
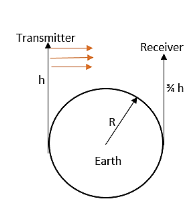
A transmitting antenna of height $h$ and the receiving antenna of height $\dfrac{3}{4}h$ are separated by a distance of $d$ for satisfactory communication in line-of-sight mode. Then, the value of $h$ is
[Given, the radius of the earth is $R$].
$\begin{align}
& A.\dfrac{{{d}^{2}}}{2R}{{\left( 2\sqrt{2}-\sqrt{6} \right)}^{2}} \\
& B.\dfrac{{{d}^{2}}}{4R}{{\left( 2\sqrt{2}-\sqrt{6} \right)}^{2}} \\
& C.\dfrac{{{d}^{2}}}{R}{{\left( 2\sqrt{2}-\sqrt{6} \right)}^{2}} \\
& D.\dfrac{{{d}^{2}}}{8R}{{\left( 2\sqrt{2}-\sqrt{6} \right)}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$

Answer
590.4k+ views
Hint: The height of antenna can be calculated using the equation,
${{d}_{m}}=\sqrt{2R{{h}_{T}}}+\sqrt{2R{{h}_{R}}}$
Where ${{d}_{m}}$ be the maximum distance of line of sight between the antenna and the transmitting antenna. Then after solving and rearranging we will get the value of ${{d}_{m}}$ in terms of $h$. The denominator of the term is factorized after this and then squares the both sides of the equation. This will lead you to the answer.
Complete answer:
first of all let us look at what all are given in the question.
The height of the transmitting antenna has been given as the equation,
${{h}_{T}}=h$
And also the height of the receiving antenna is given by the equation,
\[{{h}_{R}}=\dfrac{3}{4}h\]
As we know the radius of the earth is \[R\].
The maximum line of sight distance between these two antenna is given by the equation,
${{d}_{m}}=\sqrt{2R{{h}_{T}}}+\sqrt{2R{{h}_{R}}}$
In the question, it is mentioned that the value of ${{d}_{m}}$is,
\[{{d}_{m}}=d\]
Substituting all these values in it will give,
\[\begin{align}
& d=\sqrt{2Rh}+\sqrt{2R\times \dfrac{3}{4}h} \\
& d=\sqrt{2R}\times \left( \sqrt{h}+\sqrt{\dfrac{3h}{4}} \right) \\
\end{align}\]
Taking the \[\sqrt{2R}\] into the denominator, will give,
\[\dfrac{d}{\sqrt{2R}}=\left( \sqrt{h}+\sqrt{\dfrac{3h}{4}} \right)\]
Now let us take the common terms out,
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{d}{\sqrt{2R}}=\sqrt{h}\left( 1+\sqrt{\dfrac{3}{4}} \right) \\
& \dfrac{d}{\sqrt{2R}}=\sqrt{h}\left( \dfrac{2+\sqrt{3}}{2} \right) \\
\end{align}\]
Let us take all the terms into the left hand side keeping \[\sqrt{h}\]only in right hand side will give,
\[\dfrac{2d}{\sqrt{2R}\times \left( 2+\sqrt{3} \right)}=\sqrt{h}\]
Factoring the denominator will be given as,
\[\begin{align}
& \sqrt{h}=\dfrac{2d\left( 2-\sqrt{3} \right)}{\sqrt{2R}} \\
& \sqrt{h}=\dfrac{2\sqrt{2}d\left( 2-\sqrt{3} \right)}{2\sqrt{R}} \\
\end{align}\]
Cancelling the common terms in the equation,
\[\sqrt{h}=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}d\left( 2-\sqrt{3} \right)}{\sqrt{R}}\]
\[\sqrt{h}=\dfrac{d\left( 2\sqrt{2}-\sqrt{6} \right)}{\sqrt{R}}\]
Squaring the both sides of equations will give the value of height of the antenna.
\[h=\dfrac{{{d}^{2}}{{\left( 2\sqrt{2}-\sqrt{6} \right)}^{2}}}{R}\]
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
A transmission antenna is a basic device used in radio technology. They are made up of a conductor that passes an electric current whose intensity is varying over time and converts it into radiofrequency radiation that can travel through space. A receiving antenna is having the opposite of the process done by the transmission antenna.
${{d}_{m}}=\sqrt{2R{{h}_{T}}}+\sqrt{2R{{h}_{R}}}$
Where ${{d}_{m}}$ be the maximum distance of line of sight between the antenna and the transmitting antenna. Then after solving and rearranging we will get the value of ${{d}_{m}}$ in terms of $h$. The denominator of the term is factorized after this and then squares the both sides of the equation. This will lead you to the answer.
Complete answer:
first of all let us look at what all are given in the question.
The height of the transmitting antenna has been given as the equation,
${{h}_{T}}=h$
And also the height of the receiving antenna is given by the equation,
\[{{h}_{R}}=\dfrac{3}{4}h\]
As we know the radius of the earth is \[R\].
The maximum line of sight distance between these two antenna is given by the equation,
${{d}_{m}}=\sqrt{2R{{h}_{T}}}+\sqrt{2R{{h}_{R}}}$
In the question, it is mentioned that the value of ${{d}_{m}}$is,
\[{{d}_{m}}=d\]
Substituting all these values in it will give,
\[\begin{align}
& d=\sqrt{2Rh}+\sqrt{2R\times \dfrac{3}{4}h} \\
& d=\sqrt{2R}\times \left( \sqrt{h}+\sqrt{\dfrac{3h}{4}} \right) \\
\end{align}\]
Taking the \[\sqrt{2R}\] into the denominator, will give,
\[\dfrac{d}{\sqrt{2R}}=\left( \sqrt{h}+\sqrt{\dfrac{3h}{4}} \right)\]
Now let us take the common terms out,
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{d}{\sqrt{2R}}=\sqrt{h}\left( 1+\sqrt{\dfrac{3}{4}} \right) \\
& \dfrac{d}{\sqrt{2R}}=\sqrt{h}\left( \dfrac{2+\sqrt{3}}{2} \right) \\
\end{align}\]
Let us take all the terms into the left hand side keeping \[\sqrt{h}\]only in right hand side will give,
\[\dfrac{2d}{\sqrt{2R}\times \left( 2+\sqrt{3} \right)}=\sqrt{h}\]
Factoring the denominator will be given as,
\[\begin{align}
& \sqrt{h}=\dfrac{2d\left( 2-\sqrt{3} \right)}{\sqrt{2R}} \\
& \sqrt{h}=\dfrac{2\sqrt{2}d\left( 2-\sqrt{3} \right)}{2\sqrt{R}} \\
\end{align}\]
Cancelling the common terms in the equation,
\[\sqrt{h}=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}d\left( 2-\sqrt{3} \right)}{\sqrt{R}}\]
\[\sqrt{h}=\dfrac{d\left( 2\sqrt{2}-\sqrt{6} \right)}{\sqrt{R}}\]
Squaring the both sides of equations will give the value of height of the antenna.
\[h=\dfrac{{{d}^{2}}{{\left( 2\sqrt{2}-\sqrt{6} \right)}^{2}}}{R}\]
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
A transmission antenna is a basic device used in radio technology. They are made up of a conductor that passes an electric current whose intensity is varying over time and converts it into radiofrequency radiation that can travel through space. A receiving antenna is having the opposite of the process done by the transmission antenna.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE

Calculate the equivalent resistance between a and b class 12 physics CBSE

How many states of matter are there in total class 12 chemistry CBSE

Which of the following is the best conductor of electricity class 12 physics CBSE




