
A transformer works on both AC and DC.
A. True
B. False
Answer
590.4k+ views
Hint: The transforming action in a transformer occurs as a resultant of mutual induction between the coils in a transformer. Also remember, AC input provides altering supply of current while DC provides a steady supply of current.
Complete step by step answer:
In order for us to answer this question, we have to understand the basic working principle of a Transformer.
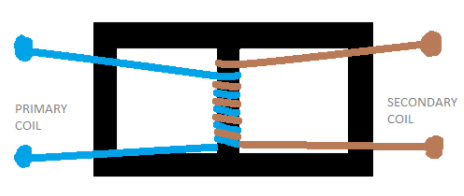
A transformer consists of two coils, a primary and a secondary coil, either twined on top each other or twined separately on two limbs of the soft iron core as shown in the pictures above.
Working principle is ‘Faraday’s law of induction’ or mutual induction to be precise.
Let us take the primary coil as the one in which we supply input current. By Faraday’s law of induction we know that, by altering current we can produce a changing magnetic field. This is what happens here. When we supply an altering current in the primary coil, it generates a changing magnetic field which in turn produces a constant voltage in the secondary coil, hence an AC output current in the circuit associated with it. In order for the fluctuating magnetic field to be produced we definitely require an altering supply of current which is AC.
So what happens with a DC input? DC input provides a steady supply of current, i.e, it can’t produce altering current which has a potential to produce an altering magnetic field by induction. So no ‘transformation’ can be possible for a DC input.
So, the answer to the question is option B, false.
The transformer can only function in AC input supply.
Additional information:
Emf equation of transformer is,
$\dfrac{{{E}_{1}}}{{{N}_{1}}}=\dfrac{{{E}_{2}}}{{{N}_{2}}}=4.44f{{\Phi }_{m}}$
Where, ${{E}_{1}}\to $ RMS value of induced emf in primary winding
${{E}_{2}}\to $ RMS value of induced emf in secondary winding
${{N}_{1}}\to $ Number of turns in primary winding
${{N}_{2}}\to $ Number of turns in secondary winding
$f\to $ Frequency of AC supply (in Hz)
${{\Phi }_{m}}\to $ Maximum flux in the core (in wb)
Note:
We have to keep in mind that the two coils are insulated, that is there isn’t any electrical connection that is present between them. Also the value of the emf produced on the secondary coil depends on the number of turns on it.
Complete step by step answer:
In order for us to answer this question, we have to understand the basic working principle of a Transformer.

A transformer consists of two coils, a primary and a secondary coil, either twined on top each other or twined separately on two limbs of the soft iron core as shown in the pictures above.
Working principle is ‘Faraday’s law of induction’ or mutual induction to be precise.
Let us take the primary coil as the one in which we supply input current. By Faraday’s law of induction we know that, by altering current we can produce a changing magnetic field. This is what happens here. When we supply an altering current in the primary coil, it generates a changing magnetic field which in turn produces a constant voltage in the secondary coil, hence an AC output current in the circuit associated with it. In order for the fluctuating magnetic field to be produced we definitely require an altering supply of current which is AC.
So what happens with a DC input? DC input provides a steady supply of current, i.e, it can’t produce altering current which has a potential to produce an altering magnetic field by induction. So no ‘transformation’ can be possible for a DC input.
So, the answer to the question is option B, false.
The transformer can only function in AC input supply.
Additional information:
Emf equation of transformer is,
$\dfrac{{{E}_{1}}}{{{N}_{1}}}=\dfrac{{{E}_{2}}}{{{N}_{2}}}=4.44f{{\Phi }_{m}}$
Where, ${{E}_{1}}\to $ RMS value of induced emf in primary winding
${{E}_{2}}\to $ RMS value of induced emf in secondary winding
${{N}_{1}}\to $ Number of turns in primary winding
${{N}_{2}}\to $ Number of turns in secondary winding
$f\to $ Frequency of AC supply (in Hz)
${{\Phi }_{m}}\to $ Maximum flux in the core (in wb)
Note:
We have to keep in mind that the two coils are insulated, that is there isn’t any electrical connection that is present between them. Also the value of the emf produced on the secondary coil depends on the number of turns on it.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




