal to 75 square units.
Note:
A parabola is a curve having a focus and a directrix, such that each point on parabola is at equal distance from them. Whereas, a trapezium is a quadrilateral which has one pair of its opposite sides parallel. Now, in this question, a trapezium is inscribed in a parabola. Hence, we will draw the largest possible trapezium which can be drawn inside a parabola to solve this question.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




